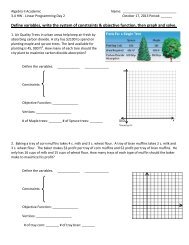
Class notes
Class notes
Class notes
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
go+,t h0,4 wgll<br />
i ;<br />
. j<br />
D.<br />
1.<br />
Example: pH Changes in buffered solutions<br />
Calculate the change in pH that occurs when 0.010 mol solid NaOH is<br />
added to 1.0L of the buffered solution in example C-1 above. Compare<br />
this pH change with that which occurs when 0.010mol solid NaOH is .... o<br />
added to 1.0L of water.<br />
2. Solution:<br />
V' ,5'<br />
' -3<br />
iÿ6,< I0<br />
k L ' '!<br />
\<br />
,, '-.\<br />
beÿ4_ÿarce<br />
loÿs 1+1<br />
€ ,OL)'-O,50ÿ O,OÿOÿ° i ÿOLx O,SOÿ --*<br />
= o,s-oÿo I ÿ _- 0°b-owd<br />
0,ÿ50- 0,010 Omo/ 0ÿ$o+ 6,010a<br />
3.<br />
¢<br />
g,<br />
ezl4ÿOÿ ÿ ÿ4+ +<br />
o.ÿtq, o<br />
,qq-ÿ x<br />
e %o/<br />
O,S'ÿ<br />
+X<br />
,Sl+X<br />
I,ÿX tO-S" =_<br />
oÿ- 40 44ÿm baÿa4 sotÿn<br />
,q(o- ÿ,qV -- + o,os