GARMIN GPS Interface Specification
GARMIN GPS Interface Specification
GARMIN GPS Interface Specification
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
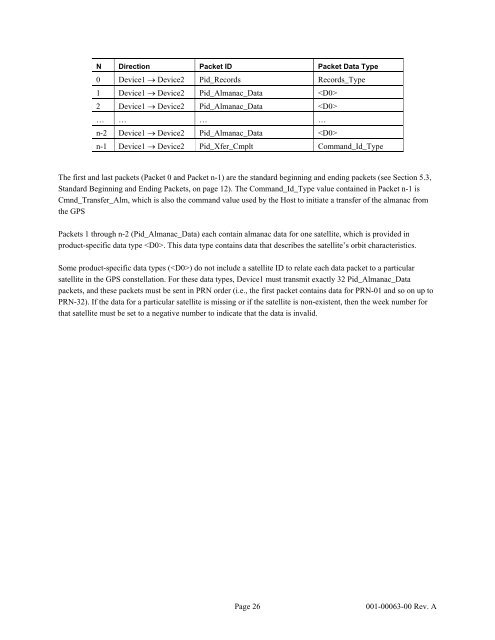
N Direction Packet ID Packet Data Type<br />
0 Device1 → Device2 Pid_Records Records_Type<br />
1 Device1 → Device2 Pid_Almanac_Data <br />
2 Device1 → Device2 Pid_Almanac_Data <br />
… … … …<br />
n-2 Device1 → Device2 Pid_Almanac_Data <br />
n-1 Device1 → Device2 Pid_Xfer_Cmplt Command_Id_Type<br />
The first and last packets (Packet 0 and Packet n-1) are the standard beginning and ending packets (see Section 5.3,<br />
Standard Beginning and Ending Packets, on page 12). The Command_Id_Type value contained in Packet n-1 is<br />
Cmnd_Transfer_Alm, which is also the command value used by the Host to initiate a transfer of the almanac from<br />
the <strong>GPS</strong><br />
Packets 1 through n-2 (Pid_Almanac_Data) each contain almanac data for one satellite, which is provided in<br />
product-specific data type . This data type contains data that describes the satellite’s orbit characteristics.<br />
Some product-specific data types () do not include a satellite ID to relate each data packet to a particular<br />
satellite in the <strong>GPS</strong> constellation. For these data types, Device1 must transmit exactly 32 Pid_Almanac_Data<br />
packets, and these packets must be sent in PRN order (i.e., the first packet contains data for PRN-01 and so on up to<br />
PRN-32). If the data for a particular satellite is missing or if the satellite is non-existent, then the week number for<br />
that satellite must be set to a negative number to indicate that the data is invalid.<br />
Page 26 001-00063-00 Rev. A