ALGEBRA Equations, formulae, expressions and ... - Suffolk Maths
ALGEBRA Equations, formulae, expressions and ... - Suffolk Maths
ALGEBRA Equations, formulae, expressions and ... - Suffolk Maths
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The National Strategies | Secondary<br />
Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9<br />
151<br />
<strong>ALGEBRA</strong><br />
As outcomes, Year 8 pupils should, for example:<br />
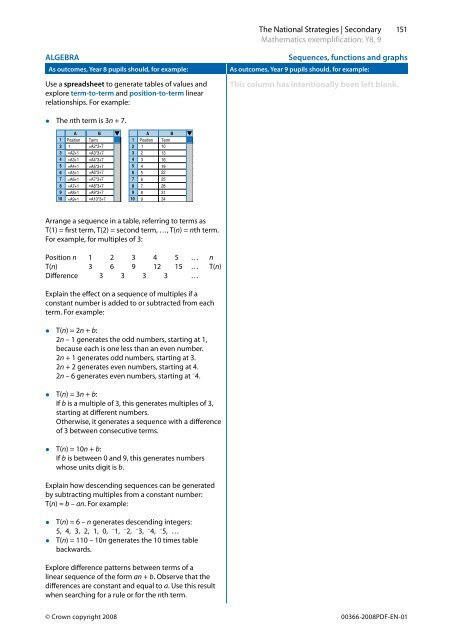
Use a spreadsheet to generate tables of values <strong>and</strong><br />
explore term-to-term <strong>and</strong> position-to-term linear<br />
relationships. For example:<br />
• The nth term is 3n + 7.<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
5<br />
6<br />
7<br />
8<br />
9<br />
10<br />
A<br />
Position<br />
1<br />
=A2+1<br />
=A3+1<br />
=A4+1<br />
=A5+1<br />
=A6+1<br />
=A7+1<br />
=A8+1<br />
=A9+1<br />
B<br />
Term<br />
=A2*3+7<br />
=A3*3+7<br />
=A4*3+7<br />
=A5*3+7<br />
=A6*3+7<br />
=A7*3+7<br />
=A8*3+7<br />
=A9*3+7<br />
=A10*3+7<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
5<br />
6<br />
7<br />
8<br />
9<br />
10<br />
A<br />
Position<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
5<br />
6<br />
7<br />
8<br />
9<br />
Term<br />
10<br />
13<br />
16<br />
19<br />
22<br />
25<br />
28<br />
31<br />
34<br />
B<br />
Sequences, functions <strong>and</strong> graphs<br />
As outcomes, Year 9 pupils should, for example:<br />
This column has intentionally been left blank.<br />
Arrange a sequence in a table, referring to terms as<br />
T(1) = first term, T(2) = second term, …, T(n) = nth term.<br />
For example, for multiples of 3:<br />
Position n 1 2 3 4 5 … n<br />
T(n) 3 6 9 12 15 … T(n)<br />
Difference 3 3 3 3 …<br />
Explain the effect on a sequence of multiples if a<br />
constant number is added to or subtracted from each<br />
term. For example:<br />
• T(n) = 2n + b:<br />
2n – 1 generates the odd numbers, starting at 1,<br />
because each is one less than an even number.<br />
2n + 1 generates odd numbers, starting at 3.<br />
2n + 2 generates even numbers, starting at 4.<br />
2n – 6 generates even numbers, starting at – 4.<br />
•<br />
T(n) = 3n + b:<br />
If b is a multiple of 3, this generates multiples of 3,<br />
starting at different numbers.<br />
Otherwise, it generates a sequence with a difference<br />
of 3 between consecutive terms.<br />
• T(n) = 10n + b:<br />
If b is between 0 <strong>and</strong> 9, this generates numbers<br />
whose units digit is b.<br />
Explain how descending sequences can be generated<br />
by subtracting multiples from a constant number:<br />
T(n) = b – an. For example:<br />
• T(n) = 6 – n generates descending integers:<br />
5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, – 1, – 2, – 3, – 4, – 5, …<br />
•<br />
T(n) = 110 – 10n generates the 10 times table<br />
backwards.<br />
Explore difference patterns between terms of a<br />
linear sequence of the form an + b. Observe that the<br />
differences are constant <strong>and</strong> equal to a. Use this result<br />
when searching for a rule or for the nth term.<br />
© Crown copyright 2008 00366-2008PDF-EN-01