Synthetic Strategy and Therapeutic Utility of Oxygen and Nitrogen Containing Heterocyclic Compounds
The oxygen and nitrogen containing heterocyclic compounds are very important in there synthetic aspect because of their enormous pharmacological applications. Several new reagents, substrates and methods are being developed every year to facilitate their synthesis. This review is an effort to sum up the methods recently utilized for the synthesis of this important group of heterocyclic compounds.
The oxygen and nitrogen containing heterocyclic compounds are very important in there synthetic aspect because
of their enormous pharmacological applications. Several new reagents, substrates and methods are being developed
every year to facilitate their synthesis. This review is an effort to sum up the methods recently utilized for the synthesis
of this important group of heterocyclic compounds.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Review Article<br />
Journal homepage: http://www.ijpsl.com<br />
ISSN:2277-4564<br />
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
<strong>Synthetic</strong> <strong>Strategy</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Therapeutic</strong> <strong>Utility</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Oxygen</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Nitrogen</strong> <strong>Containing</strong><br />
<strong>Heterocyclic</strong> <strong>Compounds</strong><br />
Lincy Joseph*, Mathew George <strong>and</strong> Surekha SR<br />
Pushpagiry College <strong>of</strong> Pharmacy,Thiruvalla,Kerala-689101<br />
ABSTRACT<br />
The oxygen <strong>and</strong> nitrogen containing heterocyclic compounds are very important in there synthetic aspect because<br />
<strong>of</strong> their enormous pharmacological applications. Several new reagents, substrates <strong>and</strong> methods are being developed<br />
every year to facilitate their synthesis. This review is an effort to sum up the methods recently utilized for the synthesis<br />
<strong>of</strong> this important group <strong>of</strong> heterocyclic compounds.<br />
Introduction<br />
<strong>Heterocyclic</strong>'s are an important class <strong>of</strong> compounds,<br />
making up more than half <strong>of</strong> all known organic compounds.<br />
In fact two thirds <strong>of</strong> organic compounds are<br />
heterocyclic compounds. A cyclic organic compound<br />
containing all carbon atoms in ring formation is referred<br />
to as a carboxylic compound. If at least one atom<br />
other than carbon forms a part <strong>of</strong> the ring system then it<br />
is designated as a heterocyclic compound [1]. <strong>Nitrogen</strong>,<br />
oxygen <strong>and</strong> sulfur are the most common hetero atoms.<br />
Besides the vast distribution <strong>of</strong> heterocyclic in natural<br />
products, they are also the major components <strong>of</strong> biological<br />
molecules such as DNA <strong>and</strong> RNA. DNA is<br />
without doubt the most important macromolecule <strong>of</strong><br />
life. Nucleotides, the building blocks <strong>of</strong> our genes are<br />
derivatives <strong>of</strong> pyrimidine <strong>and</strong> purine ring structures.<br />
Chlorophyll <strong>and</strong> heme, the oxygen carriers in plants<br />
<strong>and</strong> animals respectively are derivatives <strong>of</strong> large porphyrin<br />
rings.<br />
<strong>Heterocyclic</strong>'s are present in a wide variety <strong>of</strong> drugs,<br />
most vitamins, many natural products, biomolecules,<br />
<strong>and</strong> biologically active compounds, including antitumor,<br />
antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, antidepressant, antimalarial,<br />
anti-HIV, antimicrobial, antibacterial, antifungal,<br />
antiviral, antidiabetic, herbicidal, fungicidal, <strong>and</strong><br />
insecticidal agents. Also, they have been frequently<br />
found as a key structural unit in synthetic pharmaceuticals<br />
<strong>and</strong> agrochemicals. Some <strong>of</strong> these compounds exhibit<br />
a significant solvatochromic, photochromic, <strong>and</strong><br />
bio chemi-luminescence properties. Most <strong>of</strong> the heterocycles<br />
possess important applications in materials science<br />
such as dyestuff, fluorescent sensor, brightening<br />
agents, information storage, plastics, <strong>and</strong> analytical<br />
reagents. We can classify the oxygen <strong>and</strong> <strong>Nitrogen</strong><br />
Key words: Oxazoles, Oxaziridine, isoxazole, oxadiazole,<br />
morpholine<br />
Received 27 May 2014; accepted 25 June 2014;<br />
*Corresponding Author: Ms. Lincy Joseph<br />
Pushpagiry College <strong>of</strong> Pharmacy,Thiruvalla,Kerala-<br />
689101<br />
Email: mathewlincg@yahoo.com<br />
Copyright ©2011 Published by IJPSL. All rights reserved<br />
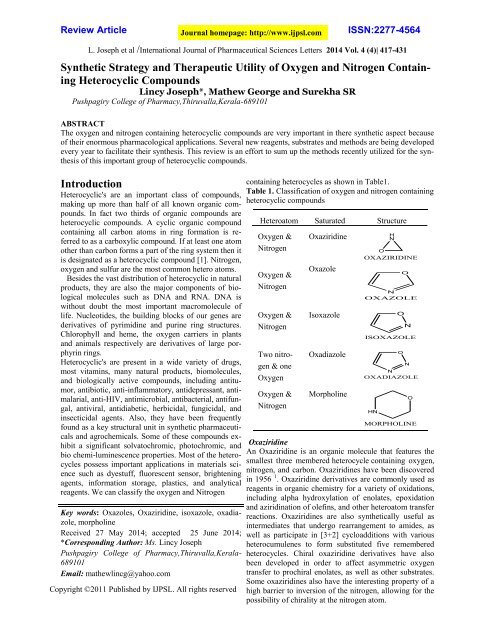
containing heterocycles as shown in Table1.<br />
Table 1. Classification <strong>of</strong> oxygen <strong>and</strong> nitrogen containing<br />
heterocyclic compounds<br />
Heteroatom Saturated Structure<br />
<strong>Oxygen</strong> &<br />
<strong>Nitrogen</strong><br />
<strong>Oxygen</strong> &<br />
<strong>Nitrogen</strong><br />
<strong>Oxygen</strong> &<br />
<strong>Nitrogen</strong><br />
Two nitrogen<br />
& one<br />
<strong>Oxygen</strong><br />
<strong>Oxygen</strong> &<br />
<strong>Nitrogen</strong><br />
Oxaziridine<br />
Oxazole<br />
Isoxazole<br />
Oxadiazole<br />
Morpholine<br />
O<br />
OXAZIRIDINE<br />
Oxaziridine<br />
An Oxaziridine is an organic molecule that features the<br />
smallest three membered heterocycle containing oxygen,<br />
nitrogen, <strong>and</strong> carbon. Oxaziridines have been discovered<br />
in 1956 1 . Oxaziridine derivatives are commonly used as<br />
reagents in organic chemistry for a variety <strong>of</strong> oxidations,<br />
including alpha hydroxylation <strong>of</strong> enolates, epoxidation<br />
<strong>and</strong> aziridination <strong>of</strong> olefins, <strong>and</strong> other heteroatom transfer<br />
reactions. Oxaziridines are also synthetically useful as<br />
intermediates that undergo rearrangement to amides, as<br />
well as participate in [3+2] cycloadditions with various<br />
heterocumulenes to form substituted five remembered<br />
heterocycles. Chiral oxaziridine derivatives have also<br />
been developed in order to affect asymmetric oxygen<br />
transfer to prochiral enolates, as well as other substrates.<br />
Some oxaziridines also have the interesting property <strong>of</strong> a<br />
high barrier to inversion <strong>of</strong> the nitrogen, allowing for the<br />
possibility <strong>of</strong> chirality at the nitrogen atom.<br />
H<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
OXAZOLE<br />
O<br />
N<br />
ISOXAZOLE<br />
O<br />
N<br />
N<br />
OXADIAZOLE<br />
HN<br />
O<br />
MORPHOLINE
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
Chemistry <strong>of</strong> Oxaziridine<br />
SCHEME 1<br />
Widmer.J. Keller-Schierlein, W.Helv,et al Oxidized<br />
imines with per acids <strong>and</strong> carbonyl compounds with<br />
amine to synthesize Oxaziridines.<br />
R<br />
N<br />
R 2 R 3 R 4 CO 3 H<br />
R 1 ,R 2 ,R 3 =Alkyl,aryl<br />
N<br />
O<br />
R 2<br />
R 3 R 2<br />
R 3<br />
A<br />
SCHEME 2<br />
HO<br />
H 3 C<br />
O<br />
CH 3<br />
O<br />
RCl+NaOH (Phase<br />
Transfer catalysis)<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
CH 3<br />
H 2 O 2 (30%.acq)<br />
R-CO-NH 2<br />
eg;acetamide,benzamide<br />
* asymetric carbon atom<br />
O<br />
R 2<br />
R 1 -NHX<br />
R 3 X==Cl,OSO 3 H,<br />
N R 1<br />
B<br />
H 3 C<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
*<br />
NH<br />
+ H 2 O<br />
R 1 =H,CH 3<br />
X=Cl,OSO 3 H<br />
SCHEME 2<br />
Perfluorinated oxaziridines may be synthesized by<br />
subjecting perfluorinated imines to perfluoromethy l<br />
fluorocarbonyl peroxide <strong>and</strong> a metal fluoride to act as an<br />
HF scavenger<br />
H 3 C<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
p- TsOH (cat/toluene)<br />
dist.water azeotropically<br />
in to a Dean-Stark Tube.<br />
O<br />
N<br />
O<br />
R 1<br />
N<br />
F<br />
R 2<br />
CF 3 OO(O)F<br />
C S F<br />
R 1<br />
N<br />
O<br />
F<br />
R 2<br />
H 3 C<br />
O<br />
O<br />
ethyl carbitol<br />
b.p 202 0 C<br />
1 eq.<br />
OH + 1/3<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
s-Trioxane<br />
m.p 62 0 C<br />
0.4 eq.<br />
+ H 2 O<br />
+<br />
O<br />
H 3 C CH 3<br />
acetone<br />
b.p 520C<br />
1.5 eq.<br />
R 1 =i-C 3 F 7 ,n-C 3 F 7 ,n-C 4 F 9<br />
R 2 =CF 3 ,C 2 F5,n-C 3 F 7<br />
p-Ts OH( cat)<br />
reflux<br />
N-Acyloxaziridines<br />
Schulz, Becker <strong>and</strong> Rieche proposed practical schemes<br />
which involve the addition <strong>of</strong> primary amine to an olefin<br />
undergoing ozonolysis produce a β aminohydroperoxide<br />
which is an unstable intermediate .dehydration <strong>of</strong> this<br />
intermediate closes the three atom ring to yield the<br />
oxaziridine.<br />
The second scheme proposed is the modification <strong>of</strong> this<br />
reaction in which hydrogen peroxide <strong>and</strong> a primary amide<br />
add to a ketone carbonyl group with a subsequent dehydration<br />
<strong>of</strong> the hydroperoxide amide intermediate to the N-<br />
Acyloxaziridines.<br />
H 3 C<br />
H 3 C<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
H2O2 (30% (1 eq.))<br />
+ R-CO-NH 2 (1 eq.)<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O CH 3<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
+ H 2 O<br />
O R<br />
+ H 2 O<br />
NH<br />
CH 3<br />
SCHEME.1<br />
H 3 C<br />
O<br />
O<br />
Ethyl carbitol<br />
B.P.202 0 C<br />
OH<br />
SOCl 2<br />
CH 2 Cl 2<br />
O<br />
H 3 C O<br />
Cl<br />
1-Chloro3,6-dioxo-octane=RCl<br />
H 3 C<br />
O<br />
p-TsOHcat/toluene<br />
dist.H 2 O,azeotropically<br />
in to a Dean Stark tube.<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
N<br />
CH 3<br />
O<br />
R<br />
+ H 2 O<br />
R = alkyl /aryl group.eg; acetamide,benzamide..<br />
418
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
Pharmacological Activity <strong>of</strong> Oxaziridines<br />
The cytotoxicity <strong>of</strong> oxaziridines photo generated after<br />
irradiation <strong>of</strong> chlordiazepoxide (CDZ) <strong>and</strong> its metabolites<br />
was investigated in vitro by a MTT assay on P388 leukemia<br />
<strong>and</strong> B16 melanoma cell lines <strong>and</strong> compared with that<br />
<strong>of</strong> the anticancer drug, melphalen. It was found that for<br />
the longer time-exposure experiment, oxaziridines had<br />
the same cytotoxicity as melphalen <strong>and</strong> this toxicity was<br />
higher when oxaziridines were photo generated in the<br />
presence <strong>of</strong> cells. In conclusion, oxaziridines generated<br />
after CDZ, demoxepam, <strong>and</strong> desmethylchlordiazepoxide<br />
ultraviolet irradiation exhibited cytotoxicity activity<br />
against cancer cell lines. A possibility <strong>of</strong> CDZ use within<br />
the context <strong>of</strong> photodynamic therapy as a treatment for<br />
small, superficial tumors should not be excluded, because<br />
oxaziridines can be generated locally by skin-tumor local<br />
irradiation after CDZ topical administration. Oxaziridine<br />
is also used in impregnated silica nanoparticles for removal<br />
<strong>of</strong> sulfur mustard from wastewater.<br />
Oxazole<br />
Oxazole is a heterocyclic organic compound that has a<br />
five-member ring molecular structure,C 3 H 3 ON, containing<br />
three carbon atoms, one oxygen atom <strong>and</strong><br />
one nitrogen atom. It is a clear to yellowish liquid with a<br />
pyridine like odor. It is soluble in alcohol <strong>and</strong> ether <strong>and</strong><br />
slightly soluble in water. Oxazoles <strong>and</strong> its derivatives are<br />
used as building block for biochemicals <strong>and</strong> pharmaceutical<br />
as well as in other industrial applications such as pesticides,<br />
dyes, fluorescent brightening agents, textile auxiliaries<br />
<strong>and</strong> plastics. The term <strong>of</strong> isoxazole is for 1,2-<br />
oxazole.<br />
Oxazoles derivatives have become increasingly important<br />
because <strong>of</strong> their use as intermediates for the preparation<br />
<strong>of</strong> new biological materials. The oxazole ring is present<br />
in numerous pharmacologically important compounds,<br />
including those used as antibiotics <strong>and</strong> antiproliferatives.<br />
The wide range <strong>of</strong> biological activities <strong>of</strong> oxazoles<br />
includes anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antibacterial,<br />
antifungal, hypoglycemic, antiproliferative, antituberculosis,<br />
muscle relaxant <strong>and</strong> HIV inhibitor activity.<br />
In addition, oxazole derivatives are useful synthetic intermediates<br />
<strong>and</strong> can be used as diversity scaffolds in combinatorial<br />
chemistry <strong>and</strong> as peptidomimetics. The presence<br />
<strong>of</strong> a halogen allows these reagents to be used as substrates<br />
in various coupling reactions, including Suzuki-Miyaura<br />
cross-coupling reactions.<br />
SYNTHESIS<br />
SCHEME 1<br />
N.A. Strotman,H. R.Chobanian et al report a complementary<br />
[3] methods for direct arylation <strong>of</strong> with high regioselectivity<br />
at both C-5 <strong>and</strong> C-2 have been developed for a<br />
wide range <strong>of</strong> aryl <strong>and</strong> heteroaryl bromides, chlorides,<br />
iodides, <strong>and</strong> triflates. Using task-specific phosphine<br />
lig<strong>and</strong>s, palladium-catalyzed C-5 arylation <strong>of</strong> oxazoles is<br />
preferred in polar solvents, whereas C-2 arylation is preferred<br />
by nonpolar solvents.<br />
Ar-X<br />
X: Cl,Br,<br />
+<br />
O<br />
N<br />
5 mol - % Pd(OAc) 2<br />
. 1<br />
eq. lig<strong>and</strong><br />
3 eq. K 2<br />
CO 3<br />
, . 4 eq . PivOH<br />
DMA, 110 0 C , 16h<br />
SCHEME2<br />
N. A.Strotman, H.R.Chobanian et al [3] in 2010 again<br />
reported a quaternary ammonium hydroxide ion exchange<br />
resin catalyzes the reaction <strong>of</strong> p-<br />
tolylsulfonylmethyl isocyanide (TosMIC) with aromatic<br />
aldehydes to give 5-aryloxazoles. The base <strong>and</strong><br />
the p-tolylsulfinic acid byproduct can be removed by<br />
simple filtration, resulting in oxazoles in high yield <strong>and</strong><br />
purity.<br />
Ar<br />
O<br />
+<br />
H<br />
Tos<br />
SCHEME 3<br />
A simple <strong>and</strong> efficient Cs 2 CO 3 -mediated reaction <strong>of</strong><br />
aromatic <strong>and</strong> unsaturated primary amides with 2,3-<br />
dibromopropene allows the synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2-aryl-5-alkylsubstituted<br />
oxazoles in a single step good yields.<br />
O<br />
R +<br />
NH 2 H 2 C<br />
B.Wu,J.Wen, et al [4] in 2009 reported an improved<br />
one-pot van Leusen oxazole synthesis using tosylmethyl<br />
isocyanide (TosMIC), aliphatic halides <strong>and</strong><br />
various aldehydes in ionic liquids allows the preparation<br />
<strong>of</strong> 4,5-disubstituted oxazoles in high yields. The<br />
recovered ionic liquids could be reused as solvent for<br />
six runs without significant loss <strong>of</strong> yields.<br />
F.Besselievre,S.Lebrequier et al in 2009 [5] reported a<br />
method in which Pd (PPh 3 ) 4 efficiently catalyses both<br />
direct arylation <strong>and</strong> alkenylation <strong>of</strong> oxazoles. The<br />
method is regio- <strong>and</strong> stereo specific respect to bromoalkenes<br />
<strong>and</strong> tolerates a wide range <strong>of</strong> functional<br />
groups.<br />
Ar<br />
ToS<br />
O<br />
N<br />
NC<br />
+<br />
(TosMIC)<br />
Br<br />
NC<br />
Br<br />
Ar<br />
Amber sep 900 OH<br />
1.85 g / mmol aldehyde<br />
O<br />
DME/MeOH (1:1)<br />
reflux, 8hr<br />
3.3 eq. Cs 2 CO 3<br />
DMSO,110 0 C, 2-3hr<br />
1.5eq,R-X<br />
2eq K 2 CO 3 TOS<br />
R<br />
r.t-12hr<br />
RX=Alkyl-Br,Bn-Cl<br />
allyl-Br<br />
R1X=Ar,vinyl,(1.2 eq)<br />
allyl(2eq)<br />
NC<br />
5 mol - % Pd(PPh 3 ) 4<br />
1.5 - 2 eq . 1.5 - 2 eq .tBuOLi<br />
Br<br />
R<br />
dioxane<br />
120 0 c ,2 -6 hr<br />
N<br />
R<br />
1.2eq -2eq R-CHO<br />
r.t-10hr<br />
Ar<br />
O<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
R<br />
Lig<strong>and</strong><br />
R<br />
R 1<br />
Ar<br />
P<br />
Bu<br />
O<br />
419<br />
N<br />
R: Ar , vinyl<br />
O<br />
R: Ar (1.5 eq . RBr /tBuOLi)<br />
N<br />
vinyl(1.5 eq . RBr /tBuOLi)
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
G.C.Senadi, W.P.Hu,J.S.Hsiao et al [6] in 2012 reported a<br />
ZnI 2 <strong>and</strong> FeCl 3 mediate a direct approach to the selective<br />
<strong>and</strong> regio controlled synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2-oxazolines <strong>and</strong> 2-<br />
oxazoles in very good yields under mild reaction conditions<br />
by cyclization <strong>of</strong> acetylenic amides. Various functionalities<br />
were well tolerated.<br />
5mol % Ph 3 PAu NTF<br />
+ NC-R 1 1.3 eq..oxidant<br />
60 0 C ,,3hrs.<br />
R<br />
O<br />
N<br />
R 1<br />
R= alkyl,Ar,vinyl<br />
R 1 = me/iPr,Bn,Ph.<br />
O - +<br />
N<br />
oxidant<br />
R<br />
O<br />
Cl<br />
+<br />
N H 2<br />
CH 3 CH 3<br />
2 eq. NEt 3<br />
2 eq. FeCl<br />
O<br />
3<br />
DCM<br />
DCE<br />
R' r.t.,2 - 12 hr<br />
R NH R'<br />
80 0 c ,3-8 hr<br />
Y.Zheng,X.Li.D.Zhang et al [7] in 2012 proposed that a<br />
broad range <strong>of</strong> functionalized oxazoles were synthesized<br />
in good yields from enamides via phenyliodine diacetate<br />
(PIDA)-mediated intramolecular cyclization. The oxidative<br />
carbon-oxygen bond formation process is heavymetal-free.<br />
R'<br />
R<br />
O<br />
NH R"<br />
1.3 eq.Phl(OAc) 2<br />
2 eq. BF 3. Et 2 O<br />
DCE<br />
reflux,.5 - 2 hr<br />
X.Liu,R.Cheng, F.Zhao,et al [8] in 2012 reported the use<br />
<strong>of</strong> iodosobenzene (PhIO) as an oxidant realizes an intermolecular<br />
oxidative C(sp 2 )-O bond formation between<br />
enamines <strong>and</strong> various carboxylic acids, including N-<br />
protected amino acids. This direct β-acyloxylation <strong>of</strong><br />
enamine compounds tolerates a wide range <strong>of</strong> functional<br />
groups <strong>and</strong> furnishes various β-acyloxy enamines that can<br />
be conveniently converted to oxazoles via cyclodehydration.<br />
R<br />
O<br />
C.Verrier,T.Martin et al [9] in 2008 proposed a straightforward<br />
route allows the synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2-(hetero)arylated<br />
<strong>and</strong> 2,5-di(hetero)arylated oxazoles through regiocontrolled<br />
palladium-catalyzed direct (hetero)arylation <strong>of</strong><br />
ethyl oxazole-4-carboxylate with iodo-, bromo-, <strong>and</strong><br />
chloro(hetero)aromatics.<br />
EtO 2 C<br />
O<br />
O<br />
N<br />
EWG<br />
R'<br />
NH 2<br />
AcOH<br />
reflux,30 min<br />
W.He,C/.Li et al [10] in 2011 proposed an efficient intermolecular<br />
reaction <strong>of</strong> gold carbene intermediates generated<br />
via gold-catalyzed alkyne oxidation using nitriles as<br />
both the reacting partner <strong>and</strong> the reaction solvent <strong>of</strong>fers a<br />
generally efficient synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2,5-disubstituted oxazoles<br />
with broad substrate scope. The overall reaction is a [2 +<br />
2 + 1] annulation <strong>of</strong> a terminal alkyne, a nitrile, <strong>and</strong> an<br />
oxygen atom from an oxidant.<br />
R<br />
N<br />
R<br />
O<br />
R"<br />
R'<br />
+ Ar Cl 5 mol - % Pd(OAc) 2<br />
.1 eq. P(o-tol) 3<br />
2 eq. Cs 2 CO 3<br />
toluene, 110 0 c,18 hr<br />
N<br />
O<br />
R'<br />
CH 3<br />
R : Ar, alkyl,vinyl<br />
R : Ar,Me,COMe, CO 2 Me<br />
R : CO 2 Me,Me,Ar, COph,H<br />
R" : alkyl, Ar<br />
R<br />
N<br />
O<br />
R'<br />
EWG<br />
R : Ar, alkyl, vinyl<br />
R' : Me, Ph<br />
R" : CO 2 Me, CN<br />
EtO 2 C<br />
O<br />
N<br />
Ar<br />
H.Jiang,H.Huang et al in 2010 [11] proposed a facile<br />
one-pot, transition-metal-free process enables the synthesis<br />
<strong>of</strong> various polysubstituted oxazoles via t-<br />
BuOOH/I 2 -mediated domino oxidative cyclization<br />
from readily available starting materials under mild<br />
conditions.<br />
2.5 eq.<br />
CH 2<br />
H N Ar<br />
+ -<br />
2<br />
H 5 C 6<br />
In a practical <strong>and</strong> simple synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2,5-disubstituted<br />
oxazoles via an iodine-catalyzed t<strong>and</strong>em oxidative cyclization,<br />
a wide range <strong>of</strong> common commercial aromatic<br />
aldehydes can be used as reaction substrates,<br />
which displayed excellent functional group compatibility.<br />
Ph<br />
added in two portions over 8 hr<br />
1. 5 eq. tBuOOH<br />
1. 2 eq I 2<br />
DMSO 80 0 C, 12 h<br />
N.Yasmin,J.K.Ray et al in 2009 [12] proposed a simple<br />
<strong>and</strong> efficient Cs 2 CO 3 -mediated reaction <strong>of</strong> aromatic <strong>and</strong><br />
unsaturated primary amides with 2,3-dibromopropene<br />
allows the synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2-aryl-5-alkyl-substituted oxazoles<br />
in a single step in good yields.<br />
R<br />
O<br />
O . 3 eq I 2<br />
1. 5 eq. t BuOOH<br />
NH 2 . HCl +<br />
C 6 H 1 eq. NaHCO<br />
H 5<br />
3<br />
DMF, 70 0 C, 10 h<br />
C.W.Cheung, S.L.Buchwald in 2012 [13] reported a<br />
copper(II)-catalyzed oxidative cyclization <strong>of</strong> enamides<br />
gives oxyzoles via vinylic C-H bond functionalization<br />
at room temperature. Various 2,5-disubstituted oxazoles<br />
bearing aryl, vinyl, alkyl, <strong>and</strong> heteroaryl substituents<br />
could be synthesized in good yields. This reaction<br />
protocol is complementary to a previously reported<br />
iodine-mediated cyclization <strong>of</strong> enamides to afford 2,<br />
4,5-trisubstitutedoxazoles.<br />
H 5 C 6<br />
O<br />
NH 2<br />
+<br />
NH<br />
C H 2<br />
O<br />
R<br />
Br<br />
Br<br />
3. 3 eq. Cs 2 CO 3<br />
DMSO, 110 0 C, 2 - 3 h<br />
7. 5 mol - % CuBr 2<br />
15 mol - ethyl nicotinate<br />
1. 2 eq. TBAB, 1. 3 eq K 2<br />
S 2<br />
O 8<br />
MeCN, r.t. , 24 h<br />
H 5 C 6<br />
Y.M.Pan,f.j.Zheng et al in 2009 [14] proposed an efficient<br />
one pot propargylation/cycloisomerisation t<strong>and</strong>em<br />
process provides a rapid <strong>and</strong>efficient access to substituted<br />
oxazoles from propargylic alcohols <strong>and</strong> amides<br />
R<br />
O<br />
N<br />
O<br />
Ph<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O H 5 C 6<br />
C 6 H 5<br />
O<br />
N<br />
420<br />
C 6 H 5<br />
CH 3<br />
R : Ar, vinyl<br />
R<br />
R : Ar, vinyl
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
with use <strong>of</strong> p-toluene sulfonic acid monohydrate (PTSA)<br />
as a bifunctional catalyst.<br />
OH<br />
Ar + NH 2 R 1<br />
R<br />
1.2 eq<br />
O<br />
1 eq PTSA<br />
Toluene<br />
reflux,.0.5-5hrs<br />
R.Martin, A.Cuenca.et al in 2007 [15] proposed a modular<br />
<strong>and</strong> practical synthesis <strong>of</strong> highly substituted oxazoles<br />
consists <strong>of</strong> a sequential copper-catalyzed amidation <strong>of</strong><br />
vinyl halides followed by cyclization promoted by iodine.<br />
A wide variety <strong>of</strong> functionalized oxazoles <strong>and</strong> polyazoles<br />
can be obtained in a selective manner from simple <strong>and</strong><br />
easily accessible precursors.<br />
R<br />
R'<br />
CH 3<br />
+<br />
A series <strong>of</strong> propargylic amides were transformed to the<br />
corresponding alkylideneoxazolines by a gold (I) catalyst.<br />
A subsequent autoxidation to hydro peroxides bearing the<br />
heteroaromatic oxazoles followed by reduction to the<br />
corresponding alcohols with sodium borohydride enables<br />
a highly efficient, <strong>and</strong> atom-economic access to a series<br />
<strong>of</strong> functionalized 2,5-disubstituted oxazoles.<br />
N<br />
+<br />
Ar - O<br />
O<br />
H 2 N<br />
R"<br />
5 mol - % CuI<br />
0. 2 eq MeNH CH 2 CH 2 NHMe<br />
1. 5 eq Cs 2 CO 3<br />
THF, 80 0 C, 3 - 8h<br />
3-Oxazoline-4-carboxylates as easily available synthetic<br />
intermediates can be oxidized to yield oxazole-4-<br />
carboxylates. Furthermore, derivatization <strong>of</strong> 3-oxazoline-<br />
4-carboxylates with Grignard reagents enables a facile<br />
preparation <strong>of</strong> 4-keto-oxazole derivatives.<br />
Ar - 2 eq.<br />
C. Wang, J. Zhang, et al in 2010 [16] reported a highly<br />
efficient copper-catalyzed t<strong>and</strong>em oxidative cyclization<br />
gives poly substituted oxazoles from readily available<br />
starting materials under mild conditions. This is an attractive<br />
alternative method for the synthesis <strong>of</strong> oxazole derivatives.<br />
Ar - 2 eq.<br />
Cl<br />
Cl<br />
1. 5 eq.<br />
O<br />
Ar'<br />
NH 2 +<br />
R R'<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
NH 2 +<br />
R R'<br />
5 mol - % Pd(OAc) 2<br />
6 mol - % DPEPhos<br />
5 eq LiOtBu<br />
dioxane 120 0 c, 14 h<br />
J.F.Sanz-Cervera, R. Blasco et al [17] in A small library<br />
<strong>of</strong> compounds with oxazole <strong>and</strong> thiazole scaffolds <strong>and</strong><br />
structural diversity in both positions 2 <strong>and</strong> 5 has been<br />
synthesized. Double acylation <strong>of</strong> a protected glycine af-<br />
R<br />
R'<br />
. 1 eq. Cu(OAc).H 2<br />
O<br />
2 eq. t BuOOH,<br />
1. 2 eq I 2<br />
DMF, r. t., ~ 7h<br />
. 1 eq. Cu(OAc).H 2<br />
O<br />
2 eq. t BuOOH,<br />
1. 2 eq I 2<br />
DMF, r. t., ~ 7h<br />
R<br />
N<br />
NH<br />
RA<br />
O<br />
O<br />
N<br />
R"<br />
1) 1. 1 eq,I 2<br />
80 0 C, ~ 4 h<br />
2) 2 eq. DBU<br />
80 0 C, ~ 4 h<br />
CH 3 ,<br />
Ar - O<br />
Ar -<br />
Ar -<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
R<br />
R<br />
R'<br />
R'<br />
R=TMS,alkyl,ph,H<br />
R 1 =Ar,alkyl,vinyl<br />
R'<br />
R<br />
DPEPhos:<br />
N<br />
O<br />
R"<br />
PPh 2<br />
O<br />
PPh 2<br />
R: alkyl,Ph, vinyl<br />
R': OR"<br />
alkyl(R'=R)<br />
Ph(R'=R)<br />
R: alkyl,Ph, vinyl<br />
R': OR"<br />
alkyl(R'=R)<br />
Ph(R'=R)<br />
intermediate α-amido-β-ketoesters, which in turn can<br />
be dehydrated to afford 1,3-oxazoles or reacted with<br />
Lawesson’s reagent to furnish 1,3-thiazoles.<br />
Ar -<br />
O<br />
N<br />
PPh3<br />
Ar'<br />
1.2 eq<br />
O<br />
+<br />
Cl CH 3<br />
1) toluene, reflux, 3 h<br />
2) 1. 1 eq. H 2<br />
O, Reflux, 3 - 4 h<br />
3) 10 eq NaOH ( 2M aq.)<br />
r.t., 15 min<br />
J.F.Sanz-Cervera et al in 2009 [17] reporetd a method<br />
in which a small library <strong>of</strong> compounds with oxazole<br />
<strong>and</strong> thiazole scaffolds <strong>and</strong> structural diversity in both<br />
positions 2 <strong>and</strong> 5 has been synthesized.double acylation<br />
<strong>of</strong> a protected glycine affords intermediate alpha-amido<br />
-beta-ketoester,which in turn can be dehydratedto afford<br />
1,3-oxazolesor reacted with Lawesson’s reagent to<br />
furnish 1,3-thiazoles.<br />
R<br />
A t<strong>and</strong>em reaction <strong>of</strong> a vinyliminophosphorane with<br />
various acylchlorides gives unexpectedly 2,4,5-<br />
trisubstituted oxazoles in a one-pot fashion.<br />
Ar<br />
O<br />
O<br />
NH<br />
R'<br />
2 eq PPh<br />
3<br />
, 2 eq I<br />
2<br />
CH Cl , r. t., 15 - 60 min<br />
CO 2 Bn 2 2<br />
E. Merkul., O. Grotkopp,et al in 2009 [18] proposed a<br />
method n which substituted oxazoles-5-ylethanones can<br />
be synthesized in a consecutive three component sequence<br />
starting with amidation <strong>of</strong> propargylamine with<br />
an acid chloride followed by cross coupling with another<br />
acid chloride. Therefore this diversity – oriented<br />
one-pot approach to substituted oxazoles can be considered<br />
as an amidation coupling cycloisomerisation<br />
(ACCI) sequence.<br />
R<br />
O<br />
R: Ar,vinyl<br />
A.Herrera, R. Martinez et al in 2006 [19] described a<br />
reaction in which 1-methyl thioacetone with different<br />
nitriles in the presence <strong>of</strong> triflicanhydrides gave 2-<br />
substituetd 5-methyl4-methyl thio group at the C4 position<br />
can easily be removed with Raney nickel.4-methyl<br />
sulfonyl derivatives were prepared by oxidation <strong>of</strong> the<br />
MeS group with m-CPBA.<br />
SMe<br />
+ Cl<br />
N<br />
PPh 3<br />
Cl<br />
2 eq<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
H 2 N<br />
1)1 eq<br />
CH<br />
H 3 C<br />
1 eq NEt , THF r.t., 1h<br />
3<br />
2) 2 mol -% PdCl (PPh ) 2 3 2<br />
HN<br />
4 mol - % CuI, NEt 3<br />
R<br />
1 eq Ar'COCl r.t., 1h<br />
2 eq.Tf 2 O<br />
CH 2 Cl 2<br />
R<br />
N<br />
1)toluene,reflux 3hrs<br />
2)1.1 eq.H 2 O,reflux,3-4hrs<br />
3)10.eq.NaOH(2M eq)<br />
r.t..,15mts.<br />
O<br />
SMe<br />
OTf<br />
O<br />
O<br />
Ar'<br />
O<br />
R<br />
O<br />
Ar -<br />
R'<br />
N<br />
CO 2 Bn<br />
Ar<br />
A<br />
R<br />
1 eq PTSA.H 2<br />
o<br />
60 0 C, 1 h<br />
1eq.R-CN<br />
0 0 C,3d<br />
HO<br />
Ar'<br />
R: Ar", alkyl<br />
R, R': Ar, alkyl<br />
R<br />
R<br />
N<br />
N<br />
N<br />
OH<br />
Ar 1<br />
R ; Ar' ,alkyl<br />
O<br />
O<br />
421<br />
O<br />
Ar'<br />
SMe
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
G. Cuny, R. Gamez et al in 2004 [20] proposed that the<br />
reaction <strong>of</strong> aldehydes <strong>and</strong> ketones ,including aliphatic <strong>and</strong><br />
aromatic ones with amides <strong>of</strong> alpha-isocyano-betaphenylpropionic<br />
acid in toluene in the presence <strong>of</strong> lithium<br />
amide give 2,4,5-trisubstituted oxazoles in good to excellent<br />
yield.<br />
NC<br />
Ph<br />
O<br />
N<br />
R'<br />
C.Wang, J.Zhang et al [22] reported a highly efficient<br />
copper –catalysed t<strong>and</strong>em oxidative cyclization give<br />
spolysubstituted oxazoles from easily available starting<br />
materials under mild conditions. This is an attractive alternative<br />
method for the synthesis <strong>of</strong> oxazoles derivatives.<br />
Ar NH 2<br />
+<br />
R''<br />
+ R<br />
O<br />
H<br />
1eq.LiBr<br />
toluene,60 0 C,4hr<br />
J.F Sanz-Cervera et al in 2009 proposed that a small library<br />
<strong>of</strong> compounds with oxazoles <strong>and</strong> thiazoles scaffolds<br />
<strong>and</strong> structural diversity in both positions 2 <strong>and</strong> 5 has been<br />
synthesized. Double acylation <strong>of</strong> a protected glycine affords<br />
intermediate alpha amido-beta ketoesters, which in<br />
turn can be dehydrated to afford 1,3-oxazoles or reacted<br />
with Lawesson’s reagent to furnish 1,3- thiazoles.<br />
R<br />
Ding.J ,Orem et al in 2012 reported t<strong>and</strong>em reaction <strong>of</strong> a<br />
vinyliminophosphorane with various acylchlorides gives<br />
unexpectedly 2,4,5 –trisubstituted oxazoles in a one pot<br />
fashion.<br />
E. Merkul, O. Grotkopp et al in 2009 described a synthesize<br />
in which oxazoles-5-ylethanonesbcan be synthesized<br />
in a consecutive three component sequence starting with<br />
amidation <strong>of</strong> propargylamine with an acid chloride followed<br />
by cross coupling with another acid chloride<br />
.therefore this diversity oriented one-pot approach to<br />
substituted oxazoles can be considered as an amidation<br />
coupling cycloisomerisation (ACCI) sequence.<br />
R<br />
O<br />
Ar<br />
O<br />
N<br />
H<br />
Cl<br />
O<br />
R<br />
O<br />
O<br />
R'<br />
O<br />
COOBn<br />
R'<br />
+<br />
Ar<br />
N<br />
Cl<br />
PPh 3<br />
0.1 eq.Cu(OAc).H 2 O<br />
2 eq.tBuOOH,1.2 eq.I 2<br />
DMF ,r.t.at 7 hrs<br />
2 eq.PPh 3. 2 eq.I 2<br />
CH 2 Cl 2 .r.t..,15-60 min<br />
1.2 eq<br />
O<br />
R<br />
1,1 eq H 2N<br />
1 eq.NEt 3,THF, r.t.,1 hr<br />
2, 2 mol %PdCl 2 (PPh 3 ) 2<br />
4 mol %CuI,1 eq.NEt 3<br />
1 eq.Ar'COCl,r t,1 hr<br />
Ar<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
1,toluene,reflux,3hr<br />
2,1.1 eq.H2O,reflux,3-4 hr<br />
3,10 eq.NaOH (2M aq)<br />
r.t,15 min<br />
R<br />
HN<br />
O<br />
r<br />
Ar'<br />
O<br />
HO<br />
R<br />
O<br />
R'<br />
R<br />
COOBn<br />
O<br />
R<br />
1 eq<br />
PTSA.H 2 O<br />
60 0 C,1 hr<br />
R'<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
R''<br />
N<br />
R'<br />
Ph<br />
R; alkyl,Ph,vinyl<br />
R''; OR''<br />
alkyl(R'=R)<br />
Ph (R'=R)<br />
R,R' ;Ar,alkyl<br />
N<br />
R<br />
OH<br />
Ar<br />
R ; Ar,alkyl<br />
O<br />
O<br />
Ar'<br />
A.Herrea, R.Martinez-Alvarez, et al in 2006 proposed a<br />
reaction <strong>of</strong> 1-(methylthio) acetone with different nitriles<br />
in the presence <strong>of</strong> triflic anhydride gave 2-<br />
substituted 5-methyl-4-methylthio-1,3- oxazole in good<br />
yield methylthio group at the C 4 position can easily be<br />
removed with Raney n ickel.4 methyl sulfonylderivatives<br />
were prepared by oxidation <strong>of</strong> the MeS group<br />
with m- CPBA.<br />
MeS<br />
G.Cuny.R.Gamez-Montano,J.Zhu, et al in 2004 [27]<br />
reported a reaction <strong>of</strong> aldehydes <strong>and</strong> ketones including<br />
aliphatic <strong>and</strong> aromatic ones,with amides <strong>of</strong> α-isocyanoβ-phenylpropionic<br />
acid in toluene in the presence <strong>of</strong><br />
lithium bromide gives 2,4,5-trisunstituted oxazoles in<br />
good to excellent yield.<br />
NC<br />
2 eq<br />
O<br />
2 eq.Tf 2 O O 1 eq.R-CN<br />
CH 2 Cl 2<br />
0 0 C,1 hr<br />
SMe<br />
OTf<br />
G.Bastug,C.Eviolitte,et al in 2012 described a reaction<br />
in which the ortho substituted anilines with functionalized<br />
orthoesters yields benzoxazole, Benzothiazole,<br />
<strong>and</strong> benzimidazole derivatives in an efficient <strong>and</strong> connective<br />
methodology the versatility <strong>of</strong> this approach<br />
enables the development <strong>of</strong> new libraries <strong>of</strong> heterocycles<br />
containing multifunctional sites.<br />
R<br />
0 0 C 3d N<br />
P.J.Boissarie, Z.E Hamilton et al proposed an efficient<br />
<strong>and</strong> convenient three component coupling <strong>of</strong> aryl halides<br />
amino alcohols <strong>and</strong> tert- butyl isocyanide under<br />
palladium catalysis provide a range <strong>of</strong> oxazolines in<br />
excellent yield the use <strong>of</strong> 1,2-amino phenols instead <strong>of</strong><br />
amino alcohols enables the synthesis <strong>of</strong> benzoxazoles.<br />
R<br />
Ph<br />
O<br />
N<br />
R'<br />
NH 2<br />
YH<br />
H<br />
N<br />
Br<br />
R''<br />
O<br />
+<br />
+<br />
R'<br />
1.3 eq<br />
O<br />
R<br />
1-1.5 eq<br />
OR'<br />
OMe<br />
OR'<br />
R''<br />
H<br />
1 eq.LiBr<br />
toluene,60 0 C,4hr<br />
1eqBF 3 .OEt 2<br />
DCM,r.t.2-4hrs<br />
5 mol %CuO,nanoparticles<br />
1.5 eq.K 2 CO 3 ,OR Cs 2 co 3<br />
DMSO,110 0 C,12-30 hr<br />
P.Saha T.Ramana et al in 2009 proposed that an experimentally<br />
simple, general, efficient <strong>and</strong> lig<strong>and</strong> free<br />
synthesis <strong>of</strong> substituted benzimidazoles, 2-amino benz<br />
imidazoles 2-amino benzothiazoles <strong>and</strong> Benzoxazoles<br />
via intramolecular cyclization <strong>of</strong> bromoaryl derivatives<br />
R<br />
HO<br />
R<br />
R<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
R<br />
O<br />
R'<br />
O<br />
N<br />
Y<br />
R''<br />
N<br />
Y;O,S,NH<br />
R';alkyl<br />
R''; alkyl<br />
422<br />
SMe<br />
Ph<br />
R'<br />
R''<br />
R' ; Ar(K 2 CO 3 )<br />
alkyl (Cs 2 CO 3 )
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
is catalyzed by copper (ii) oxide nanoparticle in DMSO<br />
under air. The heterogeneous catalyst can be recovered<br />
<strong>and</strong> recycled without loss <strong>of</strong> activity.<br />
C.Y Chen, T.Andreani et al 2011 proposed a divergent<br />
<strong>and</strong> regioselective synthesis <strong>of</strong> either 3-substituted benzisoxazoles<br />
or 2-substituted benzoxazoles from readily<br />
accessible ortho hydroxy aryl N-H ketimines proceeds in<br />
two distinct pathways through a common N-Cl imine<br />
intermediate (a) N-O bond formation to form benisoxazoles<br />
under anhydrous conditions <strong>and</strong> (b) NaOCl mediated<br />
Beckmann- type rearrangement to form benzoxazole<br />
respectively .<br />
R<br />
R'<br />
OH<br />
N<br />
H<br />
3 eq.NaOCl<br />
(10% aq)<br />
iPrOH<br />
r.t,10-30 min<br />
Table 2. Pharmacological Activity <strong>of</strong> Oxazole <strong>and</strong> its<br />
Derivatives<br />
Chemical structure<br />
O<br />
N<br />
Treatment <strong>of</strong> type II<br />
diabetes.<br />
N<br />
O<br />
CH 3<br />
O<br />
S<br />
O<br />
CH 3<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
Insulin sensitizing effects,<br />
treatment <strong>of</strong><br />
type II diabetes<br />
N<br />
CH 3<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
S<br />
N<br />
H<br />
Ditazole is a platelet<br />
aggregation inhibitor<br />
N<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
OH<br />
Oxazolone<br />
<strong>Heterocyclic</strong> 1 compounds which have a characteristic role<br />
in the synthesis <strong>of</strong> several organic molecules including<br />
amino acids, amino alcohols, thiamine, amides, peptides<br />
<strong>and</strong> poly functional compounds are called oxazolones.<br />
Certain natural <strong>and</strong> synthetic oxazolone also including<br />
benzoxazolone derivatives possess important biological -<br />
R<br />
N<br />
O<br />
R' ;alkyl<br />
Name <strong>of</strong> compound<br />
(2S)-2-methoxy-3-[-4-[2-(5-<br />
methyl-2-phenyl-4-oxazolyl)<br />
ethoxy]-7-benzothiophenyl]<br />
propanoic acid.<br />
(Aleglitazar)<br />
5-[(4-[3-(5-methyl-2-phenyl-<br />
1,3-oxazol-4-yl)propanoyl)<br />
phenyl)methyl]-1,3-<br />
thiazolodine-2,4-dione<br />
(Darglitazone)<br />
2,2 1 -(4,5-Diphenyloxazol-2-<br />
ylazanediyl)diethanol<br />
R'<br />
activities; such as antimicrobial, anti inflammatory,<br />
anticancer, anti-HIV, anti angiogenic, anticonvulsant,<br />
antitumor, antagonistic, sedative <strong>and</strong> cardio tonic activity.<br />
Various alkaloid skeletons, immunomodulators <strong>and</strong><br />
biosensors or photosensitive composition devices for<br />
proteins are constructed using oxazolones as synthones.<br />
They exhibit promising photo physical <strong>and</strong> photochemical<br />
activities, so they are used in semiconductor<br />
devices such as electro photographic photoreceptors<br />
<strong>and</strong> in non-linear optical materials.<br />
Oxazolone [27] has cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory property<br />
<strong>and</strong> tyrosinase inhibitory property. Oxazol-5(4H)-<br />
ones, also known as azlactones, is readily prepared<br />
from N-protected amino acids by dehydration. Ringopening<br />
<strong>of</strong> oxazolone leading to an enantiomerically<br />
enriched N-protected phenylalanine esters <strong>and</strong> peptidoalcohols.<br />
Oxazolone show interesting behavior towards<br />
polymerization <strong>and</strong> condensation leading to homo<br />
polymers, telomeres, condensation reagents, peptides,<br />
herbicides, fungicides, pesticides <strong>and</strong> agrochemical<br />
intermediates. Oxazolone plays very vital role in the<br />
manufacturing <strong>of</strong> various biologically active drugs as<br />
analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antidepressant, anticancer,<br />
anti-microbial, anti-diabetic <strong>and</strong> anti obesity.<br />
Synthesis- Scheme 1<br />
Synthesis <strong>of</strong> oxazolone from indolmycin In the presence<br />
<strong>of</strong> carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) K. Shankaran et al<br />
reported that the benzoxazolone prepared from pyridine<br />
analogues in good yields.<br />
NH 2<br />
CDI, CH 2<br />
Cl 2<br />
H<br />
H 3 C N OH 3 C N<br />
Scheme 2<br />
Synthesis <strong>of</strong> benzoxazol-2(3H)-ones from 1-(2-<br />
hydroxyphenyl) ureas Benzoxazol-2(3H)-ones were<br />
synthesized in excellent yields by refluxing 1,1'-<br />
carbonyldiimidazole <strong>and</strong> 2-aminophenol in dry THF<br />
for 4h by Nachman et al.<br />
O<br />
N N<br />
H<br />
NH 2<br />
N<br />
R 1 OH THF R 1 O<br />
R 2 R 2<br />
Scheme 3<br />
Synthesis <strong>of</strong> 4-methyloxazol-2-one using carbon dioxide<br />
Michele C. Kelly et al reported that highly alkali-labile<br />
oxazolone was prepared upon hydrolysis <strong>of</strong> guanine.<br />
Wide variety <strong>of</strong> oxidation reactions were targeted on<br />
the most susceptible DNA which are mediated by OH<br />
radicals, singlet oxygen, peroxynitrite <strong>and</strong> one electron<br />
oxidants.<br />
H<br />
N<br />
O<br />
O<br />
423<br />
O
N H 2<br />
HN<br />
HO<br />
N<br />
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
O 2<br />
, H 2<br />
O<br />
H<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
H 2 N<br />
H 2 N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
O<br />
NH 2<br />
NH 2<br />
NH 2<br />
CH 3<br />
Table 3. Pharmacological activities <strong>of</strong> Oxazolones <strong>and</strong> its<br />
derivatives<br />
Chemical structure<br />
C H 3<br />
H<br />
N<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
Antimicrobial<br />
O<br />
Antimicrobial<br />
N<br />
Cl<br />
O<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N + O -<br />
Nitric oxide synthase Inhibitor<br />
Name <strong>of</strong> compound<br />
5-Methyl-3Hbenzooxazol-2-one<br />
2-(2-Chloro-4-nitro-<br />
phenyl)-4-<br />
furan -2-ylmethylene-<br />
4H-oxazol-5-<br />
one<br />
4-(3-Chloro-<br />
benzylidene)-2-<br />
phenyl-4H-oxazol-5-<br />
one<br />
ISOXAZOLE<br />
Isoxazole [1] is an azole with an oxygen atom next to the<br />
nitrogen. It is also the class <strong>of</strong> compounds containing this<br />
ring. Isoxazolyl is the univalent radical derived from<br />
isoxazole. Isoxazole rings are found in some natural products,<br />
such as ibotenic acid. Isoxazoles also form the basis<br />
for a number <strong>of</strong> drugs, including the COX-2 inhibitor<br />
valdecoxib. A derivative, furoxan, is a nitric oxidedonor.<br />
An isoxazolyl group is found in many beta-lactamase<br />
-resistant antibiotics, such as cloxacillin, dicloxacilllin<br />
<strong>and</strong> flucloxacillin. The synthetic <strong>and</strong>rogenic steroid<br />
danazol also has an isoxazole ring. Isoxazoles are<br />
useful isosteres <strong>of</strong> pyridine, <strong>and</strong> have been found to inhibit<br />
voltage-gated sodium channels to control pain, enable<br />
the construction <strong>of</strong> tetracycline antibiotic derivatives,<br />
<strong>and</strong> as treatment <strong>of</strong> depression.<br />
Synthesis- SCHEME 1<br />
AuCl 3 -catalyzed [37] cycloisomerization <strong>of</strong> α,βacetylenic<br />
oximes leads to substituted isoxazoles in very<br />
good yields under moderate reaction conditions. The<br />
methodology is amenable for the selective synthesis <strong>of</strong> 3-<br />
substituted, 5-substituted or 3,5-disubstituted isoxazoles.<br />
SCHEME 2<br />
Cycloadditions <strong>of</strong> copper (I) acetylides to azides <strong>and</strong><br />
nitrile oxides provide ready access to 1,4-disubstituted<br />
1,2,3-triazoles <strong>and</strong> 3,4-disubstituted isoxazoles, respectively.<br />
The process is highly reliable <strong>and</strong> exhibits an<br />
unusually wide scope with respect to both components.<br />
Computational studies revealed a nonconcerted mechanism<br />
involving unprecedented metallacycle intermediates<br />
[8].<br />
Ar<br />
SCHEME 3<br />
Various [26] 3-substituted <strong>and</strong> 3, 5-disubstituted isoxazoles<br />
have been efficiently synthesized in good yields<br />
by the reaction <strong>of</strong> N-hydroxyl-4-toluenesulfonamide<br />
with α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. This strategy<br />
is associated with readily available starting materials,<br />
mild conditions, high regioselectivity, <strong>and</strong> wide<br />
scope.<br />
Ar<br />
AuCl 3 -catalyzed cycloisomerization <strong>of</strong> α,β-acetylenic<br />
oximes leads to substituted isoxazoles in very good<br />
yields under moderate reaction conditions. The methodology<br />
is amenable for the selective synthesis <strong>of</strong> 3-<br />
substituted, 5-substituted or 3,5-disubstituted isoxazoles.<br />
Ar<br />
OH<br />
N<br />
+ R<br />
Cl<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
N<br />
Cl<br />
H<br />
4 eq<br />
+ TsNHOH<br />
+ R'<br />
2mol %CuSO 4. 5H 2 O<br />
10 mol-%sodium ascorbate<br />
4.3 eq.KHCO 3<br />
H 2 O/tBuOH(1:1),r.t,1-4 hr<br />
5eq.K 2 CO 3<br />
MeOH/H 2 O (9:1)<br />
r.t.. 10hr<br />
2mol-%CuSO 4. 5H 2 O<br />
10mol-% sodium ascorbate<br />
4.3 eq.KHCO 3<br />
H 2 O/tBuOH(1:1),rt 1-4 hr<br />
2.5eq.K 2 CO 3<br />
60 0 C..,4hr<br />
Cycloadditions <strong>of</strong> copper (I) acetylides to azides <strong>and</strong><br />
nitrile oxides provide ready access to 1,4-disubstituted<br />
1,2,3-triazoles <strong>and</strong> 3,4-disubstituted isoxazoles, respectively.<br />
The process is highly reliable <strong>and</strong> exhibits an<br />
unusually wide scope with respect to both components.<br />
Computational studies revealed a nonconcerted mechanism<br />
involving unprecedented metallacycle intermediates.<br />
Ar<br />
Ar<br />
N<br />
O<br />
R'<br />
R;Ph,CH 2 OH<br />
CO 2 H<br />
N<br />
R'<br />
O<br />
N<br />
R: Ph,CH 2 OH,COOH<br />
O<br />
R<br />
N<br />
OH<br />
R'<br />
1 mol %AuCl 3<br />
CH 2 Cl 2 .30 0 C ,10-30 min<br />
R<br />
N<br />
O<br />
R'<br />
R ; Ph,Me,H<br />
R' Ar,alkyl,SiMe 3, H<br />
Ar<br />
O<br />
H<br />
4 eq<br />
+ TsNHOH<br />
5eq.K 2 CO 3<br />
MeOH/H 2 O (9:1)<br />
r.t.. 10hr<br />
2.5eq.K 2 CO 3<br />
60 0 Ar<br />
C..,4hr N<br />
O<br />
.<br />
424
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
Various 3-substituted <strong>and</strong> 3,5-disubstituted isoxazoles<br />
have been efficiently synthesized in good yields by the<br />
reaction <strong>of</strong> N-hydroxyl-4-toluenesulfonamide with α,βunsaturated<br />
carbonyl compounds. This strategy is associated<br />
with readily available starting materials, mild conditions,<br />
high regioselectivity, <strong>and</strong> wide scope.<br />
Ar<br />
R'<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
1.5eq.MCPBA<br />
DCM<br />
rt.4hr<br />
Enamine-triggered [3+2]-cycloaddition reactions <strong>of</strong> aldehydes<br />
<strong>and</strong> N-hydroximidoyl chlorides in the presence <strong>of</strong><br />
triethylamine gives 3, 4,5-trisubstituted 5-(pyrrolidinyl)-<br />
4,5-dihydroisoxazoles. Subsequent oxidation <strong>of</strong> the<br />
cycloadducts <strong>of</strong>fers a high yielding, regiospecific <strong>and</strong><br />
metal-free synthetic route for the synthesis <strong>of</strong> 3,4-<br />
disubstituted isoxazoles. The sequential use <strong>of</strong> iron <strong>and</strong><br />
palladium catalysts in an uninterrupted four-step sequence<br />
allows the synthesis <strong>of</strong> trisubstituted isoxazoles<br />
from readily available propargylic alcohols. The advantages<br />
<strong>of</strong> such a strategy are illustrated by the high overall<br />
yields <strong>and</strong> the time-saving procedure.<br />
Ar<br />
OH<br />
R :Me,Bu<br />
R<br />
+ 1.1 eq<br />
CbzNHOH<br />
The direct regioselective synthesis <strong>of</strong> 3,5-disubstituted<br />
isoxazoles was achieved through a sequence involving a<br />
net bromination <strong>of</strong> an electron-deficient alkene, in situ<br />
generation <strong>of</strong> a nitrile oxide, 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition,<br />
<strong>and</strong> loss <strong>of</strong> HBr from an intermediate bromoisoxazoline.<br />
This one-pot process enables the direct synthesis <strong>of</strong> 3,5-<br />
disubstituted isoxazoles from electron-deficient alkenes.<br />
Ar<br />
R'<br />
N<br />
1)5oml-%MeCN,60 0 C,2hr<br />
2)2eq.Ar'-1,0.1 eqPd 2 dba 3 ,<br />
0.2 eq.bpy, 4eqK 2 CO 3 ,50 0 C<br />
3)removal <strong>of</strong> MeCN<br />
4)MeOH,H 2 (1atm),r.t.2 hr<br />
5)air,50 0 C,6hr<br />
O<br />
R' ; iPr,Ph<br />
N<br />
Ar<br />
O<br />
Ar'<br />
R<br />
R<br />
Alumino-heteroles are obtained from simple precursors<br />
in a fully chemo- <strong>and</strong> regioselective manner by a metalative<br />
cyclisation. The carbon-aluminum bond is still<br />
able to react further with several electrophiles, without<br />
the need <strong>of</strong> transmetalation providing a straightforward<br />
access to 3,4,5-trisubstituted isoxazoles <strong>and</strong> 1,3,4,5-<br />
tetrasubstituted pyrazoles.<br />
A large number <strong>of</strong> functionally substituted 2-alkyn-1-<br />
one O-methyl oximes have been cyclized under mild<br />
reaction conditions in the presence <strong>of</strong> ICl to give the<br />
corresponding 4-iodoisoxazoles in moderate to excellent<br />
yields. The resulting 4-iodoisoxazoles undergo<br />
various palladium-catalyzed reactions to yield 3,4,5-<br />
trisubstituted isoxazoles.<br />
Ar<br />
YH 1)1 eq.AlMe 3<br />
HN toluene,r.t..,5 min<br />
R<br />
N<br />
Cl<br />
N<br />
OH<br />
Cl<br />
2)1 eq,<br />
50 0 C, 1hr<br />
OMe<br />
R'<br />
R' AlMe 3 N<br />
2 eq<br />
+ I R<br />
1.2 eq.ICI<br />
A thermally promoted cycloaddition between alkynyliodides<br />
<strong>and</strong> nitrile oxides <strong>of</strong>fers excellent regioselectivity<br />
<strong>and</strong> a broad scope with respect to both starting<br />
materials. Further functionalization <strong>of</strong> the highly decorated<br />
iodoisoxazole motifs can be achieved via Suzuki<br />
cross-coupling.<br />
R<br />
CH 2 Cl 2 ,r.t .,0.5 - 6 hrs<br />
Y<br />
Al<br />
R'<br />
4 eq<br />
EX<br />
r.t,o.n<br />
1.05 eq.Na 2 CO 3 (0.025M)<br />
in H 2 O,added over 24 hrs<br />
DMF,100 0 C,24 hrs<br />
N<br />
R<br />
N<br />
R<br />
Y<br />
E<br />
R'<br />
E (EX)<br />
D (MeODS) 25 eq<br />
Cl(NCS),(NIS)<br />
CONH 2 (Cl 3 )C-NCO<br />
O<br />
N<br />
Ar<br />
I<br />
O<br />
R'<br />
R; alkyl<br />
I<br />
R<br />
EWG 1.1eq.Br 2<br />
+<br />
CH 2 Cl 2<br />
r.t,1-3hr<br />
2 mol-%PdCl 2 (PPh 3 )<br />
4 mol-%CuI<br />
1.05 eq.Et 3 N<br />
THF,r.t.,1 hr<br />
HO<br />
N<br />
Cl<br />
O<br />
R<br />
Ar<br />
R'<br />
EWG<br />
Br<br />
-<br />
O<br />
+ N +<br />
1 eq. N<br />
OH<br />
Cl<br />
Ar<br />
1.1 eq.Et 3 N<br />
MW,90 0 C,30 min<br />
EWG<br />
R<br />
R'<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
N<br />
Ar<br />
Ar<br />
N<br />
+ R<br />
PhSe<br />
HON<br />
1 eq.NCS<br />
1.05 eq.NEt 3<br />
CHCl 3,r.t.,12 hr<br />
PhSe<br />
O<br />
N<br />
A 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition <strong>of</strong> phenyl vinylic selenide<br />
to nitrile oxides <strong>and</strong> subsequent oxidation-elimination<br />
furnished 3-substituted isoxazoles with good yields in a<br />
one-pot, two-step transformation.<br />
R<br />
+<br />
O<br />
N<br />
SePh<br />
R<br />
30% H 2O 2<br />
0 0 C,10 min. O<br />
r.t, 20 min<br />
N<br />
R<br />
R<br />
The consecutive Sonogashira coupling <strong>of</strong> acid chlorides<br />
with terminal alkynes, followed by 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition<br />
under dielectric heating <strong>of</strong> in situ generated nitrile<br />
oxides from hydroximinoyl chlorides furnishes isoxazoles<br />
in moderate to good yields in the sense <strong>of</strong> a one-pot threecomponent<br />
reaction<br />
R NO 2<br />
+ Ph<br />
0.5 eq.DABCO<br />
N<br />
CHCl 3<br />
60 0 C,20-80 hr<br />
Ph<br />
O<br />
The dehydration <strong>of</strong> primary nitro compounds can be<br />
performed by bases in the presence <strong>of</strong> dipolarophiles.<br />
Among the organic bases examined, DABCO gave the<br />
best results. The reaction is applicable to activated nitro<br />
compounds <strong>and</strong> to phenylnitromethane <strong>and</strong> affords<br />
425
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
-affords isoxazoline derivatives in higher yields compared<br />
with those <strong>of</strong> other methods. The reaction, however, is<br />
not compatible with nitroalkanes.<br />
R<br />
O<br />
H<br />
1)1.05 eq.H 2 NOH.HCl,1.05 eqNaOH<br />
tBuOH/H 2 O (1:1),30 min (TLC)<br />
2)1.05 eq.TsN(Cl)Na.3H 2 O<br />
3)1.05 eq. R' 3 mol - %CuSO 4<br />
approx.3.7 mol-%Cu,r.t ,6 hr<br />
3,5-Disubstituted isoxazoles are regioselectively obtained<br />
in good yields by a mild <strong>and</strong> convenient one-pot,<br />
three-step procedure utilizing a copper(I)-catalyzed<br />
cycloaddition reaction between in situ generated nitrile<br />
oxides <strong>and</strong> terminal acetylenes. Pyrazole or isoxazole<br />
derivatives are prepared by a palladium-catalyzed fourcomponent<br />
coupling <strong>of</strong> a terminal alkyne, hydrazine<br />
(hydroxylamine), carbon monoxide under ambient pressure,<br />
<strong>and</strong> an aryl iodide.<br />
R<br />
The reaction <strong>of</strong> various 2-alkyn-1-one O-methyl oximes<br />
with ICl, I 2 , Br 2 , or PhSeBr provided 3,5-disubstituted 4-<br />
halo(seleno)isoxazoles in good to excellent yields under<br />
mild reaction conditions.<br />
R<br />
N<br />
OMe<br />
R'<br />
1.2 eq.ICI<br />
CH 2 Cl 2 . r.t...,<br />
0.25- 0.75 hrs<br />
A series <strong>of</strong> 4-alkyl-5-aminoisoxazoles have been synthesized<br />
in high yield by nucleophilic addition <strong>of</strong> lithiated<br />
alkyl nitriles to (α)-chlorooximes.<br />
Various substituted benzisoxazoles have been prepared<br />
by a [3 + 2] cycloaddition <strong>of</strong> nitrile oxides <strong>and</strong> arynes.<br />
Both highly reactive intermediates, have been generated<br />
in situ by fluoride anion from readily prepared aryne precursors<br />
<strong>and</strong> chlorooximes. The reaction scope is quite<br />
general, affording a novel, direct route to functionalized<br />
benzisoxazoles under mild reaction conditions .<br />
R<br />
N<br />
OH<br />
Cl<br />
2 eq<br />
+<br />
R'<br />
SiMe 3<br />
OTf<br />
4 eq<br />
+<br />
Cl<br />
R'<br />
CN<br />
R<br />
N<br />
N<br />
OH<br />
OH<br />
4 eq.tBuOH<br />
THF<br />
78 0 C,15 min<br />
6 eq.CsF<br />
MeCN,r.t,8.5 hr<br />
1.5 eq NCS<br />
2 EQ.K 2 CO 3<br />
R<br />
N<br />
R<br />
O<br />
R'<br />
R<br />
N<br />
R<br />
N<br />
O<br />
O<br />
I<br />
R'<br />
R'<br />
NH 2<br />
R : Ar,alkyl<br />
R' alkyl,benzyl,Ar<br />
O<br />
R<br />
N<br />
R : aryl,iPr,vinyl<br />
R'<br />
N<br />
A divergent <strong>and</strong> regioselective synthesis <strong>of</strong> either 3-<br />
substituted benzisoxazoles or 2-substituted benzoxazoles<br />
from readily accessible ortho-hydroxyaryl N-H<br />
ketimines proceeds in two distinct pathways through a<br />
common N-Cl imine intermediate: (a) N-O bond formation<br />
to form benzisoxazole under anhydrous conditions<br />
<strong>and</strong> (b) NaOCl mediated Beckmann-type rearragement<br />
to form benzoxazole, respectively.<br />
R'<br />
R<br />
R''<br />
5 mol-%FeBr 2<br />
O<br />
MS4A<br />
CH<br />
N 2 Cl 2 ,40 0 C,16hr<br />
3<br />
Table 4. Pharmacological activity <strong>of</strong> Isoxazole <strong>and</strong> Its<br />
Derivative<br />
Chemical structure<br />
C H 3<br />
ABT-418- Treatment <strong>of</strong><br />
Alzheimer’s disease <strong>and</strong><br />
ADHD<br />
N<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
N<br />
CH 3<br />
O<br />
H<br />
C H 3<br />
NH 2<br />
N<br />
OH<br />
AMPA- Specific agonist<br />
AMPA receptor, mimic<br />
effect <strong>of</strong> neurotransmitter<br />
glutamate<br />
Used in combination with<br />
metal compound in asymmetric<br />
synthesis as a chiral<br />
catalyst Bisoxazoline lig<strong>and</strong><br />
OXADIAZOLE<br />
Oxadiazole [9] is a heterocyclic aromatic chemical<br />
compound with the molecular formula C 2 H 2 N 2 O. There<br />
are four isomers <strong>of</strong> oxadiazole:<br />
O<br />
O<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
O<br />
O<br />
N<br />
R<br />
R'<br />
N<br />
R''<br />
O<br />
R:H.Cl<br />
R' : H,Me.OMe<br />
R'' : Ar,alkyl<br />
Name <strong>of</strong> compound<br />
3-methyl-5-[(2S)-1-<br />
methylpyrrolidin-2-<br />
yl]-1,2-oxazole<br />
2-amino-3-(3-<br />
hydroxy-5-methylisoxazol-4-yl)<br />
propanoic acid<br />
2,6-Bis[4R]-4-phenyl<br />
-2-oxazolinyl]<br />
pyridine<br />
O<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
THF,r.t,12 hr<br />
O<br />
R' alkyl,Ar<br />
N<br />
N<br />
1,2,3-OXADIAZOLE<br />
N<br />
N<br />
N<br />
1,2,4-OXADIAZOLE 1,2,5-OXADIAZOLE 1,3,4-OXADIAZOLE<br />
N<br />
N<br />
426
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
Out <strong>of</strong> its four possible isomers, 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole is<br />
widely exploited for various applications. A numbers <strong>of</strong><br />
therapeutic agents such as HIV-integrase inhibitor raltagravir,<br />
a nitr<strong>of</strong>uran antibacterial furamizole, a potent PDF<br />
inhibitor BB-83698, antihypertensive agents tiodazosin<br />
<strong>and</strong> nesapidil are based on 1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety. The<br />
1, 3, 4-oxadiazole undergoes number <strong>of</strong> reactions including<br />
electrophillic substitution, nucleophilic substitution,<br />
thermal <strong>and</strong> photochemical. The present review<br />
attempts to summarize the various routes <strong>of</strong> synthesis<br />
<strong>and</strong> the reactions <strong>of</strong> 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole <strong>and</strong> its<br />
derivatives <strong>and</strong> focus on their biological potential [21].<br />
Synthesis- Scheme 1<br />
A direct [23] access to symmetrical <strong>and</strong> unsymmetrical<br />
2,5-disubstituted [1,3,4]-oxadiazoles has been accomplished<br />
through an imine C-H functionalization <strong>of</strong> N-<br />
arylidenearoyl hydrazide using a catalytic quantity <strong>of</strong> Cu<br />
(OTf) 2 . These reactions can be performed in air atmosphere<br />
<strong>and</strong> moisture making it exceptionally practical for<br />
application in organic synthesis.<br />
Ar<br />
H<br />
N<br />
O<br />
NH<br />
Ar'<br />
Scheme 2<br />
A facile <strong>and</strong> general protocol [25] for the preparation <strong>of</strong> 2<br />
-amino-1, 3, 4-oxadiazoles relies on a tosyl chloride/<br />
pyridine-mediated cyclization <strong>of</strong> thiosemicarbazides that<br />
consistently outperforms the analogous semicarbazide<br />
cyclizations. Various 5-alkyl- <strong>and</strong> 5-aryl-2-amino-1,3,4-<br />
oxadiazoles have been prepared in good yields.<br />
R HN NH NH<br />
Scheme 3<br />
An oxidative [11] desulfurization approach enables the<br />
construction <strong>of</strong> oxadiazole <strong>and</strong> thiadiazole heterocycles in<br />
the presence <strong>of</strong> iodobenzene <strong>and</strong> Oxone. The use <strong>of</strong> iodobenzene<br />
<strong>and</strong> the inexpensive readily available oxidant<br />
Oxone makes the reaction system simple <strong>and</strong> versatile for<br />
desulfurization.<br />
Synthesis <strong>of</strong> 1, 3,4-oxadiazoles<br />
Ar<br />
Ar<br />
O<br />
HN<br />
H<br />
N<br />
O<br />
S<br />
NH<br />
O<br />
N<br />
S<br />
NH<br />
R'<br />
Ar'<br />
R<br />
0.1 eq.Cu(OTf) 2<br />
1 eq Cs 2 CO 3<br />
DMF,AIR<br />
110 0 C,10-24 HR<br />
1.2 eq.TsCl<br />
2.1 eq.pyridine<br />
THF,60-70 0 C,20hrs<br />
2 eq.PhI<br />
4 eq.oxone<br />
2 eq.NEt 3<br />
MeOH,r.t,40 min<br />
0.1 eqCu(OTf) 2<br />
1 eq.Cs 2 CO 3<br />
DMF,air,<br />
110 0 C,10-24 hr<br />
A direct access to symmetrical <strong>and</strong> unsymmetrical 2,5-<br />
disubstituted [1,3,4]-oxadiazoles has been accomplished<br />
Ar<br />
Ar<br />
R<br />
Ar<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
N<br />
NH<br />
Ar'<br />
NHR'<br />
R<br />
R : Ar,Et,Bn<br />
O<br />
N<br />
Ar'<br />
through an imine C-H functionalization <strong>of</strong> N-<br />
arylidenearoylhydrazide using a catalytic quantity <strong>of</strong><br />
Cu(OTf) 2. These reactions can be performed in air atmosphere<br />
<strong>and</strong> moisture making it exceptionally practical<br />
for application in organic synthesis.<br />
R<br />
A facile <strong>and</strong> general protocol for the preparation <strong>of</strong> 2-<br />
amino-1,3,4-oxadiazoles relies on a tosyl chloride/<br />
pyridine-mediated cyclization <strong>of</strong> thiosemicarbazides<br />
that consistently outperforms the analogous semicarbazide<br />
cyclizations. Various 5-alkyl- <strong>and</strong> 5-aryl-2-amino-<br />
1,3,4-oxadiazoles have been prepared in good yields.<br />
Ar<br />
O<br />
HN N<br />
H<br />
HN<br />
An oxidative desulfurization approach enables the construction<br />
<strong>of</strong> oxadiazole <strong>and</strong> thiadiazole heterocycles in<br />
the presence <strong>of</strong> iodobenzene <strong>and</strong> Oxone. The use <strong>of</strong><br />
iodobenzene <strong>and</strong> the inexpensive readily available oxidant<br />
Oxone makes the reaction system simple <strong>and</strong> versatile<br />
for desulfurization.<br />
R<br />
S<br />
R'<br />
1.2 EQ. TsCl<br />
2.1 eq.pyridine<br />
THF,60-70 0 C,20 hr N N<br />
The reaction <strong>of</strong> a thiosemicarbazide intermediate with<br />
EDC· HCl in DMSO or p-TsCl, triethylamine in N-<br />
methyl-2-pyrrolidone gives the corresponding 2-amino-<br />
1, 3,4-oxadiazoles <strong>and</strong> 2-amino-1,3,4- thiadiazoles<br />
through regioselcective cyclization processes.<br />
Ar<br />
N<br />
H<br />
O<br />
O<br />
HN<br />
S<br />
OH<br />
S<br />
NH<br />
N<br />
H<br />
R<br />
NH<br />
N<br />
H<br />
O<br />
Ar<br />
2 eq.PhI<br />
4 EQ.Oxone<br />
2 eq.NEt 3<br />
MeOH,r.t,40 min<br />
1.2 eq,EDC.HCl<br />
DMSO<br />
60 0 C,2 hr<br />
+<br />
Ph3 P N NC + R<br />
O<br />
4 eq<br />
H<br />
CH 2 Cl 2<br />
R.T,24 hr<br />
HN<br />
R<br />
N-Isocyaniminotriphenylphosphorane, aldehydes, <strong>and</strong><br />
benzoic acids undergo a one-pot, three-component reaction<br />
under mild conditions to afford 2-aryl-5-<br />
hydroxyalkyl-1, 3,4-oxadiazoles in good yields. Symmetric<br />
<strong>and</strong> unsymmetric 1, 3,4-oxadiazoles were synthesized<br />
in situ from hydrazine hydrate <strong>and</strong> the corresponding<br />
2-acyl-4,5-dichloropyridazin-3-ones as acylating<br />
agents in polyphosphoric acid (PPA) or<br />
BF 3·OEt 2 in excellent yields. A simple <strong>and</strong> straightforward<br />
method for the direct carboxylation <strong>of</strong> aromatic<br />
heterocycles such as oxazoles, thiazoles, <strong>and</strong> oxadiazoles<br />
using CO 2 as the C1 source requires no metal<br />
catalyst <strong>and</strong> only Cs 2 CO 3 as the base. A good functional<br />
group tolerance is achieved.<br />
R<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
Ar<br />
N<br />
O<br />
O<br />
N<br />
N<br />
Ar<br />
O<br />
NH<br />
427<br />
NHR'<br />
R : Ar,Bn<br />
R<br />
R;benzyl,<br />
Ar,alkyl<br />
N<br />
R<br />
OH
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
Synthesis <strong>of</strong> 1, 2,4-oxadiazoles<br />
PTSA-ZnCl 2 is an efficient <strong>and</strong> mild catalyst for the synthesis<br />
<strong>of</strong> 3,5-disubstituted-1,2,4-oxadiazoles from amidoximes<br />
<strong>and</strong> organic nitriles.<br />
R<br />
Ar CN<br />
OH + NC R'<br />
N<br />
1eq.NH 2 OH (50%)aq.<br />
AcOH (cat)<br />
neat MW,100 0 C,1 MIN<br />
0.3 eq.PTSA<br />
0.3 eq.ZnCl 2<br />
DMF.80 0 C,4-8 hrs<br />
or MeCN (R'=Me),70 0 C,1-2 h<br />
Ar<br />
NH 2<br />
NOH<br />
R<br />
O<br />
O<br />
R<br />
1eq<br />
O<br />
O<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
Ar<br />
N<br />
R'<br />
R,R' : Ar.alkyl<br />
benzyl<br />
O<br />
N<br />
R<br />
R ; H,Me<br />
SYNTHESIS- Scheme 1<br />
A four-step [10] synthesis <strong>of</strong> cis-3,5-disubstituted morpholines<br />
from enantiomerically pure amino alcohols is<br />
described. The key step in the synthesis is a Pdcatalyzed<br />
carboamination reaction between a substituted<br />
ethanolamine derivative <strong>and</strong> an aryl or alkenyl<br />
bromide. By this method morpholine derivatives were<br />
prepared by Br<strong>and</strong>en R Rosen, jhon p wolfe et al.<br />
HN<br />
OH<br />
Boc<br />
3 steps<br />
Ar<br />
HN<br />
O<br />
R<br />
R'-Br<br />
Pd-catalyst<br />
base<br />
R'<br />
Ar<br />
N<br />
O<br />
R<br />
20:1 dr<br />
A one-pot reaction between nitriles, hydroxylamine<br />
<strong>and</strong> Meldrum’s acids under microwave irradiation <strong>and</strong><br />
solvent-free conditions gives 3,5-disubstituted 1,2,4-<br />
oxadiazoles in good to excellent yields.<br />
Scheme 2<br />
OH<br />
H 3C<br />
+<br />
COCl<br />
R 1<br />
R 2<br />
10% NaOH<br />
stirring<br />
R 3<br />
R 2<br />
R 1<br />
anhydr.AlCl 3<br />
80-90 0 C<br />
Ar<br />
OH<br />
N<br />
NH 2<br />
+ HO<br />
O<br />
R<br />
O<br />
OEt<br />
1.1 eq.DCC<br />
dioxane<br />
110 0 C,8-12 hr<br />
Ar<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
R<br />
O<br />
OEt<br />
R 3<br />
H 3C<br />
O<br />
O<br />
R 2<br />
A series <strong>of</strong> α-amino acid-derived 1,2,4-oxadiazoles have<br />
been synthesized via a convenient <strong>and</strong> inexpensive onepot<br />
protocol in good yields <strong>and</strong> in relatively short reaction<br />
times.<br />
Table 5. Pharmacological activity <strong>of</strong> Oxadiazole <strong>and</strong> its<br />
derivatives<br />
Chemical structure<br />
O<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
O<br />
Pharmacological action<br />
Anti mycobacterial<br />
R3<br />
R 1<br />
OH<br />
O<br />
anhydr.K 2CO 3<br />
DMSO<br />
CH 3<br />
a;R 1 =R 2 =H,R 3 =OCH 3<br />
c;R 1 =CH 3 ,R 2 =R 3 =H<br />
e;R 1= R 3 =H,R 2 =Cl<br />
g; R 1 =R 2 =H,R 3 =Br<br />
i ;R 1 =R 2 =H,R 3 =Cl<br />
Cl<br />
N<br />
R 3<br />
O<br />
R 2<br />
H 3C<br />
R 1<br />
O<br />
O<br />
b; R 1 =R 2 =H,R 3 =CH 3<br />
d ; R 1 =R 3 =H,R 2 =CH 3<br />
f ; R 1 =Br,R 2 =R 3 =H<br />
H ; R 1 =R 2 =H,R 3 =F<br />
j ; ;R1=R 2 =R 3 =H<br />
N<br />
O<br />
C H 3<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
O<br />
S<br />
Morpholine<br />
Morpholine[20] is an organic chemical compound having<br />
the chemical formula O(CH 2 CH 2 ) 2 NH. This heterocycle,<br />
pictured at right, features both amine <strong>and</strong> ether functional<br />
groups. Because <strong>of</strong> the amine, morpholine is a base;<br />
its conjugate acid is called morpholinium. For example,<br />
neutralizing morpholine with hydrochloric acid makes the<br />
salts morpholinium chloride.<br />
Br<br />
O CH3<br />
Anti convulsant<br />
Anti inflammatory<br />
substituted 2-methylphenyl benzoates (3a-j) were synthesized<br />
by stirring 2-methyl phenol (1, 1 equivalent)<br />
with corresponding benzoyl chlorides (2a-j, 1 equivalent)<br />
for 30 minutes in alkaline medium using 10%<br />
sodium hydroxide solution with excellent yield (85–<br />
90%). Substituted hydroxyl benzophenones (4a-j) were<br />
synthesized by refluxing a mixture <strong>of</strong> 3a-j (1 equivalent)<br />
<strong>and</strong> anhydrous aluminium chloride (1.5 equivalents)<br />
for 20 minutes with 80–83% yield. Condensation<br />
<strong>of</strong> 4a-j (1 equivalent) with 4-(2-chloroethyl) morpholine<br />
hydrochloride (1 equivalent) for 3 hours in<br />
presence <strong>of</strong> anhydrous potassium carbonate (1.5<br />
equivalents) <strong>and</strong> dimethyl sulphoxide furnished substituted<br />
benzophenone-N-ethyl morpholine ethers with 70<br />
–75% yield.<br />
Scheme 3<br />
Morpholine may be produced by the dehydration <strong>of</strong><br />
diethanolamine with sulfuric acid was prepared by<br />
Klaus Weissermel, Hans-Jürgen Arpe, Charlet R. Lindley,<br />
Stephen Hawkins et al.<br />
428
HO<br />
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
H<br />
N<br />
OH<br />
H 2 SO 4<br />
H 2 O<br />
Pharmacological activity <strong>of</strong> Morpholine &its derivatives<br />
4-Phenyl morpholine derivatives have been reported to<br />
possess anti-inflammatory antimicrobial <strong>and</strong> central<br />
nervous system activities . Schiff bases have been reported<br />
to possess biological properties apart from antimicrobial<br />
activities . In our previous work , it was observed<br />
that substitution <strong>of</strong> 4-phenyl morpholine to quinazoline<br />
moiety results in potent analgesic, anti-inflammatory, <strong>and</strong><br />
antimicrobial activities.<br />
Synthesis <strong>of</strong> isoxazolyltriazole derivatives as fungicides<br />
With a view to obtaining biologically active isoxazole<br />
derivatives containing triazole moiety, synthesis <strong>of</strong> a series<br />
<strong>of</strong> compounds have been conceived <strong>and</strong> the synthetic<br />
strategy is described in the Scheme 3. The triazole moiety<br />
has been found to be an important taxophore to exhibit<br />
fungitoxic properties inhibiting the cell wall synthesis <strong>and</strong><br />
also known as C-14 demethylation inhibitor (to act as<br />
fungicide). Most <strong>of</strong> the exploited azole fungicides contain<br />
an aromatic ring system, <strong>and</strong> to the best <strong>of</strong> the author’s<br />
knowledge no compound with isoxazole heterocyclic<br />
moiety has so for been synthesized <strong>and</strong> studied for their<br />
fungitoxic properties.<br />
Scheme 3<br />
O<br />
R<br />
CH 3 COOEt<br />
COOEt (NH 2 -OH) 2 H 2 SO 4<br />
R R<br />
NaOMe<br />
MeOH<br />
7a-k<br />
MeOH<br />
8a-k<br />
Transesterification<br />
R<br />
K 2 CO 3<br />
Acetonitrile<br />
O<br />
N<br />
13a-k<br />
COOEt<br />
HN<br />
N<br />
N<br />
N<br />
12<br />
N<br />
N<br />
R<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
11a-k<br />
N<br />
CH 2 Cl<br />
SOCl 2, DMF<br />
Heptane R<br />
65-8 0 C<br />
The target molecule 5-aryl-3-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl<br />
methyl) isoxazole (13a-k) is prepared by N-alkylation <strong>of</strong><br />
1H-1,2,4-triazole (12) with 5-aryl-3-chloromethyl- isoxazole<br />
under mild basic conditions using different bases in<br />
polar solvent (Scheme 5). The yields obtained are in the<br />
range <strong>of</strong> 80-90 %. The possibility <strong>of</strong> formation <strong>of</strong> C-4<br />
alkylated product is ruled out based on the unequivocal<br />
characterization <strong>of</strong> the product using spectral data. The<br />
target molecule 5-aryl-3-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl methyl)<br />
isoxazole (13a-k) is prepared by N-alkylation <strong>of</strong> 1H-1,2,4<br />
-triazole (12) with 5-aryl-3-chloromethyl- isoxazole under<br />
mild basic conditions using different bases in polar<br />
solvent (Scheme 5). The yields obtained are in the range<br />
<strong>of</strong> 80-90 %. The possibility <strong>of</strong> formation <strong>of</strong> C-4 alkylated<br />
product is ruled out based on the unequivocal characterization<br />
<strong>of</strong> the product using spectral data.<br />
O<br />
9a-k<br />
O<br />
10a-k<br />
N<br />
N<br />
H<br />
N<br />
O<br />
COOMe<br />
NaBH 4<br />
AlCl 3 , THF<br />
Reflux<br />
R = H, 2-Cl, 2-OMe, 3-Cl, 3-OMe, 4-Me, 4-Cl, 4-Br, 4-F, 4-OMe, 2,4-diOMe.<br />
CH 2 OH<br />
Scheme 4<br />
R<br />
O<br />
N<br />
HN N<br />
CH 2 Cl +<br />
N<br />
K 2 CO 3 , CH 3 CN<br />
Reflux<br />
11a-k 12 13a-k<br />
R = H, 2-Cl, 2-OMe, 3-Cl, 3-OMe, 4-Me, 4-Cl, 4-Br, 4-F, 4-OMe, 2,4-diOMe<br />
Preparation <strong>of</strong> 2-isoxazolyl benzimidazole derivatives<br />
Some <strong>of</strong> the benzimidazole derivatives containing a<br />
heterocyclic moiety at 2-position are thiabendazole<br />
(17) <strong>and</strong> cambendazole (18) which are commercially<br />
important.<br />
N<br />
N<br />
N<br />
S<br />
N<br />
H<br />
H<br />
Thiabendazole (17) Cambendazole (18)<br />
To synthesize novel 2-isoxazolyl substituted<br />
benz- imidazoles using N-butyl-N,N-dimethyl-aphenylethylammonium<br />
bromide (16) as the catalyst.<br />
Retro synthetic analysis <strong>of</strong> target molecules requires<br />
appropriately substituted 5-aryl-3-isoxazol carbaldehyde<br />
(19a-i) as an active intermediate. The sequence <strong>of</strong><br />
synthetic methodology is depicted below (Scheme 6)<br />
<strong>and</strong> each step <strong>of</strong> synthesis has been discussed in detail.<br />
The reaction <strong>of</strong> o-phenylenenediamine (OPDA) <strong>and</strong> 5-<br />
aryl-3-isoxazolecarbaldehyde at reflux temperature <strong>of</strong><br />
1,2-dichloroethane in the presence <strong>of</strong> 10 mol % <strong>of</strong> catalyst<br />
for 3-4 hours to give title compounds (21a-m).<br />
R 1<br />
O N<br />
9 a-i<br />
COOMe<br />
Reduction<br />
i-PrOCOHN<br />
R 1 = H, 2-Cl, 3-Cl, 3-OMe, 4-Me, 4-Cl, 4-Br, 4-F, 4-OMe. R = H, OMe<br />
REFERENCES<br />
[1] Mahtew B soellner An introduction <strong>of</strong> oxaziridines.january<br />
30,2003<br />
[2] (3+2) cycloaddition reaction between aliphatic<br />
alkynes <strong>and</strong> oxaziridines. Luigino troisi,arilena<br />
Fabio,Francesca rosato <strong>and</strong> valeria<br />
vidett,ARKIVOC ,2009,(14),pp-324-336.<br />
[3] Highly regioselective palladium catalysed direct<br />
arylation <strong>of</strong> oxazole at c-2 or c-5 with aryl bromide,chlorides<br />
<strong>and</strong> triflates..Chobanian N.A. Strotman,H.<br />
et al Organic letters (2010),12 (16),page<br />
no:3578-3581.<br />
[4] One-Pot Van Leusen Synthesis <strong>of</strong> 4,5-<br />
Disubstituted Oxazoles in Ionic Liquids B. Wu, J.<br />
Wen, J. Zhang, J. Li, Y.-Z. Xiang, X.-Q. Yu,<br />
Synlett,( 2009), 500-504.<br />
R 1<br />
R 1<br />
R<br />
O N<br />
19a-i<br />
O N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
CHO<br />
+<br />
R<br />
N<br />
N<br />
N<br />
N<br />
Catalyst / DCE<br />
reflux, 3-4 h.<br />
H<br />
N<br />
N<br />
21 a-m<br />
20<br />
R<br />
429<br />
S<br />
NH 2<br />
NH 2<br />
N
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
[5] C-H Bond Activation: A Versatile Protocol for the<br />
Direct Arylation <strong>and</strong> Alkenylation <strong>of</strong> Oxazoles F.<br />
Besselièvre, S. Lebrequier, F. Mahuteau-Betzer, S.<br />
Piguel, Synthesis, 2009, 3511-3512<br />
[6] Facile, Selective, <strong>and</strong> Regiocontrolled Synthesis <strong>of</strong><br />
Oxazolines <strong>and</strong> Oxazoles Mediated by ZnI 2 <strong>and</strong><br />
FeCl 3 G. C. Senadi, W.-P. Hu, J.-S. Hsiao, J. K V<strong>and</strong>avasi,<br />
C.-Y. Chen, J.-J. Wang, Org. Lett., 2012,<br />
14, 4478-4481.<br />
[7] Y. Du, X. LiD C. Ren, Y. Zheng,. Zhang-Negrerie, ,<br />
K. Zhao, J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77, 10353-10361<br />
[8] An Efficient [2 + 2 + 1] Synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2,5-<br />
Disubstituted Oxazoles via Gold-Catalyzed Intermolecular<br />
Alkyne OxidationW. He, C. Li, L. Zhang, J.<br />
Am. Chem. Soc.,2011, 133, 8482-8485<br />
[9] Palladium-Catalyzed Direct (Hetero)arylation <strong>of</strong><br />
Ethyl Oxazole-4-carboxylate: An Efficient Access to<br />
(Hetero)aryloxazoles Verrier, T. Martin, C. Hoarau,<br />
F. Marsais, J. Org. Chem., 2008, 73, 7383-7386.<br />
[10] Direct β-Acyloxylation <strong>of</strong> Enamines via PhIO-<br />
Mediated Intermolecular Oxidative C-O Bond Formation<br />
<strong>and</strong> Its Application to the Synthesis <strong>of</strong> Oxazoles<br />
X. Liu, R. Cheng, F. Zhao, D. Zhang-Negrerie,<br />
Y. Du, K. Zhao, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 5480-5483.<br />
[11] TBHP/I 2 -Mediated Domino Oxidative Cyclization<br />
for One-Pot Synthesis <strong>of</strong> Polysubstituted Oxazoles<br />
H. Jiang, H. Huang, H. Cao, C. Qi, Org. Lett., 2010,<br />
12, 5561- 5563.<br />
[12] A Simple One-Pot Synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2-Aryl-5-alkyl-<br />
Substituted Oxazoles by Cs 2 CO 3 -Mediated Reactions<br />
<strong>of</strong> Aromatic Primary Amides with 2,3-<br />
DibromopropeneN. Yasmin, J. K. Ray, Synlett, 2009,<br />
2825-2827<br />
[13] Room Temperature Copper(II)-Catalyzed Oxidative<br />
Cyclization <strong>of</strong> Enamides to 2,5-Disubstituted Oxazoles<br />
via Vinylic C-H FunctionalizationC. W.<br />
Cheung, S. L. Buchwald, J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77,<br />
7526-7537<br />
[14] Brønsted Acid-Catalyzed Propargylation/<br />
Cycloisomerization T<strong>and</strong>em Reaction: One-Pot Synthesis<br />
<strong>of</strong> Substituted Oxazoles from Propargylic Alcohols<br />
<strong>and</strong> AmidesY.-M. Pan, F.-J. Zheng, H.-X.<br />
Lin, Z.-P. Zhan, J. Org. Chem., 2009, 74, 3148-3151.<br />
[15] Sequential Copper-Catalyzed Vinylation/Cyclization:<br />
An Efficient Synthesis <strong>of</strong> Functionalized OxazolesR.<br />
Martín, A. Cuenca, S. L. Buchwald, Org. Lett., 2007,<br />
9, 5521-5524.<br />
[16] Facile Synthesis <strong>of</strong> Polysubstituted Oxazoles via A<br />
Copper-Catalyzed T<strong>and</strong>em Oxidative CyclizationC.<br />
Wang, J. Zhang, S. Wang, J. Fan, Z. Wang, Org.<br />
Lett., 2010, 12, 2338-2341<br />
[17] Solution versus Fluorous versus Solid-Phase Synthesis<br />
<strong>of</strong> 2,5-Disubstituted 1,3-Azoles. Preliminary Antibacterial<br />
Activity StudiesJ. F. Sanz-Cervera, R.<br />
Blasco, J. Piera, M. Cynamon, I. Ibáñez, M. Murguía,<br />
S. Fustero, J. Org. Chem., 2009, 74<br />
[18] 2-Oxazol-5-ylethanones by Consecutive Three-<br />
Component<br />
Amidation-Coupling-<br />
Cycloisomerization (ACCI) SequenceE. Merkul,<br />
O. Grotkopp, T. J. J. Müller, Synthesis, 2009, 502-<br />
507.<br />
[19] New Easy Approach to the Synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2,5-<br />
Disubstituted <strong>and</strong> 2,4,5-Trisubstituted 1,3-<br />
Oxazoles. The Reaction <strong>of</strong> 1-(Methylthio)acetone<br />
with NitrilesHerrera, R. Martinez-Alvarez, P.<br />
Ramiro, D. Molero, J. Almy, J. Org. Chem., 2006,<br />
71, 3026-3032<br />
[20] Solution-phase parallel oxazole synthesis with<br />
TosMIC. . A. Kulkarnia, A. Ganesan, Tetrahedron<br />
Lett., 1999, 40, 5637-5638. Facile Preparation <strong>of</strong><br />
Oxazole-4-carboxylates <strong>and</strong> 4-Ketones from Aldehydes<br />
using 3-Oxazoline-4-carboxylates as IntermediatesK.<br />
Murai, Y. Takahara, T. Matsushita, H.<br />
Komatsu, H. Fujioka, Org. Lett., 2010, 12, 3456-<br />
3459.<br />
[21] Rhodium-catalyzed direct oxidative crosscoupling<br />
<strong>of</strong> 2-aryl pyridine with benzothiazolesL.<br />
Ackermann, C. Kornhaass, Y. Zhu, Org. Lett.,<br />
2012, 14, 1824-1826<br />
[22] S. From Propargylic Amides to Functionalized<br />
Oxazoles: Domino Gold Catalysis/Oxidation by<br />
DioxygenK. Hashmi, M. C. B. Jaimes, A. M.<br />
Schuster, F. Rominger, J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77,<br />
6394-6408.<br />
[23] Zn(OTf) 2 -Catalyzed Cyclization <strong>of</strong> Proparyl Alcohols<br />
with Anilines, Phenols, <strong>and</strong> Amides for Synthesis<br />
<strong>of</strong> Indoles, Benz<strong>of</strong>urans, <strong>and</strong> Oxazoles<br />
through Different Annulation Mechanisms. M.P.<br />
Kumar, R.-S. Liu, J. Org. Chem., 2006, 71, 4951-<br />
4955<br />
[24] Sequential Copper-Catalyzed Vinylation/<br />
Cyclization: An Efficient Synthesis <strong>of</strong> Functionalized<br />
Oxazoles. R. Martín, A. Cuenca, S. L. Buchwald,<br />
Org. Lett., 2007, 9, 5521-5524<br />
[25] Room Temperature Copper(II)-Catalyzed Oxidative<br />
Cyclization <strong>of</strong> Enamides to 2,5-Disubstituted<br />
Oxazoles via Vinylic C-H FunctionalizationC. W.<br />
Cheung, S. L. Buchwald, J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77,<br />
7526-7537.<br />
[26] A Simple One-Pot Synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2-Aryl-5-alkyl-<br />
Substituted Oxazoles by Cs 2 CO 3 -Mediated Reactions<br />
<strong>of</strong> Aromatic Primary Amides with 2,3-<br />
Dibromopropene.N.Yasmin, J. K. Ray, Synlett,<br />
2009, 2825-2827.<br />
[27] Simple <strong>and</strong> Efficient Preparation <strong>of</strong> 2,5-<br />
Disubstituted Oxazoles via a Metal-Free-Catalyzed<br />
Cascade Cyclization.C. Wan, L. Gao, Q. Wang, J.<br />
Zhang, Z. Wang, Org. Lett., 2010, 12, 3902-3905.<br />
[28] TBHP/I 2 -Mediated Domino Oxidative Cyclization<br />
for One-Pot Synthesis <strong>of</strong> Polysubstituted OxazolesH.<br />
Jiang, H. Huang, H. Cao, C. Qi, Org. Lett.,<br />
2010, 12, 5561-5563.<br />
430
L. Joseph et al /International Journal <strong>of</strong> Pharmaceutical Sciences Letters 2014 Vol. 4 (4)| 417-431<br />
[29] Unexpected Synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2,4,5-Trisubstituted Oxazoles<br />
via a T<strong>and</strong>em Aza-Wittig/Michael/<br />
Isomerization Reaction <strong>of</strong> VinyliminophosphoraneH.<br />
Xie, D. Yuan, M.-W. Ding, J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77,<br />
2954-2958.<br />
[30] Methods For the Synthesis <strong>of</strong> Oxazolones : A Review,<br />
Suman Bala, Minaxi Saini <strong>and</strong> Sunil Kamboj.international<br />
journal <strong>of</strong> chem. Tech research;vol.3,no;3,pp1102-1118.<br />
[31] Cu(II) Catalyzed Imine C-H Functionalization Leading<br />
to Synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2,5-Substituted 1,3,4-Oxadiazoles<br />
Srimanta Guin, Tuhin Ghosh, Saroj Kumar Rout,<br />
Arghya Banerjee <strong>and</strong> Bhisma K. Patel* . , Org. Lett.,<br />
2011, 13, 5976-5979.<br />
[32] A Novel <strong>Strategy</strong> for the Construction <strong>of</strong> Azole Heterocycles<br />
via an Oxidative Desulfurization Approach<br />
Using Iodobenzene <strong>and</strong> Oxone Kavitkumar N. Patel,<br />
Nikhil C. Jadhav, Prashant B. Jagadhane, Vikas N.<br />
Telvekar*. Synlett, 2012, 23, 1970-1972.<br />
[33] Superior Reactivity <strong>of</strong> Thiosemicarbazides in the<br />
Synthesis <strong>of</strong> 2-Amino-1,3,4-oxadiazoles Sarah J.<br />
Dolman,* Francis Gosselin, Paul D. O'Shea <strong>and</strong> Ian<br />
W. Davies. , J. Org. Chem., 2006, 71, 9548-9551.<br />
[34] PTSA-ZnCl 2 : An Efficient Catalyst for the Synthesis<br />
<strong>of</strong> 1,2,4-Oxadiazoles from Amidoximes <strong>and</strong> Organic<br />
Nitriles.John Kallikat Augustine*, Vani Akabote,<br />
Shrivatsa Ganapati Hegde <strong>and</strong> Padma Alagarsamy, J.<br />
Org. Chem., 2009, 74, 5640-5643.<br />
[35] A Novel, One-Pot, Three-Component Synthesis <strong>of</strong><br />
1,2,4-Oxadiazoles under Microwave Irradiation<br />
<strong>and</strong> Solvent-Free Conditions.Mehdi Adib*,<br />
Mohammad Mahdavi, Niusha Mahmoodi,<br />
Hooshang Pirelahi, Hamid Reza Bijanzadeh,<br />
Synlett, 2006, 1765-1767.<br />
[36] ‘One-Pot’ Synthesis <strong>of</strong> Chiral N-Protected α-<br />
Amino Acid-Derived 1,2,4-Oxadiazoles Antonio<br />
L. Braga, Diogo S. Lüdtke, Eduardo E. Alberto,<br />
Luciano Dornelles*, Wolmar A. Severo Filho,<br />
Valeriano A. Corbellini, Daiane M. Rosa, Ricardo<br />
S. Schwab A. L. Braga, D. S. Lüdtke, E. E. Alberto,<br />
L. Dornelles, W. A. Severo Filho, V. A.<br />
Corbellini, D. M. Rosa, R. S. Schwab, Synthesis,<br />
2004, 1589-1594.<br />
[37] 1Highly Efficient Access to Strained Bicyclic Ketals<br />
via Gold-Catalyzed Cycloisomerization <strong>of</strong> Bishomopropargylic<br />
Diols, Sylvain Antoniotti , Emilie<br />
Genin , Veronique Michelet , And Jean-Pierre<br />
Genêt;J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127 (28), pp 9976<br />
–9977 .<br />
Cite this article as:<br />
Lincy Joseph, Mathew George <strong>and</strong> Surekha SR.<br />
<strong>Synthetic</strong> <strong>Strategy</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Therapeutic</strong> <strong>Utility</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Oxygen</strong><br />
<strong>and</strong> <strong>Nitrogen</strong> <strong>Containing</strong> <strong>Heterocyclic</strong> <strong>Compounds</strong>.<br />
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Lett. 2014 : 4: (2) 417-431<br />
Source <strong>of</strong> Support: Nil.<br />
Conflict <strong>of</strong> interest: None declared.<br />
431