Cryptanalysis of RSA Factorization - Library(ISI Kolkata) - Indian ...
Cryptanalysis of RSA Factorization - Library(ISI Kolkata) - Indian ...
Cryptanalysis of RSA Factorization - Library(ISI Kolkata) - Indian ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3 1.2 Symmetric Key Cryptography<br />
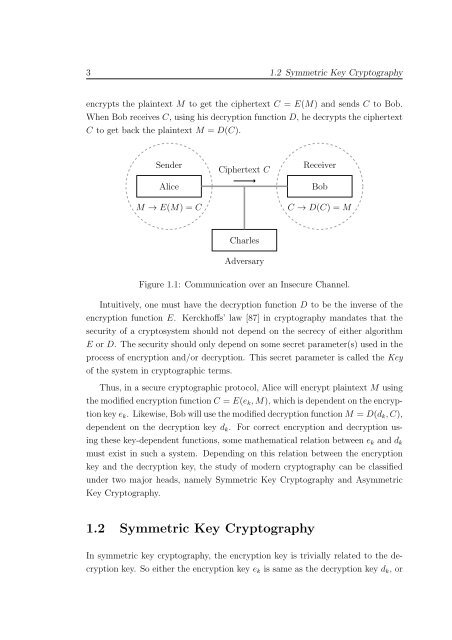
encrypts the plaintext M to get the ciphertext C = E(M) and sends C to Bob.<br />
When Bob receives C, using his decryption function D, he decrypts the ciphertext<br />
C to get back the plaintext M = D(C).<br />
Sender<br />
Alice<br />
M → E(M) = C<br />
Ciphertext C<br />
Receiver<br />
Bob<br />
C → D(C) = M<br />
Charles<br />
Adversary<br />
Figure 1.1: Communication over an Insecure Channel.<br />
Intuitively, one must have the decryption function D to be the inverse <strong>of</strong> the<br />
encryption function E. Kerckh<strong>of</strong>fs’ law [87] in cryptography mandates that the<br />
security <strong>of</strong> a cryptosystem should not depend on the secrecy <strong>of</strong> either algorithm<br />
E or D. The security should only depend on some secret parameter(s) used in the<br />
process <strong>of</strong> encryption and/or decryption. This secret parameter is called the Key<br />
<strong>of</strong> the system in cryptographic terms.<br />
Thus, in a secure cryptographic protocol, Alice will encrypt plaintext M using<br />
themodifiedencryptionfunctionC = E(e k ,M), whichisdependentontheencryptionkeye<br />
k . Likewise,BobwillusethemodifieddecryptionfunctionM = D(d k ,C),<br />
dependent on the decryption key d k . For correct encryption and decryption using<br />
these key-dependent functions, some mathematical relation between e k and d k<br />
must exist in such a system. Depending on this relation between the encryption<br />
key and the decryption key, the study <strong>of</strong> modern cryptography can be classified<br />
under two major heads, namely Symmetric Key Cryptography and Asymmetric<br />
Key Cryptography.<br />
1.2 Symmetric Key Cryptography<br />
In symmetric key cryptography, the encryption key is trivially related to the decryption<br />
key. So either the encryption key e k is same as the decryption key d k , or