Introduction to Phytoremediation - CLU-IN
Introduction to Phytoremediation - CLU-IN
Introduction to Phytoremediation - CLU-IN
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
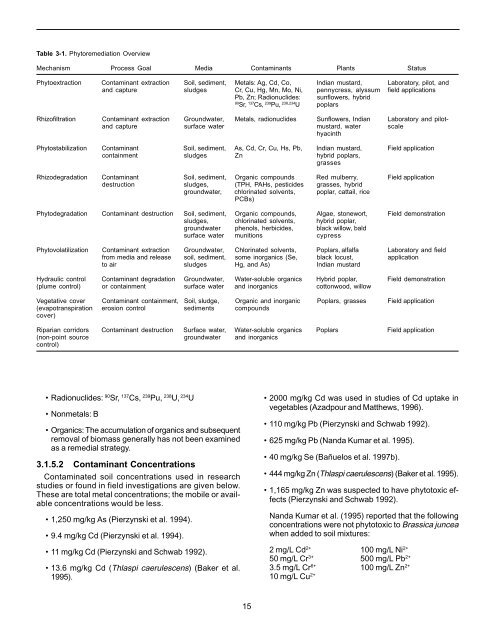
Table 3-1. Phy<strong>to</strong>remediation Overview<br />
Mechanism Process Goal Media Contaminants Plants Status<br />
Phy<strong>to</strong>extraction Contaminant extraction Soil, sediment, Metals: Ag, Cd, Co, Indian mustard, Labora<strong>to</strong>ry, pilot, and<br />
and capture sludges Cr, Cu, Hg, Mn, Mo, Ni, pennycress, alyssum field applications<br />
Pb, Zn; Radionuclides: sunflowers, hybrid<br />
90 Sr, 137 Cs, 239 Pu, 238,234 U poplars<br />
Rhizofiltration Contaminant extraction Groundwater, Metals, radionuclides Sunflowers, Indian Labora<strong>to</strong>ry and pilotand<br />
capture surface water mustard, water scale<br />
hyacinth<br />
Phy<strong>to</strong>stabilization Contaminant Soil, sediment, As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hs, Pb, Indian mustard, Field application<br />
containment sludges Zn hybrid poplars,<br />
grasses<br />
Rhizodegradation Contaminant Soil, sediment, Organic compounds Red mulberry, Field application<br />
destruction sludges, (TPH, PAHs, pesticides grasses, hybrid<br />
groundwater, chlorinated solvents, poplar, cattail, rice<br />
PCBs)<br />
Phy<strong>to</strong>degradation Contaminant destruction Soil, sediment, Organic compounds, Algae, s<strong>to</strong>newort, Field demonstration<br />
sludges, chlorinated solvents, hybrid poplar,<br />
groundwater phenols, herbicides, black willow, bald<br />
surface water munitions cypress<br />
Phy<strong>to</strong>volatilization Contaminant extraction Groundwater, Chlorinated solvents, Poplars, alfalfa Labora<strong>to</strong>ry and field<br />
from media and release soil, sediment, some inorganics (Se, black locust, application<br />
<strong>to</strong> air sludges Hg, and As) Indian mustard<br />
Hydraulic control Contaminant degradation Groundwater, Water-soluble organics Hybrid poplar, Field demonstration<br />
(plume control) or containment surface water and inorganics cot<strong>to</strong>nwood, willow<br />
Vegetative cover Contaminant containment, Soil, sludge, Organic and inorganic Poplars, grasses Field application<br />
(evapotranspiration erosion control sediments compounds<br />
cover)<br />
Riparian corridors Contaminant destruction Surface water, Water-soluble organics Poplars Field application<br />
(non-point source groundwater and inorganics<br />
control)<br />
• Radionuclides: 90 Sr, 137 Cs, 239 Pu, 238 U, 234 U<br />
• Nonmetals: B<br />
• Organics: The accumulation of organics and subsequent<br />
removal of biomass generally has not been examined<br />
as a remedial strategy.<br />
3.1.5.2 Contaminant Concentrations<br />
Contaminated soil concentrations used in research<br />
studies or found in field investigations are given below.<br />
These are <strong>to</strong>tal metal concentrations; the mobile or available<br />
concentrations would be less.<br />
• 1,250 mg/kg As (Pierzynski et al. 1994).<br />
• 9.4 mg/kg Cd (Pierzynski et al. 1994).<br />
• 11 mg/kg Cd (Pierzynski and Schwab 1992).<br />
• 13.6 mg/kg Cd (Thlaspi caerulescens) (Baker et al.<br />
1995).<br />
15<br />
• 2000 mg/kg Cd was used in studies of Cd uptake in<br />
vegetables (Azadpour and Matthews, 1996).<br />
• 110 mg/kg Pb (Pierzynski and Schwab 1992).<br />
• 625 mg/kg Pb (Nanda Kumar et al. 1995).<br />
• 40 mg/kg Se (Bañuelos et al. 1997b).<br />
• 444 mg/kg Zn (Thlaspi caerulescens) (Baker et al. 1995).<br />
• 1,165 mg/kg Zn was suspected <strong>to</strong> have phy<strong>to</strong><strong>to</strong>xic effects<br />
(Pierzynski and Schwab 1992).<br />
Nanda Kumar et al. (1995) reported that the following<br />
concentrations were not phy<strong>to</strong><strong>to</strong>xic <strong>to</strong> Brassica juncea<br />
when added <strong>to</strong> soil mixtures:<br />
2 mg/L Cd 2+ 100 mg/L Ni 2+<br />
50 mg/L Cr 3+ 500 mg/L Pb 2+<br />
3.5 mg/L Cr 6+ 100 mg/L Zn 2+<br />
10 mg/L Cu 2+