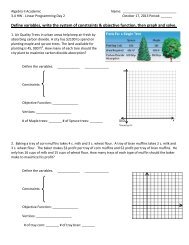
Ecosystem Review Sheet Using the diagram, answer the following ...
Ecosystem Review Sheet Using the diagram, answer the following ...
Ecosystem Review Sheet Using the diagram, answer the following ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Name:_______________________________________<br />
<strong>Ecosystem</strong> <strong>Review</strong> <strong>Sheet</strong><br />
<strong>Using</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>diagram</strong>, <strong>answer</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>following</strong> questions:<br />
1. What is <strong>the</strong> herbivore in this food chain? Grasshopper<br />
2. What is <strong>the</strong> producer in this food chain? Flower<br />
3. What would happen to this food chain if <strong>the</strong> flowers were covered in fertilizer<br />
It would poison <strong>the</strong> grasshopper, frog, and snake<br />
4. <strong>Using</strong> this food chain, draw an energy pyramid.<br />
<strong>Using</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>diagram</strong> above, <strong>answer</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>following</strong> questions:<br />
5. What is <strong>the</strong> one herbivore in this food web? Squirrel<br />
6. What is <strong>the</strong> top consumer in this food web? Bear<br />
7. Besides <strong>the</strong> bear, what is <strong>the</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r omnivore in <strong>the</strong> food web? Raccoon<br />
8. What would happen to <strong>the</strong> food web if <strong>the</strong> raccoon was removed from <strong>the</strong> web?<br />
There would be more fish and plants because <strong>the</strong> raccoon wouldn’t eat <strong>the</strong>m, but <strong>the</strong><br />
bear would have to eat more food because one of its food sources would be gone
Use <strong>the</strong> Food Pyramid for #17 and #18:<br />
12. Which one of <strong>the</strong>se organisms is <strong>the</strong> most plentiful?<br />
Algae<br />
13. What is <strong>the</strong> primary consumer?<br />
Copepods<br />
9. Which one of <strong>the</strong>se organisms would receive all of <strong>the</strong>ir<br />
nutrients from abiotic sources? Grass<br />
10. Which one of <strong>the</strong>se organisms recycles materials? Fungus<br />
11. Which one of <strong>the</strong>se organisms receives its energy from a<br />
producer? Grasshopper<br />
14. What is <strong>the</strong> difference between a food chain and food web?<br />
Food webs show multiple connections between <strong>the</strong> different producers and consumers<br />
15. What type of energy is passed from a producer to a consumer?<br />
Chemical Energy<br />
16. List and describe <strong>the</strong> 7 plant adaptations related to water:<br />
1. Flexible Roots- allow roots to move with water and not break<br />
2. Sun Absorption- Chlorophyll only on top of leaves<br />
3. No Root- some plants can absorb water through <strong>the</strong>ir leaves and stems<br />
4. Spines- small leaves to stop H20 evaporation, protect plants from animals<br />
5. Water Storage- water stored in stem<br />
6. Waxy Stem- stops water evaporation<br />
7. Drip tip & Waxy leaves- allows water to run off so fungi doesn’t grow<br />
Define <strong>the</strong> <strong>following</strong> terms and write an example for each term on a separate paper<br />
17. Biotic Living organisms- bird<br />
18. Abiotic nonliving factors-sun<br />
19. Population All <strong>the</strong> organisms in an ecosystem that belong to <strong>the</strong> same species<br />
20. Consumer Organisms that cannot make <strong>the</strong>ir own food<br />
21. Prey An organism that is hunted and killed for food<br />
22. Producer An organism that can make its own food
23. <strong>Ecosystem</strong> All of <strong>the</strong> organisms living in an area and <strong>the</strong> nonliving factors of <strong>the</strong>ir environment<br />
24. Habitat The place an organism lives<br />
25. Herbivore An animal that only eats producers<br />
26. Xylem A pipe in a plant that carries water to all parts of <strong>the</strong> plant<br />
27. Phloem A pipe in a plant that carries food to all parts of <strong>the</strong> plant<br />
28. Turgor Pressure The outward force of <strong>the</strong> central vacuole on <strong>the</strong> inside of <strong>the</strong> cell wall<br />
29. Phototropism <strong>the</strong> direction an organism grows in response to light<br />
30. Hydrotropism <strong>the</strong> direction an organism grows in response to water<br />
31. Gravitropism <strong>the</strong> direction an organism grows in response to gravity<br />
32. Thigmotropism <strong>the</strong> direction an organism grows in response to touch<br />
33. Chlorophyll <strong>the</strong> pigment in chloroplast that absorbs light energy<br />
34. Chloroplast The organelle where photosyn<strong>the</strong>sis takes place<br />
35. Write <strong>the</strong> formula for photosyn<strong>the</strong>sis and explain <strong>the</strong> process in complete sentences.<br />
Photosyn<strong>the</strong>sis is <strong>the</strong> process that converts light energy into chemical energy that takes place<br />
in <strong>the</strong> chloroplast organelle of plants. Sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll in <strong>the</strong> plants leaves.<br />
The plants also take in carbon dioxide from humans and animals, and soak up water from <strong>the</strong>ir<br />
roots. Sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water combined in a plant will produce glucose which is<br />
sugar/food for <strong>the</strong> plant, and release oxygen for animals and humans to consume.