Alkaline sulphate fluids produced in a magmatic hydrothermal system
Alkaline sulphate fluids produced in a magmatic hydrothermal system
Alkaline sulphate fluids produced in a magmatic hydrothermal system
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
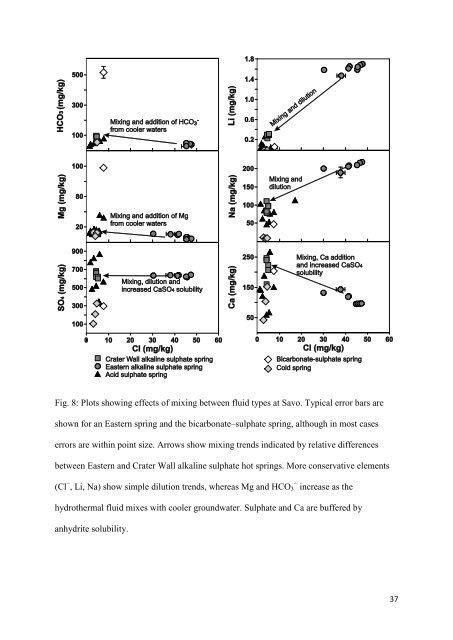
Fig. 8: Plots show<strong>in</strong>g effects of mix<strong>in</strong>g between fluid types at Savo. Typical error bars are<br />
shown for an Eastern spr<strong>in</strong>g and the bicarbonate–<strong>sulphate</strong> spr<strong>in</strong>g, although <strong>in</strong> most cases<br />
errors are with<strong>in</strong> po<strong>in</strong>t size. Arrows show mix<strong>in</strong>g trends <strong>in</strong>dicated by relative differences<br />
between Eastern and Crater Wall alkal<strong>in</strong>e <strong>sulphate</strong> hot spr<strong>in</strong>gs. More conservative elements<br />
(Cl − , Li, Na) show simple dilution trends, whereas Mg and HCO − 3 <strong>in</strong>crease as the<br />
<strong>hydrothermal</strong> fluid mixes with cooler groundwater. Sulphate and Ca are buffered by<br />
anhydrite solubility.<br />
37