9-6a Solving Quadratic Equations Using Square ... - Math Slide Show
9-6a Solving Quadratic Equations Using Square ... - Math Slide Show
9-6a Solving Quadratic Equations Using Square ... - Math Slide Show
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
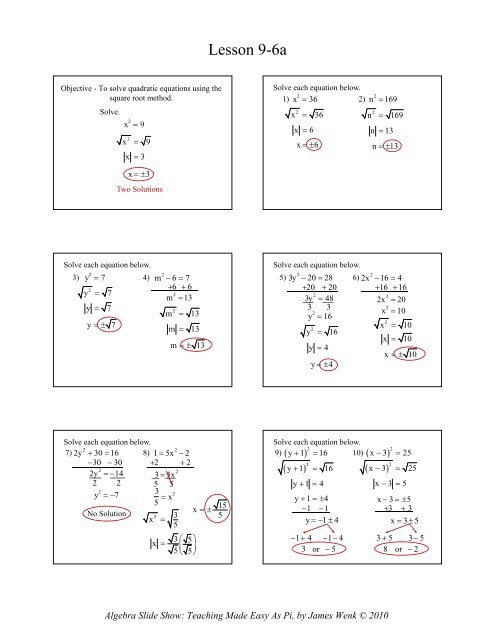
Lesson 9-<strong>6a</strong><br />
Objective - To solve quadratic equations using the<br />
square root method.<br />
Solve.<br />
x 2 = 9<br />
2<br />
x =<br />
9<br />
x = 3<br />
Solve each equation below.<br />
1) 2)<br />
x 2 = 36 n 2 =169<br />
2<br />
x = 36<br />
x = 6<br />
2<br />
n = 169<br />
n = 13<br />
x = ±6 n =±13<br />
x =±3<br />
Two Solutions<br />
Solve each equation below.<br />
3) y 2 = 7 4) m 2 − 6 = 7<br />
+6 + 6<br />
2<br />
y = 7<br />
m 2 =13<br />
y = 7<br />
y =± 7<br />
2<br />
m = 13<br />
m = 13<br />
m =± 13<br />
Solve each equation below.<br />
5) 3y 2 − 20 = 28 6) 2x 2 −16 = 4<br />
+20 + 20 +16 +16<br />
3y 2 = 48<br />
2x 2 = 20<br />
3 3<br />
x 2 = 10<br />
y<br />
2 = 16<br />
2<br />
y = 16<br />
y = 4<br />
y = ±4<br />
2<br />
x = 10<br />
x = 10<br />
x =± 10<br />
Solve each equation below.<br />
7) 2y 2 + 30 =16 8) 1 = 5x 2 − 2<br />
−30 − 30 +2 + 2<br />
2y 2 =−14 3 = 5x 2<br />
2 2 5 5<br />
y 2 =−77<br />
3 2<br />
5 = x<br />
No Solution<br />
x<br />
=<br />
2 3<br />
x<br />
=<br />
5<br />
3 ⎛ 5⎞<br />
5<br />
⎜ ⎟<br />
⎝ 5⎠<br />
x =±<br />
15<br />
5<br />
Solve each equation below.<br />
9) y+ 1 = 16 10)<br />
( ) 2<br />
( y+ 1) 2<br />
= 16<br />
y+ 1 = 4<br />
y + 1= ±<br />
4<br />
−1 −1<br />
y = −1 ± 4<br />
−1+ 4 −1− 4<br />
3 or − 5<br />
( x − 3) 2<br />
= 25<br />
( x − 3) 2<br />
= 25<br />
x − 3 = 5<br />
x − 3 = ±5<br />
+3 + 3<br />
x = 3±<br />
5<br />
3 + 5 3− 5<br />
8 or − 2<br />
Algebra <strong>Slide</strong> <strong>Show</strong>: Teaching Made Easy As Pi, by James Wenk © 2010
Lesson 9-<strong>6a</strong> (cont.)<br />
Height of a Falling Object<br />
Acceleration Due to Gravity ≈16 ft / sec 2<br />
h =−16t 2 + s<br />
h = height of object (in feet)<br />
t = time (in seconds)<br />
s = initial drop height (in feet)<br />
If a penny is dropped from the top of the<br />
Empire State Building which is 1453 feet<br />
tall, how long will it take to hit the ground?<br />
h = −16t 2 + s<br />
0 = −16t 2 +1453<br />
−1453<br />
−1453<br />
−1453 = −16t 2<br />
−16 −16<br />
90.8125 = t 2<br />
t = 90.8125 ≈ 9.5 sec .<br />
s = 1453 ft.<br />
h = 0 ft.<br />
Word Problems Involving <strong>Quadratic</strong>s<br />
If the square of two consecutive integers are added,<br />
the result is 61. Find the integers.<br />
Let x = 1st integer =−6 x = 5<br />
or<br />
x + 1 = 2nd integer =−5 x+ 1=<br />
6<br />
2 2<br />
x + (x+ 1) = 61<br />
2 2<br />
x + x + 2x+ 1=<br />
61<br />
−61 −61<br />
2<br />
2x + 2x − 60 = 0<br />
2 2<br />
2<br />
x + x− 30=<br />
0<br />
2<br />
x + x− 30=<br />
0<br />
(x + 6)(x − 5) = 0<br />
x =−6<br />
or x = 5<br />
The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 20 inches. One<br />
leg of the right triangle is 4 inches longer than the<br />
other leg. Find the lengths of both legs.<br />
20 Let x = smaller leg = 12 inches<br />
x<br />
x + 4 = larger leg = 16 inches<br />
x + 4<br />
a + b = c<br />
2 2 2<br />
2 2 2<br />
x + (x+ 4) = 20<br />
2 2<br />
x + x + 8x + 16 = 400<br />
− 400 − 400<br />
2<br />
2x + 8x − 384 = 0<br />
2 2<br />
2<br />
4 1<br />
x + 4x − 192 = 0<br />
•<br />
192<br />
2•<br />
96<br />
3•<br />
64<br />
+ 16 − 12 = 4•<br />
48<br />
6•<br />
32<br />
8•<br />
24<br />
12 • 16<br />
(x )(x ) 0<br />
x =−16<br />
or 12<br />
Find the dimensions of a rectangle whose perimeter<br />
is 38 inches and whose area is 84 square inches.<br />
19 - x<br />
P = 38 in.<br />
x<br />
Let x = width = 7 inches<br />
19 - x = length = 12 inches<br />
19 in.<br />
l • w = A<br />
2<br />
0= x − 19x+<br />
84<br />
(19 − x) • x = 84<br />
0 = (x −7 )(x −12)<br />
2<br />
19x − x = 84<br />
2 2<br />
+ x + x<br />
x = 7 or 12<br />
2<br />
19x = x + 84<br />
−19x<br />
−19x<br />
2<br />
0= x − 19x+<br />
84<br />
1•<br />
84<br />
2•<br />
42<br />
3•<br />
28<br />
4•<br />
21<br />
6•<br />
14<br />
7•<br />
12<br />
A picture frame measures 30”x 20”. The picture<br />
2<br />
inside the frame has a area of 416 in . Find the<br />
width of the frame.<br />
if if<br />
x Let x = frame width x = 2 x = 23<br />
416 in 2 30 - 2x = picture length = 26 −16<br />
x 20 - 2x = picture width = 16<br />
20 x x<br />
30<br />
l• w=<br />
A<br />
(30− 2x)(20− 2x) = 416<br />
2<br />
600 − 100x + 4x = 416<br />
− 416 − 416<br />
2<br />
4x − 100x + 184 = 0<br />
4 4<br />
2<br />
x − 25x+ 46=<br />
0<br />
(x −2)(x − 23) = 0<br />
x = 2 or x = 23<br />
frame width = 2 in.<br />
Algebra <strong>Slide</strong> <strong>Show</strong>: Teaching Made Easy As Pi, by James Wenk © 2010