T Catalogue 2010
T Catalogue 2010
T Catalogue 2010
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Y<br />
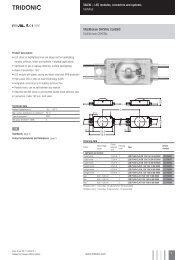
CIE Colour Space Chromaticity Diagram Assembly of LED Colour<br />
0.9<br />
0.8<br />
0.7<br />
0.6<br />
0.5<br />
0.4<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
0<br />
MacAdam ellipse<br />
yellow<br />
Planckian curve<br />
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4<br />
X<br />
MacAdam ellipse<br />
daylight white (6,500 K)<br />
0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8<br />
Yellow<br />
A B<br />
Daylight white<br />
A B<br />
Relative intensity (%)<br />
Relative intensity (%)<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
400<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
400<br />
440 480 520 560 600<br />
Wavelength (nm)<br />
A<br />
A<br />
440 480 520 560 600<br />
Wavelength (nm)<br />
B<br />
B<br />
640 680<br />
640 680<br />
Colours have a special influence on brand recognition. It is hardly<br />
surprising then that great importance is attached to this aspect.<br />
The most frequently used method for assessing colour rendering<br />
is the MacAdam ellipse. Colour differences can be detected or not,<br />
depending on the precision with which the colour quality is specified.<br />
The picture shows the colour locations of the MacAdam ellipse for<br />
the colours yellow and daylight white in the CIE chromaticity diagram<br />
of 1931. In addition to the colour location in the CIE chromaticity<br />
diagram, the intensity of the die and of the glob-top ( colour conversion<br />
layer ) is shown. The Planckian curve defines an area of the chromaticity<br />
diagram in which there is no discernible colour difference for the human<br />
eye in terms of white light. This phenomenon is used to define<br />
the phosphor to ensure the optimum white light impression.<br />
This means that T modules are available with<br />
defined colour temperatures of 3,000 K ( warm white ),<br />
4,200 K ( neutral white ) and 6,500 K ( daylight white )<br />
to provide light of impressive uniformity. New encapsulation<br />
materials with reduced yellowing are being<br />
used to achieve higher luminances and therefore<br />
outstanding luminous flux stability.<br />
The 140° wide-beam characteristic also helps to ensure<br />
homogeneous illumination with a small mounting depth<br />
and reduced number of light sources. In addition, the<br />
optimised thermal management of chip-on-board technology<br />
reduces the temperature of the light-emitting<br />
diodes and therefore improves their reliability.<br />
The wide range of high-intensity LED modules in white,<br />
colour or RGB underlines the power of innovation of<br />
Tridonic in this pioneering sector.<br />
T <strong>Catalogue</strong> <strong>2010</strong><br />
www.tridonic.com<br />
17