hash functions
hash functions
hash functions
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
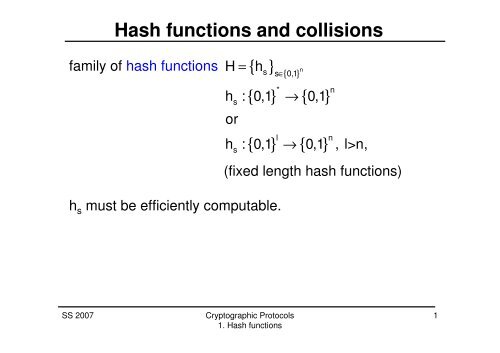
Hash <strong>functions</strong> and collisions<br />
family of <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong> H = { h }<br />
∈ { }<br />
s<br />
s<br />
s s 0,1 n<br />
{ } → { }<br />
* n<br />
h : 0,1 0,1<br />
or<br />
l<br />
{ } → { }<br />
h : 0,1<br />
n<br />
0,1 , l>n,<br />
(fixed length <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong>)<br />
h s must be efficiently computable.<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
1
Hash <strong>functions</strong> and collisions<br />
family of <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong> H = { h }<br />
∈ { }<br />
s<br />
s<br />
s s 0,1 n<br />
{ } → { }<br />
* n<br />
h : 0,1 0,1<br />
or<br />
l<br />
{ } → { }<br />
h : 0,1<br />
n<br />
0,1 , l>n,<br />
(fixed length <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong>)<br />
h s must be efficiently computable.<br />
collision<br />
( x,y) ∈{ 0,1 } * or ( x,y) ∈ { 0,1 } l<br />
with h ( x) = h ( y)<br />
s<br />
s<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
2
Collision-resistance<br />
Definition 1.1 The family of <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong><br />
H = { h } { }<br />
n<br />
s s ∈ 0,1<br />
is called (t,ε)-collision resistant if all probabilistic algorithms<br />
A running for at most t steps satisfy<br />
( ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) )<br />
Pr s ← U , x,y ← A s : h x = h y ,x ≠ y < ε.<br />
n s s<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
3
One-way function family<br />
Definition 1.2 The family of fixed length <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong><br />
l<br />
{ } { }<br />
{ } { }<br />
H = h n ,h : 0,1 → 0,1 , is called (t,ε)-one-way,<br />
s<br />
s∈<br />
0,1<br />
s<br />
if all probabilistic algorithms A running for at most t steps<br />
satisfy<br />
( n l ( s ( )) s ( ) s ( ))<br />
Pr s ← U , x ← U, x' ← A s,h x : h x' = h x < ε.<br />
n<br />
one-way=preimage-resistant<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
4
One-way vs. collision-resistance<br />
Theorem 1.3 Assume the family of fixed length <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong><br />
l<br />
{ } { }<br />
{ } { }<br />
H = h n ,h : 0,1 → 0,1 , is (t,ε)-collision-resistant,<br />
s<br />
s∈<br />
0,1<br />
s<br />
then H is (t-cl,2ε+ρ(H))-one-way for some fixed constant c.<br />
n<br />
Here<br />
−1<br />
( ) ( ) ( )<br />
( )<br />
n l s s<br />
ρ H : = Pr s ← U ,x ← U,z ← h x : h z = 1 .<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
5
Second-preimage-resistance<br />
Definition 1.4 The family of fixed length <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong><br />
l<br />
{ } { }<br />
{ } { }<br />
s<br />
s∈<br />
0,1<br />
s<br />
H = h n ,h : 0,1 → 0,1 , is called (t,ε)-secondpreimage-resistant,<br />
if all probabilistic algorithms A running<br />
for at most t steps satisfy<br />
n<br />
( ( ))<br />
⎛s ← U<br />
n, x1 ← U;<br />
l<br />
x2 ← A s,hs x<br />
1<br />
: ⎞<br />
Pr < ε.<br />
⎜<br />
hs ( x1) hs ( x<br />
2 ), x1 x ⎟<br />
⎝<br />
= ≠<br />
2 ⎠<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
6
Collisions vs. 2nd-preimages<br />
Theorem 1.5 Assume the family of fixed length <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong><br />
l<br />
{ } { }<br />
{ } { }<br />
H = h n ,h : 0,1 → 0,1 , is (t,ε)-collision-resistant,<br />
s<br />
s∈<br />
0,1<br />
s<br />
then H is (t,ε)-second-preimage-resistant.<br />
n<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
7
One-way vs. 2nd-preimage-resistance<br />
Theorem 1.6 Assume the family of fixed length <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong><br />
l<br />
{ } { }<br />
{ } { }<br />
s<br />
s∈<br />
0,1<br />
s<br />
H = h n ,h : 0,1 → 0,1 , is (t,ε)-2nd-preimageresistant,<br />
then H is (t-cl,2ε+ρ(H))-one-way for some fixed<br />
constant c.<br />
n<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
8
From 2nd-preimages to collisions<br />
Algorithm A computes 2nd-preimages.<br />
Algorithm B on input s∈{0,1} n , z=h s (x 1 ) with x 1 ∈{0,1} l :<br />
1. Set x 2 ←A(s,z). If A does not return an element<br />
x 2 ∈{0,1} l , return failure.<br />
2. If x 1 ≠x 2 , return (x 1 ,x 2 ), else return failure.<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
9
From preimages to 2nd-preimages<br />
Algorithm A computes preimages.<br />
Algorithm B on input s∈{0,1} n :<br />
1. Choose x 1 ←U l and compute z←h s (x 1 ).<br />
2. Set x 2 ←A(s,z). If A does not return an element<br />
x 2 ∈{0,1} l , return failure.<br />
3. If x 1 ≠x 2 , return (x 1 ,x 2 ), else return failure.<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
10
One-way vs. collision-resistance<br />
Corollary 1.7 Assume the family of fixed length <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong><br />
l<br />
{ } { }<br />
{ } { }<br />
H = h n ,h : 0,1 → 0,1 , is (t,ε)-collision-resistant,<br />
s<br />
s∈<br />
0,1<br />
s<br />
then H is (t-cl,2ε+2 n-l )-one-way for some fixed constant c.<br />
n<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
11
One-way vs. collision-resistance<br />
Definition 1.8 The family of fixed length <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong><br />
l<br />
{ } { }<br />
n { } { }<br />
H = h ,h : 0,1 → 0,1 , l>n,<br />
s<br />
s∈<br />
0,1<br />
s<br />
n<br />
is called regular,<br />
if |h s (x)|=2 l-n for all s ∈{0,1} n and all x ∈{0,1} l<br />
Corollary 1.9 Assume the regular family of <strong>hash</strong> <strong>functions</strong><br />
l<br />
{ } { }<br />
{ } { }<br />
H = h n ,h : 0,1 → 0,1 , is (t,ε)-collision-resistant,<br />
s<br />
s∈<br />
0,1<br />
s<br />
then H is (t-cl,2ε)-one-way for some fixed constant c.<br />
n<br />
SS 2007<br />
Cryptographic Protocols<br />
1. Hash <strong>functions</strong><br />
12