Paulk/_____pd Date: Science Cells and Levels of Organization Stud
Paulk/_____pd Date: Science Cells and Levels of Organization Stud
Paulk/_____pd Date: Science Cells and Levels of Organization Stud
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Name: _________________________ <strong>Paulk</strong>/_____<strong>pd</strong><br />
<strong>Date</strong>: __________________________ <strong>Science</strong><br />
<strong>Cells</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Levels</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Organization</strong> <strong>Stud</strong>y Guide - KEY<br />
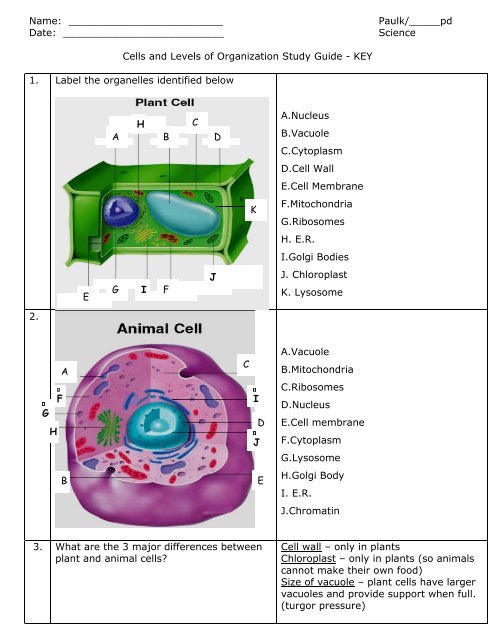
1. Label the organelles identified below<br />
2.<br />
G<br />
H<br />
F<br />
A<br />
E<br />
A<br />
G<br />
H<br />
I<br />
B D<br />
B E<br />
3. What are the 3 major differences between<br />
plant <strong>and</strong> animal cells?<br />
F<br />
C<br />
J<br />
C<br />
K<br />
I<br />
D<br />
J<br />
A.Nucleus<br />
B.Vacuole<br />
C.Cytoplasm<br />
D.Cell Wall<br />
E.Cell Membrane<br />
F.Mitochondria<br />
G.Ribosomes<br />
H. E.R.<br />
I.Golgi Bodies<br />
J. Chloroplast<br />
K. Lysosome<br />
A.Vacuole<br />
B.Mitochondria<br />
C.Ribosomes<br />
D.Nucleus<br />
E.Cell membrane<br />
F.Cytoplasm<br />
G.Lysosome<br />
H.Golgi Body<br />
I. E.R.<br />
J.Chromatin<br />
Cell wall – only in plants<br />
Chloroplast – only in plants (so animals<br />
cannot make their own food)<br />
Size <strong>of</strong> vacuole – plant cells have larger<br />
vacuoles <strong>and</strong> provide support when full.<br />
(turgor pressure)
4. What are organelles? Parts <strong>of</strong> the cell that have a specific<br />
function within the cell<br />
5. What is the function <strong>of</strong> the cell membrane? Controls what items can enter or leave<br />
the cell<br />
6. What is the function <strong>of</strong> the cell wall? Gives the cell membrane added<br />
support/gives plant cells their box-like<br />
shape<br />
7. What is the function <strong>of</strong> the nucleus? Directs most all <strong>of</strong> the activities <strong>of</strong> the<br />
cell<br />
8. What is the function <strong>of</strong> the cytoplasm? The liquid part <strong>of</strong> the cell in which the<br />
9. What organelle helps the cell manage<br />
energy, by converting high energy glucose<br />
into smaller energy units<br />
10. What plant cell organelle uses radiant<br />
energy from the Sun to turn carbon dioxide<br />
<strong>and</strong> water into sugar?<br />
11. What is the function <strong>of</strong> the vacuole?<br />
other organelles float<br />
mitochondria<br />
chloroplasts<br />
12. What is the function <strong>of</strong> ribosomes? produce proteins<br />
13. What organelle breaks down <strong>and</strong> recycles<br />
waste within the cell?<br />
14 What organelle is a network <strong>of</strong> passages<br />
that transports materials from one part <strong>of</strong><br />
the cell to another <strong>and</strong> provides a maze-like<br />
assembly line for the production <strong>of</strong> proteins<br />
<strong>and</strong> other substances?<br />
Stores food, water, wastes, <strong>and</strong> other<br />
materials for animal cells.<br />
In plant cells it also helps to maintain<br />
turgor pressure by storing water.<br />
lysosomes<br />
E.R.=endoplasmic reticulum<br />
15 What is the function <strong>of</strong> Golgi bodies? Receives materials from E.R., packages<br />
them, <strong>and</strong> distributes them to other<br />
16 What makes the plant cell more rigid than<br />
an animal cell?<br />
parts <strong>of</strong> the cell.<br />
Cell wall<br />
17 Where is chromatin located? Inside the nucleus<br />
18 Name the genetic materials found in the<br />
nucleus.<br />
1) DNA<br />
2) Chromosomes<br />
3) Genes<br />
4) Chromatin<br />
19 What is the cell theory? • All living things are composed <strong>of</strong> cells.<br />
• <strong>Cells</strong> are the basic unit <strong>of</strong> structure <strong>and</strong><br />
function in living things.<br />
• All cells are produced from other cells.<br />
• All cells are similar because they do<br />
things such as extracting energy from<br />
food to help organisms survive.<br />
20 What is the difference between structure Structure: the way parts are arranged<br />
<strong>and</strong> function?<br />
Function: the job something performs<br />
21 What is a tissue? A group <strong>of</strong> cells that carry out a common<br />
function
22 What is an organ? A group <strong>of</strong> tissues that carry out a<br />
common function<br />
23 What is an organ system? A group <strong>of</strong> organs that work together to<br />
carry out a common function.<br />
24 What is an organism? A group <strong>of</strong> organ systems that work<br />
together to carry out a common<br />
function.<br />
25 Draw a flow map with the levels <strong>of</strong><br />
organization we studied from simplest to<br />
most complex.<br />
26 When new cells are created, it’s called<br />
_______________.<br />
27 How is the cell membrane similar to the<br />
function <strong>of</strong> skin?<br />
28 What is turgor pressure <strong>and</strong> which part <strong>of</strong><br />
the cell controls it?<br />
29<br />
30.<br />
31.<br />
What would have to happen to the cell<br />
above to increase the turgor pressure?<br />
If a scientist wanted to classify samples as<br />
cells, tissues, organs, or systems what<br />
would be the best way to organize this<br />
information?<br />
1. Bar Graph 2. Line Graph<br />
<strong>Cells</strong>TissuesOrgansOrgan<br />
SystemsOrganism<br />
reproduction<br />
it controls what enters <strong>and</strong> exits the cell<br />
just like the skin gives <strong>of</strong>f wastes <strong>and</strong><br />
takes in some essentials<br />
Turgor pressure is the internal cell<br />
pressure, against the cell wall, caused<br />
when the vacuole is full <strong>of</strong> water help<br />
plants to st<strong>and</strong> tall.<br />
More water would have to enter the<br />
vacuole. This would cause pressure on<br />
the cell wall, making the plant more<br />
rigid.<br />
1. Bar graphs are used to compare<br />
things between different groups.<br />
2. Line graphs are used to track how<br />
something changes over time.<br />
3. A data table is a type <strong>of</strong> diagram that<br />
organizes <strong>and</strong> represents a set <strong>of</strong><br />
data.<br />
4. A tally chart is a chart that shows
3. Data Table 4. Tally Chart<br />
32. How do you determine the overall total<br />
magnification <strong>of</strong> the object being viewed<br />
with the microscope?<br />
how many there are <strong>of</strong> something or<br />
how <strong>of</strong>ten something happens.<br />
The Data Table would be best for<br />
classifying samples into different<br />
categories.<br />
Multiply the magnification <strong>of</strong> the<br />
eyepiece <strong>and</strong> the objective lens (the one<br />
you placed over the specimen)<br />
Determine the overall total magnification <strong>of</strong> the microscopes pictured below.<br />
10X<br />
25X 40X 10X<br />
1. __250X____ 2._____400X___ 3.___100X____