Dear Reader: Innovations across the entire package - Pharma ...
Dear Reader: Innovations across the entire package - Pharma ...
Dear Reader: Innovations across the entire package - Pharma ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Excipients & Actives for <strong>Pharma</strong><br />
No. 26, 2011<br />
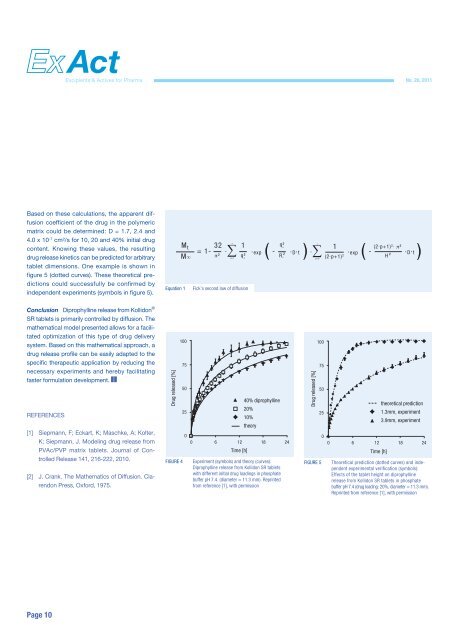
Based on <strong>the</strong>se calculations, <strong>the</strong> apparent diffusion<br />
coefficient of <strong>the</strong> drug in <strong>the</strong> polymeric<br />
matrix could be determined: D = 1.7, 2.4 and<br />
4.0 x 10 -7 cm²/s for 10, 20 and 40% initial drug<br />
content. Knowing <strong>the</strong>se values, <strong>the</strong> resulting<br />
drug release kinetics can be predicted for arbi trary<br />
tablet dimensions. One example is shown in<br />
figure 5 (dotted curves). These <strong>the</strong>oretical predictions<br />
could successfully be confirmed by<br />
independent experiments (symbols in figure 5).<br />
Equation 1<br />
M t<br />
M∞<br />
= 1-<br />
32<br />
π²<br />
·∑∞<br />
n=1<br />
Fick’s second law of diffusion<br />
1<br />
·exp<br />
q² ( -<br />
n<br />
R c<br />
q² n<br />
² ·D·t ) ·∑∞<br />
p=0<br />
1<br />
(2·p+1) 2 ·exp ( - (2·p+1)2· π²<br />
H ²<br />
·D·t<br />
)<br />
Conclusion Diprophylline release from Kollidon ®<br />
SR tablets is primarily controlled by diffusion. The<br />
ma<strong>the</strong>matical model presented allows for a facilitated<br />
optimization of this type of drug delivery<br />
system. Based on this ma<strong>the</strong>matical approach, a<br />
drug release profile can be easily adapted to <strong>the</strong><br />
specific <strong>the</strong>rapeutic application by reducing <strong>the</strong><br />
necessary experiments and hereby facilitating<br />
faster formulation development.<br />
REFERENCES<br />
[1] Siepmann, F; Eckart, K; Maschke, A; Kolter,<br />
K; Siepmann, J. Modeling drug release from<br />
PVAc/PVP matrix tablets. Journal of Controlled<br />
Release 141, 216-222, 2010.<br />
[2] J. Crank. The Ma<strong>the</strong>matics of Diffusion. Clarendon<br />
Press, Oxford, 1975.<br />
Drug released [%]<br />
100<br />
75<br />
50<br />
25<br />
0<br />
FIGURE 4<br />
40% diprophylline<br />
20%<br />
10%<br />
<strong>the</strong>ory<br />
0 6 12 18 24<br />
Time [h]<br />
Experiment (symbols) and <strong>the</strong>ory (curves):<br />
Diprophylline release from Kollidon SR tablets<br />
with different initial drug loadings in phosphate<br />
buffer pH 7.4. (diameter = 11.3 mm). Reprinted<br />
from reference [1], with permission<br />
Drug released [%]<br />
100<br />
75<br />
50<br />
25<br />
0<br />
FIGURE 5<br />
<strong>the</strong>oretical prediction<br />
1.3mm, experiment<br />
3.9mm, experiment<br />
0 6 12 18 24<br />
Time [h]<br />
Theoretical prediction (dotted curves) and independent<br />
experimental verification (symbols):<br />
Effects of <strong>the</strong> tablet height on diprophylline<br />
release from Kollidon SR tablets in phosphate<br />
buffer pH 7.4 (drug loading: 20%, diameter = 11.3 mm).<br />
Reprinted from reference [1], with permission<br />
Page 10