Modeling the Heat Gain of a Window With an Interior Shade ... - inive
Modeling the Heat Gain of a Window With an Interior Shade ... - inive
Modeling the Heat Gain of a Window With an Interior Shade ... - inive
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Proceedings <strong>of</strong> Clima 2007 WellBeing Indoors<br />
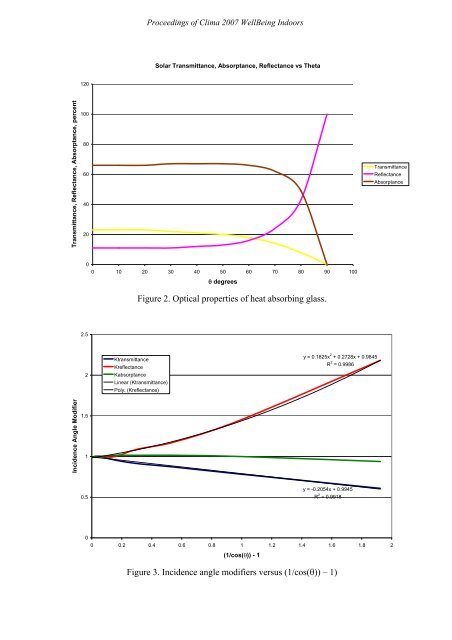
Solar Tr<strong>an</strong>smitt<strong>an</strong>ce, Absorpt<strong>an</strong>ce, Reflect<strong>an</strong>ce vs Theta<br />
120<br />
Tr<strong>an</strong>smitt<strong>an</strong>ce, Reflect<strong>an</strong>ce, Absorpt<strong>an</strong>ce, percent<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
Tr<strong>an</strong>smitt<strong>an</strong>ce<br />
Reflect<strong>an</strong>ce<br />
Absorpt<strong>an</strong>ce<br />
0<br />
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100<br />
θ degrees<br />
Figure 2. Optical properties <strong>of</strong> heat absorbing glass.<br />
2.5<br />
2<br />
Ktr<strong>an</strong>smitt<strong>an</strong>ce<br />
Kreflect<strong>an</strong>ce<br />
Kabsorpt<strong>an</strong>ce<br />
Linear (Ktr<strong>an</strong>smitt<strong>an</strong>ce)<br />
Poly. (Kreflect<strong>an</strong>ce)<br />
y = 0.1825x 2 + 0.2728x + 0.9845<br />
R 2 = 0.9986<br />
Incidence Angle Modifier<br />
1.5<br />
1<br />
0.5<br />
y = -0.2054x + 0.9945<br />
R 2 = 0.9918<br />
0<br />
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2<br />
(1/cos(θ)) - 1<br />
Figure 3. Incidence <strong>an</strong>gle modifiers versus (1/cos(θ)) – 1)