Curriculum Focal Points
Curriculum Focal Points
Curriculum Focal Points
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
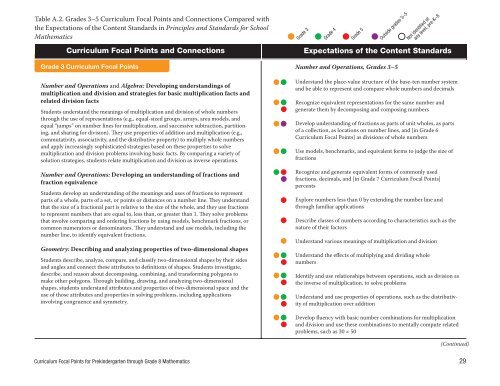
Table A.2. Table Grades A.2. 3–5 Grades <strong>Curriculum</strong> 3–5 <strong>Curriculum</strong> <strong>Focal</strong> <strong>Points</strong> <strong>Focal</strong> and <strong>Points</strong> Connections and Connections Compared Compared with with<br />
the Expectations the Expectations of the Content of the Standards Content Standards in Principles Principles and Standards Standards for School for School<br />
Mathematics Mathematics<br />
<strong>Curriculum</strong> <strong>Curriculum</strong> <strong>Focal</strong> <strong>Points</strong> <strong>Focal</strong> and <strong>Points</strong> Connections and Connections<br />
Grade 3<br />
Grade Grade 34<br />
Grade Grade 45<br />
Grade Outside 5 grades 3–5<br />
Outside Not identified grades at3–5<br />
any level, pre-K–8<br />
Not identified at<br />
any level, pre-K–8<br />
Expectations Expectations of the Content of the Content Standards Standards<br />
Grade 3 <strong>Curriculum</strong> Grade 3 <strong>Curriculum</strong> <strong>Focal</strong> <strong>Points</strong> <strong>Focal</strong> <strong>Points</strong><br />
Number and Number Operations and Operations and Algebra: and Developing Algebra: Developing understandings understandings of of<br />
multiplication multiplication and division and and division strategies and strategies for basic multiplication for basic multiplication facts and facts and<br />
related division related facts division facts<br />
Students understand Students understand the meanings the of meanings multiplication of multiplication and division and of whole division numbers of whole numbers<br />
through the through use of representations the use of representations (e.g., equal-sized (e.g., equal-sized groups, arrays, groups, area arrays, models, area and models, and<br />
equal “jumps” equal on “jumps” number on lines number for multiplication, lines for multiplication, and successive and subtraction, successive subtraction, partitioning,<br />
and sharing ing, and for sharing division). for They division). use properties They use of properties addition of and addition multiplication and multiplication (e.g., (e.g.,<br />
partition-<br />
commutativity, commutativity, associativity, associativity, and the distributive and the distributive property) to property) multiply to whole multiply numbers whole numbers<br />
and apply increasingly and apply increasingly sophisticated sophisticated strategies based strategies on these based properties on these to properties solve to solve<br />
multiplication multiplication and division and problems division involving problems basic involving facts. basic By comparing facts. By comparing a variety of a variety of<br />
solution strategies, solution students strategies, relate students multiplication relate multiplication and division and as inverse division operations. as inverse operations.<br />
Number and Number Operations: and Operations: Developing Developing an understanding understanding of fractions of and fractions and<br />
fraction equivalence<br />
fraction equivalence<br />
Students develop Students an develop understanding understanding of the meanings of the and meanings uses of and fractions uses of to fractions represent to represent<br />
parts of a whole, parts of parts a whole, of a set, parts or points of a set, or or distances points or on distances a number on line. a number They understand line. They understand<br />
that the size that of a the fractional size of a part fractional is relative part to is the relative size of to the whole, size of and the whole, they use and fractions they use fractions<br />
to represent to numbers represent that numbers are equal that to, are less equal than, to, or less greater than, than or greater 1. They than solve 1. problems They solve problems<br />
that involve that comparing involve comparing and ordering and fractions ordering by fractions using models, by using benchmark models, benchmark fractions, or fractions, or<br />
common numerators common numerators denominators. or denominators. They understand They understand use models, and use including models, the including the<br />
number line, number to identify line, equivalent to identify fractions. equivalent fractions.<br />
Geometry: Geometry: Describing Describing and analyzing and analyzing properties properties of two-dimensional of two-dimensional shapes shapes<br />
Students describe, Students analyze, describe, compare, analyze, and compare, classify and two-dimensional classify two-dimensional shapes by their shapes sides by their sides<br />
and angles and connect angles and these connect attributes these to attributes definitions to of definitions shapes. Students of shapes. investigate, Students investigate,<br />
describe, and describe, reason and about reason decomposing, about decomposing, combining, combining, and transforming and transforming polygons to polygons to<br />
make other make polygons. other Through polygons. building, Through drawing, building, and drawing, analyzing and two-dimensional<br />
analyzing two-dimensional<br />
shapes, students shapes, understand students understand attributes and attributes properties and of properties two-dimensional of two-dimensional space and the space and the<br />
use of those use attributes of those and attributes properties and in properties solving problems, in solving including problems, applications including applications<br />
involving congruence involving congruence and symmetry. and symmetry.<br />
Number and Number Operations, and Operations, Grades 3–5 Grades 3–5<br />
Understand Understand the place-value the place-value structure of structure the base-ten of the number base-ten system number system<br />
and be able and to represent be able to and represent compare and whole compare numbers whole and numbers decimals and decimals<br />
Recognize equivalent Recognize representations equivalent representations for the same for number the same and number and<br />
generate them generate by decomposing them by decomposing and composing and composing numbers numbers<br />
Develop understanding Develop understanding of fractions of as fractions parts of unit as parts wholes, of unit as parts wholes, as parts<br />
of a collection, of a as collection, locations as on locations number on lines, number and [in lines, Grade and 6 [in Grade 6<br />
<strong>Curriculum</strong> <strong>Curriculum</strong> <strong>Focal</strong> <strong>Points</strong>] <strong>Focal</strong> as divisions <strong>Points</strong>] as of divisions whole numbers of whole numbers<br />
Use models, Use benchmarks, models, benchmarks, and equivalent and forms equivalent to judge forms the to size judge of the size of<br />
fractions fractions<br />
Recognize and Recognize generate and equivalent generate forms equivalent of commonly forms of commonly used used<br />
fractions, decimals, fractions, and decimals, [in Grade and 7 [in <strong>Curriculum</strong> Grade 7 <strong>Curriculum</strong> <strong>Focal</strong> <strong>Points</strong>] <strong>Focal</strong> <strong>Points</strong>]<br />
percents percents<br />
Explore numbers Explore less numbers than 0 by less extending than 0 by the extending number the line number and line and<br />
through familiar through applications familiar applications<br />
Describe classes Describe of numbers classes of according numbers to according characteristics to characteristics such as the such as the<br />
nature of their nature factors of their factors<br />
Understand Understand various meanings various of meanings multiplication of multiplication and divisionand division<br />
Understand Understand the effects of the multiplying effects of multiplying and dividing and whole dividing whole<br />
numbers numbers<br />
Identify and Identify use relationships and use relationships between operations, between operations, such as division such as division as<br />
the inverse the of multiplication, inverse of multiplication, to solve problems to solve problems<br />
Understand Understand use properties and use of properties operations, of operations, such as the such distributivity<br />
of multiplication ity of multiplication over addition over<br />
as the distributiv-<br />
addition<br />
Develop fluency Develop with fluency basic number with basic combinations number combinations for multiplication for multiplication<br />
and division and division use these and combinations use these combinations to mentally to compute mentally related compute related<br />
problems, such problems, as 30 × such 50 as 30 × 50<br />
(Continued) (Continued)<br />
<strong>Curriculum</strong> <strong>Focal</strong> <strong>Points</strong> for Prekindergarten through Grade 8 Mathematics 29