Lebanon - What is GIS - World Health Organization
Lebanon - What is GIS - World Health Organization
Lebanon - What is GIS - World Health Organization
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Lebanon</strong> Role of contractual arrangements in improving health system performance<br />
input from contracted parties, the study was not designed for th<strong>is</strong> purpose and therefore th<strong>is</strong><br />
was limited in scope.<br />
4. Synthes<strong>is</strong> of data. Information from multiple sources was synthesized. In light of the<br />
breadth of contractual arrangements in <strong>Lebanon</strong>, several case studies were conducted,<br />
rather than focusing on one study, to examine the performance of different levels of the<br />
health sector in <strong>Lebanon</strong>. Reviewing several case studies jointly also allowed for<br />
identification of important opportunities for improving performance through strategies of<br />
coordination and integration.<br />
5. Summary of findings and recommendations. Based on examination of current situation, a<br />
scorecard <strong>is</strong> developed to illustrate where contractual arrangements have succeeded and<br />
failed, and to identify future steps that can be taken to improve performance. A set of<br />
recommendations are provided. These build on identified strengths and weaknesses. They<br />
represent a point for d<strong>is</strong>cussion with different stakeholders in <strong>Lebanon</strong>.<br />
The checkl<strong>is</strong>t provided by the Regional Office for assessing the role of contractual<br />
arrangements was useful both in guiding in the actual research and in developing the report.<br />
However, it was not possible to answer all questions in the checkl<strong>is</strong>t meaningfully for all the<br />
different contractual arrangements in <strong>Lebanon</strong>. Th<strong>is</strong> <strong>is</strong> mostly due to the sheer number of these<br />
arrangements.<br />
FINDINGS<br />
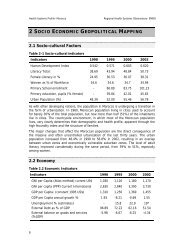
<strong>Health</strong> sector in <strong>Lebanon</strong><br />
<strong>Lebanon</strong> <strong>is</strong> a middle-income country of approximately 4 million inhabitants (80%<br />
urbanized) who live in 6 admin<strong>is</strong>trative regions, or mohafazat. The greater Beirut area houses<br />
more than 40% of the population. Around 45% of Lebanese are under the age of 21 years and<br />
10% are over age 65. <strong>Lebanon</strong> has favourable health indicators compared with other countries of<br />
the Eastern Mediterranean Region: life expectancy <strong>is</strong> 72 years for females and 69 years for<br />
males; overall and infant mortality rates are 7 and 28 per 1000, respectively (regional health<br />
inequalities are notable). <strong>Lebanon</strong> has undergone an epidemiological transition, with over 80%<br />
of the current mortality burden due to noncommunicable d<strong>is</strong>eases and 10% due to injuries. The<br />
morbidity profile, compiled in the context of a national burden of d<strong>is</strong>ease study, suggests a<br />
similar pattern.<br />
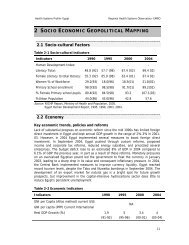
<strong>Health</strong> <strong>is</strong> an important component of economic activities, consuming 12%–13% of GDP.<br />
Most health spending, however, <strong>is</strong> out-of-pocket (around 70%–75%), more heavily shouldered<br />
by the poorer segments. Slightly more than 10% of all public expenditures go to health. The<br />
main public financers are: the Min<strong>is</strong>try of Public Heatlh (receives 4% of the total budget and 1%<br />
of GDP), NSSF, Civil Service Cooperative (CSC), Min<strong>is</strong>try of Defense, Min<strong>is</strong>try of the Interior