Phytoremediation of Volatile Organic Compounds in ... - CLU-IN
Phytoremediation of Volatile Organic Compounds in ... - CLU-IN
Phytoremediation of Volatile Organic Compounds in ... - CLU-IN
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
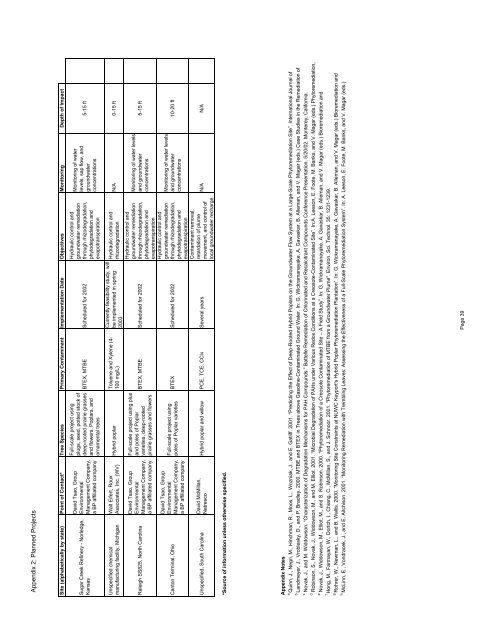
Appendix 2: Planned Projects<br />
Site (alphabetically by state) Po<strong>in</strong>t <strong>of</strong> Contact* Tree Species Primary Contam<strong>in</strong>ant Implementation Date Objectives Monitor<strong>in</strong>g Depth <strong>of</strong> Impact<br />
5-15 ft<br />
Monitor<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> water<br />
levels, sap flow, and<br />
groundwater<br />
concentrations<br />
Hydraulic control and<br />
groundwater remediation<br />
through rhizodegradation,<br />
phytodegradation and<br />
evapotranspiration<br />
BTEX, MTBE Scheduled for 2002<br />
Full-scale project us<strong>in</strong>g<br />
plugs, seed, potted stock <strong>of</strong><br />
deep-rooted prairie grasses<br />
and flowers, Poplars, and<br />
ornamental trees<br />
David Tsao, Group<br />
Environmental<br />
Management Company,<br />
a BP affiliated company<br />
Sugar Creek Ref<strong>in</strong>ery - Norledge,<br />
Kansas<br />
N/A 0-15 ft<br />
Hydraulic control and<br />
rhizodegradation<br />
Currently feasibility study, will<br />
be implemented <strong>in</strong> spr<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2003<br />
Toluene and Xylene (4-<br />
100 mg/L)<br />
Hybrid poplar<br />
Walt Eifert, Roux<br />
Associates, Inc. (WV)<br />
Unspecified chemical<br />
manufactur<strong>in</strong>g facility, Michigan<br />
5-15 ft<br />
Monitor<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> water levels<br />
and groundwater<br />
concentrations<br />
Hydraulic control and<br />
groundwater remediation<br />
through rhizodegradation,<br />
phytodegradation and<br />
evapotranspiration<br />
Hydraulic control and<br />
groundwater remediation<br />
through rhizodegradation,<br />
phytodegradation and<br />
evapotranspiration<br />
Contam<strong>in</strong>ant removal,<br />
retardation <strong>of</strong> plume<br />
movement, and control <strong>of</strong><br />
local groundwater recharge<br />
BTEX, MTBE Scheduled for 2002<br />
Full-scale project us<strong>in</strong>g plus<br />
and poles <strong>of</strong> Poplar<br />
varieties, deep-rooted<br />
prairie grasses and flowers<br />
David Tsao, Group<br />
Environmental<br />
Management Company,<br />
a BP affiliated company<br />
Raleigh SS825, North Carol<strong>in</strong>a<br />
10-20 ft<br />
Monitor<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> water levels<br />
and groundwater<br />
concentrations<br />
BTEX Scheduled for 2002<br />
Full-scale project us<strong>in</strong>g<br />
poles <strong>of</strong> Poplar varieties<br />
David Tsao, Group<br />
Environmental<br />
Management Company,<br />
a BP affiliated company<br />
Canton Term<strong>in</strong>al, Ohio<br />
N/A N/A<br />
Hybrid poplar and willow PCE, TCE, CCl4 Several years<br />
David McMillan,<br />
Natresco<br />
Unspecified, South Carol<strong>in</strong>a<br />
*Source <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>formation unless otherwise specified.<br />
Appendix Notes<br />
a<br />
Qu<strong>in</strong>n, J., Negri, M., H<strong>in</strong>chman, R., Moos, L., Wozniak, J., and E. Gatliff. 2001. “Predict<strong>in</strong>g the Effect <strong>of</strong> Deep-Rooted Hybrid Poplars on the Groundwater Flow System at a Large-Scale <strong>Phytoremediation</strong> Site”. International Journal <strong>of</strong><br />
b<br />
Landmeyer, J., Vroblesky, D., and P. Bradley. 2000. MTBE and BTEX <strong>in</strong> Trees above Gasol<strong>in</strong>e-Contam<strong>in</strong>ated Ground Water. In: G. Wickramanayake, A. Gavaskar, B. Alleman, and V. Magar (eds.) Case Studies <strong>in</strong> the Remediation <strong>of</strong><br />
c<br />
Novak, J., and M. Widdowson. “Characterization <strong>of</strong> Degradation Mechanisms for PAH <strong>Compounds</strong>.” Battelle Remediation <strong>of</strong> Chlor<strong>in</strong>ated and Recalcitrant <strong>Compounds</strong> Conference Presentation. 5/20/02. Monterey, California.<br />
d<br />
Rob<strong>in</strong>son, S., Novak, J., Widdowson, M., and M. Elliot. 2001. “Microbial Degradation <strong>of</strong> PAHs under Various Redox Conditions at a Creosote-Contam<strong>in</strong>ated Site”. In:A. Leeson, E. Foote, M. Banks, and V. Magar (eds.) <strong>Phytoremediation</strong>,<br />
e<br />
Novak, J., Widdowson, M., Elliot, M., and S. Rob<strong>in</strong>son. 2000. “<strong>Phytoremediation</strong> <strong>of</strong> a Creosote Contam<strong>in</strong>ated Site – A Field Study”. In: G. Wickramanayake, A. Gavaskar, B. Alleman, and V. Magar (eds.) Bioremediation and<br />
f<br />
Hong, M., Farmayan, W., Dortch, I., Chiang, C., McMillan, S., and J. Schnoor. 2001. "<strong>Phytoremediation</strong> <strong>of</strong> MTBE from a Groundwater Plume". Environ. Sci. Technol. 35: 1231-1239.<br />
g<br />
Rohrer, W., Newman, L., and B. Wallis. 2000. “Monitor<strong>in</strong>g Site Constra<strong>in</strong>ts at NUWC Keyport's Hybrid Poplar <strong>Phytoremediation</strong> Plantation”. In: G. Wickramanayake, A. Gavaskar, B. Alleman, and V. Magar (eds.) Bioremediation and<br />
h<br />
McL<strong>in</strong>n, E., Vondracek, J., and E. Aitchison. 2001. “Monitor<strong>in</strong>g Remediation with Trembl<strong>in</strong>g Leaves: Assess<strong>in</strong>g the Effectiveness <strong>of</strong> a Full-Scale <strong>Phytoremediation</strong> System”. In: A. Leeson, E. Foote, M. Banks, and V. Magar (eds.)<br />
Page 39