Trigonometry.
Trigonometry.
Trigonometry.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
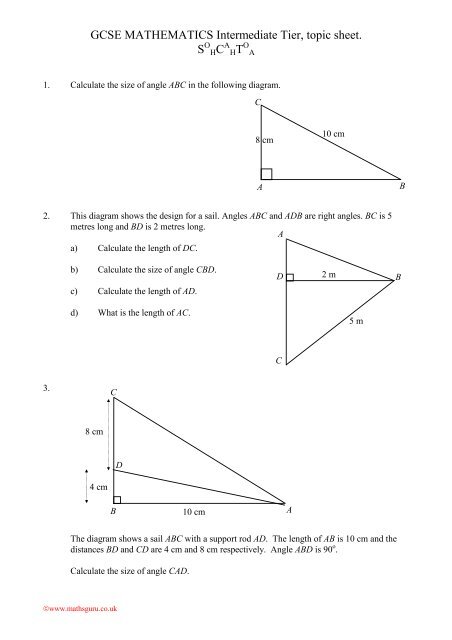
GCSE MATHEMATICS Intermediate Tier, topic sheet.<br />
S O HC A HT O A<br />
1. Calculate the size of angle ABC in the following diagram.<br />
C<br />
8 cm<br />
10 cm<br />
A<br />
B<br />
2. This diagram shows the design for a sail. Angles ABC and ADB are right angles. BC is 5<br />
metres long and BD is 2 metres long.<br />
A<br />
a) Calculate the length of DC.<br />
b) Calculate the size of angle CBD.<br />
c) Calculate the length of AD.<br />
D<br />
2 m<br />
B<br />
d) What is the length of AC.<br />
5 m<br />
C<br />
3.<br />
C<br />
8 cm<br />
D<br />
4 cm<br />
B<br />
10 cm<br />
A<br />
The diagram shows a sail ABC with a support rod AD. The length of AB is 10 cm and the<br />
distances BD and CD are 4 cm and 8 cm respectively. Angle ABD is 90 o .<br />
Calculate the size of angle CAD.<br />
www.mathsguru.co.uk
4. a) The angle of elevation of the top of a building from a point 75 m horizontally from<br />
the foot of the building is 48 o . Calculate the height of the building.<br />
b) Triangle PQR is right-angled at R, the length of PQ is 35 m and the length of QR is<br />
12 m. Calculate the size of QPR ˆ .<br />
Q<br />
35 m<br />
12 m<br />
P<br />
R<br />
5. Calculate the size of angle CAD in the diagram below.<br />
C<br />
D<br />
16 cm<br />
12 cm<br />
B<br />
8 cm<br />
A<br />
6. In the diagram below, angle BAC = 60 o , CD = 12 cm and AC = 10 cm.<br />
Calculate the length of BD.<br />
B<br />
D<br />
12 cm<br />
C<br />
10 cm<br />
60 o<br />
A<br />
www.mathsguru.co.uk
SOLUTIONS / ANSWERS.<br />
REMEMBER THAT S O HC A HT O A ONLY<br />
APPLIES TO RIGHT-ANGLED<br />
TRIANGLES.<br />
1. First label the sides with Opp (for Opposite), Hyp (for Hypotenuse) and Adj (for Adjacent)<br />
etc.<br />
C<br />
Opp = 8 cm<br />
Hyp = 10 cm<br />
Angle ABC<br />
A<br />
B<br />
Since we are dealing with O and H, we use the Sin button on the calculator.<br />
Sin ABC = H<br />
O = 10<br />
8 .<br />
{always follow the Sin, Cos, Tan with the angle!}<br />
So, Sin ABC = 10<br />
8 .<br />
There is no point trying to press the Sin button since we do not know the angle ABC.<br />
Instead we use Inv Sin<br />
So, push Inv Sin 10<br />
8 to get the answer ABC = 53.13 o .<br />
{use the fraction button a<br />
b c }<br />
2. a) Use the Pythagoras theorem in the right-angled triangle BDC.<br />
5 2 = 2 2 + DC 2<br />
25 = 4 + DC 2<br />
21 = DC 2<br />
DC = 4.582575695 m {don’t round up because you’ll probably need this answer<br />
again.}<br />
b) Again, use the right-angled triangle BDC.<br />
A 2<br />
Cos CBD =<br />
H = 5<br />
CBD = 66.42182152 o .<br />
D<br />
Adj = 2 m<br />
B<br />
Hyp = 5 m<br />
angle CBD<br />
{after pressing Inv Cos etc.}<br />
C<br />
www.mathsguru.co.uk
c) Now use the right-angled triangle ABD.<br />
A<br />
Opp<br />
90 66.42182152 o = 23.57817848 o<br />
D<br />
Adj = 2 m<br />
B<br />
Tan 23.57817848 o O<br />
=<br />
A =<br />
which means 0.43643578 =<br />
AD<br />
2<br />
AD .<br />
2<br />
Thus, after multiplying by 2 we get AD = 0.872871561 m.<br />
d) AC = AD + DC = 0.872871561 + 4.582575695 = 5.455447256 m.<br />
3.<br />
C<br />
angle CAD<br />
8 cm<br />
D<br />
4 cm<br />
B<br />
10 cm<br />
A<br />
Since the required angle is NOT part of a right-angled triangle we must work around the<br />
problem.<br />
First consider triangle ABC.<br />
C<br />
Opp = 12 cm<br />
Tan x =<br />
O<br />
A =<br />
12<br />
10<br />
{Inv Tan}<br />
x = 50.19442891 o .<br />
B<br />
Adj = 10 cm<br />
x<br />
A<br />
www.mathsguru.co.uk
Now consider triangle ABD.<br />
D<br />
Opp = 4 cm<br />
B<br />
Adj = 10 cm<br />
y<br />
A<br />
Tan y =<br />
O<br />
A =<br />
4<br />
10<br />
{Inv Tan}<br />
y = 21.80140949 o .<br />
To finish off, simply note that angle CAD = x y = 50.19442891 21.80140949<br />
= 28.39301942 o .<br />
4. a) You must first draw a diagram for this.<br />
Building<br />
48 o<br />
75 m<br />
Using Tan: tan 48 o O<br />
=<br />
A =<br />
which means 1.110612515 =<br />
height<br />
75<br />
height .<br />
75<br />
Multiplying by 75 gives<br />
height = 83.30 m {2 decimal places}.<br />
O 12<br />
b) Using Sin: sin QPR =<br />
H = 35<br />
{Inv Sin}<br />
QPR = 20.05 o {2 decimal places}.<br />
Q<br />
Hyp = 35 m<br />
Opp = 12 m<br />
P<br />
R<br />
5. This is very similar to question 3) but uses Inv Cos instead of Inv Tan.<br />
Answer = 11.8 o {1 decimal place}.<br />
6. Use S O HC A HT O A in the right-angled triangle ABC to get BC = 17.32050808 cm.<br />
This means that BD = 17.32050808 12 = 5.3 cm {1 decimal place}.<br />
www.mathsguru.co.uk