An Introduction to Recursive Partitioning Using the ... - Mayo Clinic
An Introduction to Recursive Partitioning Using the ... - Mayo Clinic
An Introduction to Recursive Partitioning Using the ... - Mayo Clinic
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
24 patients revived / 144 not revived<br />
H<br />
HHHHHHHH<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
X 1 =1<br />
22 / 13<br />
H HHHH<br />
<br />
<br />
X 1 =2, 3 or 4<br />
2 / 131<br />
H HHHH<br />
<br />
<br />
X 2 =1<br />
20/5<br />
X 2 =2 or 3<br />
2/8<br />
X 3 =1<br />
2/31<br />
X 3 =2 or 3<br />
0 / 100<br />
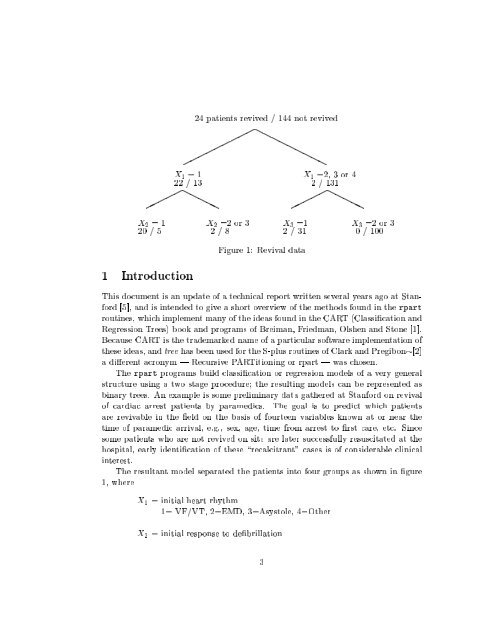
Figure 1: Revival data<br />
1 <strong>Introduction</strong><br />
This document is an update of a technical report written several years ago at Stanford<br />
[5], and is intended <strong>to</strong> give a short overview of <strong>the</strong> methods found in <strong>the</strong> rpart<br />
routines, which implement many of <strong>the</strong> ideas found in <strong>the</strong> CART (Classication and<br />
Regression Trees) book and programs of Breiman, Friedman, Olshen and S<strong>to</strong>ne [1].<br />
Because CART is <strong>the</strong> trademarked name of a particular software implementation of<br />
<strong>the</strong>se ideas, and tree has been used for <strong>the</strong> S-plus routines of Clark and Pregibon[2]<br />
a dierent acronym | <strong>Recursive</strong> PARTitioning or rpart | was chosen.<br />
The rpart programs build classication or regression models of a very general<br />
structure using a two stage procedure; <strong>the</strong> resulting models can be represented as<br />
binary trees. <strong>An</strong> example is some preliminary data ga<strong>the</strong>red at Stanford on revival<br />
of cardiac arrest patients by paramedics. The goal is <strong>to</strong> predict which patients<br />
are revivable in <strong>the</strong> eld on <strong>the</strong> basis of fourteen variables known at or near <strong>the</strong><br />
time of paramedic arrival, e.g., sex, age, time from arrest <strong>to</strong> rst care, etc. Since<br />
some patients who are not revived on site are later successfully resuscitated at <strong>the</strong><br />
hospital, early identication of <strong>the</strong>se \recalcitrant" cases is of considerable clinical<br />
interest.<br />
The resultant model separated <strong>the</strong> patients in<strong>to</strong> four groups as shown in gure<br />
1, where<br />
X 1 = initial heart rhythm<br />
1= VF/VT, 2=EMD, 3=Asys<strong>to</strong>le, 4=O<strong>the</strong>r<br />
X 2 = initial response <strong>to</strong> debrillation<br />
3