comparison of graphical data analysis methods - Hochschule ...
comparison of graphical data analysis methods - Hochschule ...
comparison of graphical data analysis methods - Hochschule ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
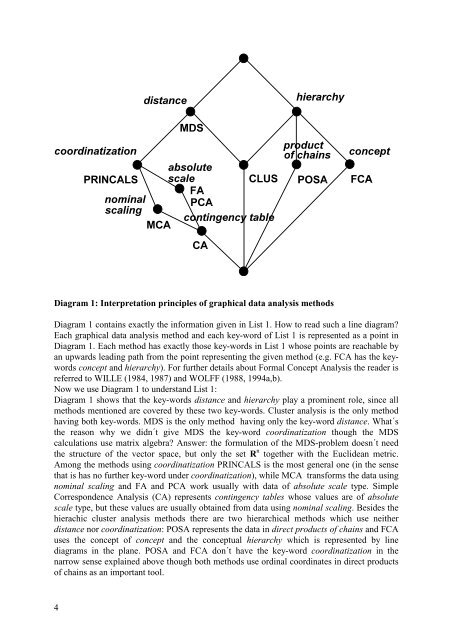
Diagram 1: Interpretation principles <strong>of</strong> <strong>graphical</strong> <strong>data</strong> <strong>analysis</strong> <strong>methods</strong><br />
Diagram 1 contains exactly the information given in List 1. How to read such a line diagram?<br />
Each <strong>graphical</strong> <strong>data</strong> <strong>analysis</strong> method and each key-word <strong>of</strong> List 1 is represented as a point in<br />
Diagram 1. Each method has exactly those key-words in List 1 whose points are reachable by<br />
an upwards leading path from the point representing the given method (e.g. FCA has the keywords<br />
concept and hierarchy). For further details about Formal Concept Analysis the reader is<br />
referred to WILLE (1984, 1987) and WOLFF (1988, 1994a,b).<br />
Now we use Diagram 1 to understand List 1:<br />
Diagram 1 shows that the key-words distance and hierarchy play a prominent role, since all<br />
<strong>methods</strong> mentioned are covered by these two key-words. Cluster <strong>analysis</strong> is the only method<br />
having both key-words. MDS is the only method having only the key-word distance. What´s<br />
the reason why we didn´t give MDS the key-word coordinatization though the MDS<br />
calculations use matrix algebra? Answer: the formulation <strong>of</strong> the MDS-problem doesn´t need<br />
the structure <strong>of</strong> the vector space, but only the set R n together with the Euclidean metric.<br />
Among the <strong>methods</strong> using coordinatization PRINCALS is the most general one (in the sense<br />
that is has no further key-word under coordinatization), while MCA transforms the <strong>data</strong> using<br />
nominal scaling and FA and PCA work usually with <strong>data</strong> <strong>of</strong> absolute scale type. Simple<br />
Correspondence Analysis (CA) represents contingency tables whose values are <strong>of</strong> absolute<br />
scale type, but these values are usually obtained from <strong>data</strong> using nominal scaling. Besides the<br />
hierachic cluster <strong>analysis</strong> <strong>methods</strong> there are two hierarchical <strong>methods</strong> which use neither<br />
distance nor coordinatization: POSA represents the <strong>data</strong> in direct products <strong>of</strong> chains and FCA<br />
uses the concept <strong>of</strong> concept and the conceptual hierarchy which is represented by line<br />
diagrams in the plane. POSA and FCA don´t have the key-word coordinatization in the<br />
narrow sense explained above though both <strong>methods</strong> use ordinal coordinates in direct products<br />
<strong>of</strong> chains as an important tool.<br />
4