Tenses in English
Tenses in English
Tenses in English
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Tense <strong>in</strong> <strong>English</strong><br />
İngilizce dilbilgis<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong> en önemli öğesi zaman konusudur, çünkü diğer tüm konular ya direkt ya da dolaylı<br />
olarak zamanlarla ilişkilidir. Tense’ler bir cümledeki eylem<strong>in</strong> geçmişte mi, mevcut zamanda mı yoksa<br />
gelecekte mi yapılacağı hakkında bilgi verir. Tense kavramına ek olarak bir de Aspect vardır. Bu kavram<br />
ise cümledeki eylem<strong>in</strong> sürekli mi yoksa belirli bir süreç içeris<strong>in</strong>de mi yapıldığı hakkında bilgi verir.<br />
Tense kavramı cümlen<strong>in</strong> içeris<strong>in</strong>deki eylem<strong>in</strong> ne zaman yapıldığına işaret eder. Temel olarak 3 tane Tense<br />
vardır; Past, Present ve Future.<br />
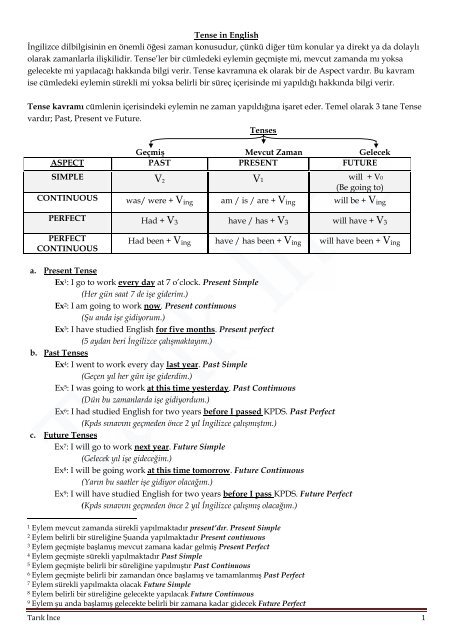
<strong>Tenses</strong><br />
Geçmiş Mevcut Zaman Gelecek<br />
ASPECT PAST PRESENT FUTURE<br />
SIMPLE V 2 V1 will + V0<br />
(Be go<strong>in</strong>g to)<br />
CONTINUOUS was/ were + V <strong>in</strong>g am / is / are + V <strong>in</strong>g will be + V <strong>in</strong>g<br />
PERFECT Had + V 3 have / has + V 3 will have + V 3<br />
PERFECT<br />
CONTINUOUS<br />
Had been + V <strong>in</strong>g have / has been + V <strong>in</strong>g will have been + V <strong>in</strong>g<br />
a. Present Tense<br />
Ex 1 : I go to work every day at 7 o’clock. Present Simple<br />
(Her gün saat 7 de işe giderim.)<br />
Ex 2 : I am go<strong>in</strong>g to work now. Present cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
(Şu anda işe gidiyorum.)<br />
Ex 3 : I have studied <strong>English</strong> for five months. Present perfect<br />
(5 aydan beri İngilizce çalışmaktayım.)<br />
b. Past <strong>Tenses</strong><br />
Ex 4 : I went to work every day last year. Past Simple<br />
(Geçen yıl her gün işe giderdim.)<br />
Ex 5 : I was go<strong>in</strong>g to work at this time yesterday. Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
(Dün bu zamanlarda işe gidiyordum.)<br />
Ex 6 : I had studied <strong>English</strong> for two years before I passed KPDS. Past Perfect<br />
(Kpds sınavını geçmeden önce 2 yıl İngilizce çalışmıştım.)<br />
c. Future <strong>Tenses</strong><br />
Ex 7 : I will go to work next year. Future Simple<br />
(Gelecek yıl işe gideceğim.)<br />
Ex 8 : I will be go<strong>in</strong>g work at this time tomorrow. Future Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
(Yarın bu saatler işe gidiyor olacağım.)<br />
Ex 9 : I will have studied <strong>English</strong> for two years before I pass KPDS. Future Perfect<br />
(Kpds sınavını geçmeden önce 2 yıl İngilizce çalışmış olacağım.)<br />
1 Eylem mevcut zamanda sürekli yapılmaktadır present’dır. Present Simple<br />
2 Eylem belirli bir süreliğ<strong>in</strong>e Şuanda yapılmaktadır Present cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
3 Eylem geçmişte başlamış mevcut zamana kadar gelmiş Present Perfect<br />
4 Eylem geçmişte sürekli yapılmaktadır Past Simple<br />
5 Eylem geçmişte belirli bir süreliğ<strong>in</strong>e yapılmıştır Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
6 Eylem geçmişte belirli bir zamandan önce başlamış ve tamamlanmış Past Perfect<br />
7 Eylem sürekli yapılmakta olacak Future Simple<br />
8 Eylem belirli bir süreliğ<strong>in</strong>e gelecekte yapılacak Future Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
9 Eylem şu anda başlamış gelecekte belirli bir zamana kadar gidecek Future Perfect<br />
Tarık İnce 1
Aspect kavramı ise cümlede yapılan eylem<strong>in</strong> süreklimi, kısa bir süreliğ<strong>in</strong>e mi yoksa iki zaman arasında mı<br />
yapıldığı hakkında bilgi verir.<br />
ASPECT<br />
Simple<br />
Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
Perfect simple<br />
Eylem sürekli, tamamlanmış<br />
Eylem belirli bir süreliğ<strong>in</strong>e, tamamlanmamış<br />
Eylem iki zaman aralığında, henüz tamamlanmış<br />
Perfect Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
Eylem iki zman aralığında, henüz tamamlanmamış<br />
a. Simple: cümle içeris<strong>in</strong>deki eylem<strong>in</strong> sürekli yapıldığını vurgular.<br />
Eylem geçmişte sürekli yapılmış ancak şimdi yapılmıyor ise: Past Simple,<br />
I slept at 10 o’clock when I was a child. 10<br />
Eylem hem geçmişte, hem şimdi, hem de gelecekte yapılacak ise; present simple,<br />
I sleep at 12 o’clock every day. 11<br />
Eylem gelecekte sürekli yapılacak ise; Future Simple.<br />
I will sleep at 11 o’clock when I start to work. 12<br />
b. Cont<strong>in</strong>uous: cümledeki eylem<strong>in</strong> belirli bir süreliğ<strong>in</strong>e yapıldığını vurgular.<br />
Eylem geçmişte belirli bir zaman aralığında yapılmış ise; Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous,<br />
I was watch<strong>in</strong>g TV from 8 to 10 yesterday. 13<br />
Eylem sadece iç<strong>in</strong>de bulunduğumuz zaman dilim<strong>in</strong>de yapılıyor ise; Present Cont<strong>in</strong>uous,<br />
I am watch<strong>in</strong>g tv now. 14<br />
Eylem gelecekte belirli bir zaman aralığında yapılacak ise; Future Cont<strong>in</strong>uous.<br />
I will be watch<strong>in</strong>g tv from 8 to 10 tomorrow. 15<br />
c. Perfect: cümledeki eylem<strong>in</strong> iki zaman aralığında yapıldığını ya da bir eylem<strong>in</strong> diğer eylemden önce<br />
yapıldığını vurgular.<br />
Eylem geçmişte başka bir eylemden daha önce yapılmış ise; Past Perfect<br />
I had f<strong>in</strong>ished my work before Ahmet came. 16<br />
Eylem geçmişte başlayıp günümüze kadar gelmiş ise; Present Perfect<br />
S<strong>in</strong>ce we met, she has worked <strong>in</strong> the same school. 17<br />
Eylem gelecekte belirli bir eylemden daha önce yapılacak ise; Future Perfect.<br />
I will have f<strong>in</strong>ished my homework by the time my mother comes. 18<br />
10 Çocukken her zaman saat 10 da uyurdum. Geçmişte Sürekli: Past Simple<br />
11 Her gün saat 12 de uyurum. Mevcut zamanda Sürekli: Present Simple<br />
12 Çalışmaya başladığımda saat 11 de uyuyacağım. Gelecekte Sürekli: Future Simple<br />
13 Dün saat 8 den 10’a kadar TV izliyordum. Geçmişte belirli bir süre: Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
14 Şu anda TV izliyorum. Mevcut Zamanda şimdi: Present Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
15 Yarın 8 den 10’a kadar TV izliyor olacağım. Gelecek Zamanda belirli bir süre: Future Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
16 Ahmet gelmeden önce ödevimi bitirmiştim. Geçmişte bir eylemden önce yapılmış: Past Perfect<br />
17 Tanıştığımızdan beri aynı okulda çalışmaktadır. Geçmişte başlamış bu güne kadar gelmiş: Present Perfect<br />
18 Annem geldiğ<strong>in</strong>de, ödevimi bitirmiş olacağım. Gelecekte bir eylemden önce tamamlanmış olacak: Future Perfect<br />
Tarık İnce 2
Yapı:<br />
Present Simple<br />
OLUMLU OLUMSUZ SORU<br />
Özne + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
V1<br />
Vs<br />
Özne + yardımcı NOT + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We do not V1<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
does not V1<br />
Yardımcı +Özne + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I<br />
You<br />
Do We V1<br />
They<br />
Does<br />
He<br />
She V1<br />
It<br />
Not: Simple tense’ler<strong>in</strong> olumlu cümleler<strong>in</strong>de yardımcı fiil kullanılmaz.<br />
Kullanım<br />
a. Habitual actions and Daily rout<strong>in</strong>es/activities<br />
Alışkanlıklarımızdan ve günlük rut<strong>in</strong>lerimizden bahsederken;<br />
Ex:<br />
I wash my hair every morn<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
I go to c<strong>in</strong>ema once a week.<br />
I always dr<strong>in</strong>k tea <strong>in</strong> the morn<strong>in</strong>gs.<br />
b. Natural truths and scientific knowledge<br />
Doğal gerçeklerde bilimsel bilgilerde kullanılır.<br />
The world revolves around the sun.<br />
Ankle <strong>in</strong>juries don’t recover quickly!<br />
Sıklık zarfları<br />
Always<br />
Usually<br />
Generally<br />
Often<br />
Most of the time<br />
Mostly<br />
Frequently<br />
Sometimes<br />
Occasionally<br />
Seldom<br />
Rarely<br />
Barely<br />
Hardly<br />
Scarcely<br />
Never<br />
Every year- day<br />
Each year<br />
Once a year<br />
Twice a week<br />
Three times a day<br />
c. Series of planned future actions of travel agents and time tables.<br />
Acenteler<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong> belirlemiş olduğu aktivitelerde ve varış-kalkış boardlarında.<br />
The first bus leaves at 6 o’clock.<br />
The group arrive the hotel at 9 o’clock and then they have breakfast at 9:30. They<br />
visit historical places and have lunch at 2. After lunch, they practice yoga with a<br />
famous yoga teacher.<br />
d. Newspaper headl<strong>in</strong>es and sports events.<br />
Gazete başlıklarında ve spor müsabakalarının canlı anlatımında<br />
President visits the families of the victims.<br />
Ilker Başbuğ denies the accusations.<br />
Commentator: Messi kicks the ball and scores a goal.<br />
e. Type 0 and Type 1 Conditional clauses<br />
Type 0 ve Type 1 Koşul cümleler<strong>in</strong>de<br />
If you heat the water, it boils.<br />
If you study hard, you will be successful.<br />
If you do not respect others, no one wants to talk with to you.<br />
f. Time clauses<br />
Zaman cümlecikler<strong>in</strong>de; özellikle Future tense’n<strong>in</strong> bulunduğu zaman<br />
cümleler<strong>in</strong>de bağlacın bulunduğu cümlede kullanılır.<br />
As soon as I receive your mail, I will answer it.<br />
He will do his homework before he goes out.<br />
Tarık İnce 3
Yapı:<br />
Present Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
OLUMLU OLUMSUZ SORU<br />
Özne +yardımcı fiil+ Yüklem<br />
I am V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
You<br />
We are V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She is V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
It<br />
Özne + yardımcı NOT +<br />
Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I am V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
You<br />
We are V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She is V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
It<br />
Yardımcı +Özne + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
Am<br />
I<br />
You<br />
Are We V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
They<br />
He<br />
Is She V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
It<br />
Kullanım<br />
a. Actions happen<strong>in</strong>g now<br />
Konuşma anında meydana gelen olaylardan bahsederken kullanılır;<br />
I am <strong>in</strong> the classroom and I am study<strong>in</strong>g <strong>English</strong> now.<br />
You are read<strong>in</strong>g a book at present.<br />
He is listen<strong>in</strong>g to music at the moment.<br />
People are dy<strong>in</strong>g hunger <strong>in</strong> Africa.<br />
Zaman zarfları<br />
Now<br />
Right now<br />
At the moment<br />
At present<br />
Currently<br />
For the time be<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Look! Listen!<br />
Nowadays<br />
These days<br />
Tomorrow<br />
More and more<br />
Comparatives<br />
Each year<br />
Once / twice a weekyear<br />
Three times a day<br />
b. Actions happen<strong>in</strong>g around now but not exactly at the time of speak<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Son zamanlarda geçici süreliğ<strong>in</strong>e meydana gelen olaylardan bahsederken;<br />
My father is redecorat<strong>in</strong>g our house nowadays.<br />
She is stay<strong>in</strong>g with her friends these days.<br />
We are work<strong>in</strong>g like a slave for the be<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
c. Actions planned for the future<br />
Gelecekte yapmayı planladığımız eylemlerden bahsederken;<br />
President is visit<strong>in</strong>g Syria tomorrow.<br />
My friends are fly<strong>in</strong>g to London next week.<br />
d. Chang<strong>in</strong>g actions<br />
Değişmekte olan eylemlerden bahsederken;<br />
The climate is gett<strong>in</strong>g warmer and warmer.<br />
Turkish economy is gett<strong>in</strong>g better day by day.<br />
Not:<br />
Involuntary actions such as senses; feel, look, smell, taste, hear, see etc<br />
I feel happy now.<br />
The class smells bad!<br />
The soup tastes cold.<br />
Verbs express<strong>in</strong>g emotions; like, hate, fear, love, respect, wish etc.<br />
I appreciate your struggle.<br />
Mental activities; agree, understand, assume, remember, expect, trust, suppose,<br />
realize, recognize etc. I agree with you on this matter.<br />
Possession verbs; have, belong, possess, own.<br />
Bu tür fiiller cont<strong>in</strong>uous tense’lerde kullanılmazlar. Bu tür herhangi bir çaba ya da<br />
enerji sarf etmeden oluşan eylemler konuşma anında dahi meydana gelmiş olsa<br />
Present Simple Tense ile kullanılırlar.<br />
Tarık İnce 4
Present Perfect Simple<br />
OLUMLU OLUMSUZ SORU<br />
Özne +yardımcı fiil + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We have V3<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She has V3<br />
It<br />
Özne + yardımcı NOT + Yüklem<br />
I Fiil<br />
You<br />
We have not V3<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She has not V3<br />
It<br />
Yardımcı +Özne + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I<br />
You<br />
Have We V3<br />
They<br />
He<br />
Has She V3<br />
It<br />
Kullanım<br />
a. Actions happened at an <strong>in</strong>def<strong>in</strong>ite time <strong>in</strong> the past , emphasis on the action<br />
Geçmişte olmuş ama zamanı belli olmayan eylemlerden bahsederken;<br />
Eğer eylem<strong>in</strong> ne zaman yapıldığı verilirse Past Simple kullanılır.<br />
I have washed my car.<br />
I washed my car <strong>in</strong> this morn<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
b.Action started <strong>in</strong> the past and its effects are still cont<strong>in</strong>u<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the present.<br />
Geçmişte olmuş ama etkisi şu ana gelen eylemlerden bahsederken;<br />
I have already eaten my lunch. I am full now.<br />
He has broken his leg. His leg is bandaged now.<br />
c. Actions done at a specific time <strong>in</strong> the past. How many times?<br />
Geçmişte şimdiye kadar yapmış olduğumuz eylemlerden bahsederken;<br />
Astronauts have gone to space three times s<strong>in</strong>ce 1990.<br />
d. Today, this morn<strong>in</strong>g/even<strong>in</strong>g etc. if these periods of time are not f<strong>in</strong>ished at<br />
the time of speak<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Eğer bahsedilen zaman dilimi sona ermemişse;<br />
She has gone to school <strong>in</strong> this morn<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Ilker Başbuğ denies the accusations.<br />
e. SUPERLATIVES & “THE FIRST, SECOND, LAST TIME”,<br />
It’s the best meal I’ve ever had<br />
It’s the first time he’s given a speech<br />
Present Perfect Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
OLUMLU OLUMSUZ SORU<br />
Özne +yardımcı fiil + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
have been V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Özne + yardımcı NOT + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We have not beenV<strong>in</strong>g<br />
They<br />
Yardımcı +Özne + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I<br />
You<br />
Have We been V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She been V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
It<br />
He<br />
has beenV<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Has<br />
She has not been V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
It<br />
Kullanım<br />
a. The present perfect cont<strong>in</strong>uous is very similar <strong>in</strong> mean<strong>in</strong>g to the present perfect<br />
simple tense. We use it to talk about actions started <strong>in</strong> the past, but is still<br />
happen<strong>in</strong>g. Duration of the action is emphasized.<br />
Anlam olarak Perfect Simple ile aralarında büyük bir fark yoktur. Geçmişte<br />
başlamış ve hala devam etmekte olan olaylardan bahsederken kullanılır.<br />
Eylem<strong>in</strong> yapıldığı süreç önemlidir.<br />
It has been ra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g for two days. It started two days ago and now it is still ra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Zaman zarfları<br />
Already – Just - Yet<br />
Ever<br />
For - S<strong>in</strong>ce<br />
Recently<br />
Lately<br />
Until now<br />
So far<br />
Up to now, hitherto,<br />
Over/For/ the last 2 weeks<br />
Twice, three times<br />
The best<br />
This is the first time<br />
Olumsuz cümlelerde still<br />
Tarık İnce 5
Yapı:<br />
Past Simple<br />
OLUMLU OLUMSUZ SORU<br />
Özne + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
V2<br />
Özne + yardımcı Fiil NOT + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They did not V1<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
Yardımcı Fiil+Özne + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
Did They V1<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
Kullanım<br />
a. Actions completed at a def<strong>in</strong>ite time <strong>in</strong> the past<br />
Geçmişte belirli bir zamanda yapılmış tamamlanmış olaylarda;<br />
I graduated from high school <strong>in</strong> 2003.<br />
Millions of people died <strong>in</strong> Hiroshima.<br />
Zaman zarfları<br />
Yesterday<br />
Last night<br />
Ago<br />
In 2011<br />
Before Christmas<br />
When I was a child<br />
That night / day / year<br />
Previously / Formerly<br />
Last week /month /year<br />
Ataturk<br />
b.Actions completed <strong>in</strong> the past chronically<br />
Geçmişte bir biri ardına olmuş olaylardan bahsederken;<br />
He opened the door and entered the room.<br />
We met at university and then we decided to marry.<br />
c. Habitual actions <strong>in</strong> the past “used to - would”<br />
Geçmişteki alışkanlıklarımızdan bahsederken;<br />
I used to smoke two packets of cigarette. But now I do not smoke.<br />
My father would go fish<strong>in</strong>g when we lived <strong>in</strong> our village. But now, he does not go.<br />
Tip: would state verb ile kullanılmaz.<br />
There used to be a library near the bank.<br />
There would be a library near the bank.<br />
d.Time clauses<br />
I. Cümle BAĞLAÇ CÜMLESİ III. CÜMLE<br />
____PAST ______________, When Simple Past, __________ PAST ______<br />
____PAST _____________, by the time Simple Past, _____PAST ______<br />
____ PAST ______________, S<strong>in</strong>ce Simple Past, _______ __ PAST _______<br />
____ PAST ______________, Until Simple Past, ______ ___PAST _______<br />
____ PAST ______________, Till Simple Past, ________ ___ PAST _______<br />
____ PAST ______________, as soon as Simple Past, ______ PAST _______<br />
____ PAST ______________, Once Simple Past, ___________PAST _______<br />
Not: İngilizce de zaman bağlaçlarının bulunduğu cümlelerde Tense Agreement<br />
“zaman uyuşması” olmak zorundadır. Yani zaman bağlaçlarıyla bağlanan<br />
cümlelerden biri PAST ise kendis<strong>in</strong>den sonar gelen cümleler de PAST olmalıdır.<br />
Cümleler<strong>in</strong> Past, Present ya da Future mu olacağını cümle içeris<strong>in</strong>deki zaman<br />
zarfları belirler.<br />
Cümleler<strong>in</strong> Simple, Cont<strong>in</strong>uous ya da Perfect mi olacağını ise cümleleri birbir<strong>in</strong>e<br />
bağlamak iç<strong>in</strong> kullanılan Zaman Bağlaçları belirler.<br />
When bağlacı iç<strong>in</strong>de kullanıldığı cümlen<strong>in</strong> Simple olmasını gerektirtir,<br />
kendis<strong>in</strong>den önceki ya da sonra ki cümle Simple, Cont<strong>in</strong>uous ve ya nadiren de<br />
Perfect olabilir.<br />
Tarık İnce 6
Extra notes!<br />
Past simple is not necessarily to be used <strong>in</strong> the past. We can use past simple to<br />
emphasize UNREAL situations or be more POLITE <strong>in</strong> present and future.<br />
Past simple sadece geçmişteki olayları vurgulamak iç<strong>in</strong> kullanılmaz. Aynı zamanda<br />
present ve future’da gerçek dışı durumları ve kibarlığı vurgulamak iç<strong>in</strong>de<br />
kullanılabilir.<br />
If type II<br />
If past Simple + would/could V0 = unreal present<br />
I wish<br />
If only<br />
As if<br />
As though<br />
It is time<br />
It is about time<br />
It is high time<br />
Would sooner<br />
Would rather<br />
Past Simple = unreal present<br />
It is time<br />
It is about time<br />
It is high time<br />
to V0<br />
+ SUBJECT Past Simple = unreal situation<br />
I. Unreal situations<br />
Gerçek dışı durumları vurgulamak iç<strong>in</strong>;<br />
a. If clauses type II<br />
If I studied hard, I would pass all my exams.<br />
(Eğer çok çalışmış olsam tüm sınavlarımı geçerdim.)<br />
If I won the lottery, I could buy a Q7.<br />
(eğer piyangoyu tutturmuş olsam bir Q7 alabilirdim)<br />
b. Wish clauses: keşke belirten cümleler;<br />
I wish I knew Arabic.<br />
(Keşke Arapça bilsem.)<br />
If only BJK won the cup this season.<br />
(keşke Beşiktaş bu sezon şampiyon olsa)<br />
He acts as if she were a little child.<br />
(küçük bir çocukmuş gibi davranıyor.)<br />
She talks as though everyth<strong>in</strong>g was my fault.<br />
(her şey<strong>in</strong> suçlusu benmişim gibi konuşuyor.)<br />
II. Preference<br />
Bir başkasının bir şeyi yapmasını istediğimizde;<br />
Ahmet drives to school every day, but I would rather he took a bus <strong>in</strong>stead.<br />
(Ahmet her gün okula arabayla gidiyor, onun otobüsle gitmes<strong>in</strong>i isterim)<br />
She is th<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g to give up writ<strong>in</strong>g a book, but I would sooner she did not.<br />
(kitap yazmayı bırakmayı düşünüyor, ben bırakmamasını isterim)<br />
Hurry up friends! It is time we went to home.<br />
(acele ed<strong>in</strong> arkadaşlar! Eve gitme vaktimiz geldi ve geçiyor.)<br />
Come on children! It is about time you started read<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
(evet çocuklar! Okumaya başlamak üzeres<strong>in</strong>iz.)<br />
Tarık İnce 7
Yapı:<br />
Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
OLUMLU OLUMSUZ SORU<br />
Özne +yardımcı fiil+ Yüklem<br />
Özne + yardımcı NOT + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
Yardımcı +Özne + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I<br />
You<br />
was/were V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
We were V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
was V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
I was not V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
You<br />
We were not V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She was not V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
It<br />
Was<br />
I<br />
You<br />
Were We V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
They<br />
Was<br />
He<br />
She V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
It<br />
Kullanım<br />
a. Actions ongo<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> a def<strong>in</strong>ite time <strong>in</strong> the past;<br />
Geçmişte belirli bir zaman aralığında meydana gelen olaylardan bahsederken;<br />
I was study<strong>in</strong>g lesson at this time yesterday.<br />
He was talk<strong>in</strong>g with his mother when I saw him.<br />
b. Time clauses<br />
Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous tek başına kullanılmaktan ziyade özellikle zaman bağlaçlarıyla<br />
birlikte kullanılır.<br />
I. Aynı süreç içeris<strong>in</strong>de devam eden iki uzun eylemden bahsederken;<br />
While Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous, Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
While I was read<strong>in</strong>g a book, they were listen<strong>in</strong>g to music.<br />
My mother was cook<strong>in</strong>g while my sister watch<strong>in</strong>g tv.<br />
II. Bir eylem belirli bir süreç içeris<strong>in</strong>de devam ederken başka bir kısa eylem<strong>in</strong><br />
araya girmesi;<br />
While Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous, Simple Past<br />
While Ali was study<strong>in</strong>g lesson, Kağan entered the room.<br />
Simple Past While Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
Fatih and Tuğba saw me while I was walk<strong>in</strong>g with her.<br />
Zaman zarfları<br />
This time yesterday Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous,__________________<br />
While Past Cont.____________________<br />
When Past Simple, Past cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
As Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous,_________________<br />
Just as Past Cont<strong>in</strong>uous_____________<br />
Tarık İnce 8
Past Perfect Simple<br />
OLUMLU OLUMSUZ SORU<br />
Özne +yardımcı fiil + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
HAD V3<br />
Özne + yardımcı NOT + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
had not<br />
V3<br />
Yardımcı +Özne + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
HAD<br />
V3<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
Kullanım<br />
a. An action happened at an <strong>in</strong>def<strong>in</strong>ite time <strong>in</strong> the past before another action<br />
- 2 actions happened <strong>in</strong> the past<br />
- The action that happened earlier is emphasized by Past Perfect.<br />
Geçmişte olmuş iki eylemden daha önce yapılmış olanını vurgulamak iç<strong>in</strong>;<br />
After<br />
Before<br />
By the time<br />
Until - Till<br />
Hardly……<br />
Scarcely … When<br />
Barely ……<br />
No sooner… Than<br />
I had eaten my lunch before he <strong>in</strong>vited me to restaurant. So, I didn’t go there.<br />
Extra notes!<br />
We can use past Perfect to emphasize UNREAL situations or be more POLITE <strong>in</strong><br />
the past.<br />
Past Perfect geçmişle gerçek dışı durumları ve kibarlığı vurgulamak iç<strong>in</strong>de<br />
kullanılabilir.<br />
Unreal situations<br />
Gerçek dışı durumları vurgulamak iç<strong>in</strong>;<br />
a. If clauses type II<br />
If I had studied hard, I would have passed all my exams.<br />
(Eğer çok çalışmış olsaydım tüm sınavlarımı geçmiş olurdum.)<br />
If I had won the lottery, I could have bought buy a Q7.<br />
(eğer piyangoyu tutturmuş olsaydım bir Q7 almış olabilirdim)<br />
b.Wish clauses: keşke belirten cümleler;<br />
I wish I had known Arabic.<br />
(Keşke Arapça bilmiş olsaydım.)<br />
If only BJK had won the cup last season.<br />
(keşke Beşiktaş geçen sezon şampiyon olsaydı)<br />
He acted as if he had been a little child.<br />
(küçük bir çocukmuş gibi davranıyordu.)<br />
She talked as though everyth<strong>in</strong>g had been my fault.<br />
(her şey<strong>in</strong> suçlusu benmişim gibi konuşuyor.)<br />
If type III<br />
If past Perfect + would/could Have V3 unreal past<br />
I wish<br />
If only Past Perfect = unreal Past<br />
As if<br />
As though<br />
Would sooner<br />
Would rather<br />
somebody Past Perfect unreal past<br />
III. Preference<br />
Bir başkasının bir şeyi yapmasını istediğimizde;<br />
Ahmet drove to school every day, but I would rather he had taken a bus.<br />
(Ahmet her gün okula arabayla gidiyordu, onun otobüsle gitmes<strong>in</strong>i isterdim)<br />
She was th<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g to give up writ<strong>in</strong>g a book, but I would sooner she had not.<br />
(kitap yazmayı bırakmayı düşünüyordu, ben bırakmamasını isterdim)<br />
Tarık İnce 9
Future Simple<br />
OLUMLU OLUMSUZ SORU<br />
Özne + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
Will<br />
V0<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
Özne + yardımcı Fiil NOT + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
Will<br />
Not V0<br />
Yardımcı Fiil+Özne + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
Will<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
Kullanım<br />
a. It is used for predictions and expectations about future<br />
Gelecek hakkında tahm<strong>in</strong> yapmak ya da beklentilerimizden bahsetderken<br />
I will go Istanbul.<br />
Perhaps she will w<strong>in</strong> the prize.,<br />
V0<br />
Zaman zarfları<br />
Tomorrow<br />
Geleceğe yönelik fiiller;<br />
Hope<br />
Expect<br />
Th<strong>in</strong>k<br />
Promise<br />
Be go<strong>in</strong>g to: planned actions <strong>in</strong> future.<br />
Gelecekte planlanmış eylemlerden bahsederken kullanılır.<br />
I am go<strong>in</strong>g to visit my sister tomorrow even<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Ali is go<strong>in</strong>g to play her last match tomorrow.<br />
Yas<strong>in</strong> is go<strong>in</strong>g to marry next Saturday.<br />
b. Type 1 Conditional clauses<br />
Bir<strong>in</strong>ci tip Koşul cümleler<strong>in</strong>de<br />
If you study hard, you will be successful.<br />
If you do not respect others, no one will want to talk with to you.<br />
c. Time clauses<br />
Zaman cümlecikler<strong>in</strong>de; özellikle present tense’n<strong>in</strong> bulunduğu zaman<br />
cümleler<strong>in</strong>de ana cümlede;<br />
As soon as I receive your mail, I will answer it.<br />
He will do his homework before he goes out.<br />
Future Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
OLUMLU OLUMSUZ SORU<br />
Özne + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
Will be V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
Özne + yardımcı NOT + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
Will Not be V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
Yardımcı +Özne + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
Will<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
be V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Zaman zarfları<br />
This time tomorrow<br />
Kullanım<br />
c. Actions ongo<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> a def<strong>in</strong>ite time <strong>in</strong> the future;<br />
Gelecekte belirli bir zaman dilim<strong>in</strong>de meydana gelecek olaylar iç<strong>in</strong>;<br />
He will be study<strong>in</strong>g lesson from 3 to 4 tomorrow.<br />
Kağan will be play<strong>in</strong>g with his toys at this time tomorrow.<br />
Tarık İnce 10
Future Perfect Simple<br />
OLUMLU OLUMSUZ SORU<br />
Özne + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
Will have V3<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
Özne + yardımcı Fiil NOT + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
Will Not have V3<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
Yardımcı Fiil+Özne + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
Will have V3<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
After<br />
Before<br />
By the time<br />
By now<br />
By 2015<br />
Until - Till<br />
Kullanım<br />
b. An action will happen at an <strong>in</strong>def<strong>in</strong>ite time <strong>in</strong> the future before another<br />
action.<br />
- 2 actions happened <strong>in</strong> the future<br />
- One action happens earlier than the other.<br />
Gelecekte olacak olan eylemden daha önce yapılacak olan eylemi vurgular;<br />
I will have eaten my lunch before he <strong>in</strong>vites me to restaurant.<br />
When Emre f<strong>in</strong>ishes this project, he will have worked on it for three years.<br />
Ali will have arrived London by now.<br />
Until you understand me, I will have died.<br />
Future Perfect Simple<br />
OLUMLU OLUMSUZ SORU<br />
Özne + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
ll have been V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Özne + yardımcı Fiil NOT + Yüklem<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
Will not have been V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
Kullanım<br />
a. An action <strong>in</strong> progress at some time <strong>in</strong> the future.<br />
I will have been study<strong>in</strong>g for two hours when you come.<br />
Kağan will have been walk<strong>in</strong>g by the end of this year.<br />
Yardımcı + Özne + Yüklem<br />
Fiil<br />
I<br />
You<br />
We<br />
They<br />
Will have been V<strong>in</strong>g<br />
He<br />
She<br />
It<br />
By the end of this month<br />
By 2020<br />
Tarık İnce 11
Tense Agreement <strong>in</strong> time clause “zaman uyuşması”<br />
Diğer tüm dillerdeki gibi İngilizce dilbilgis<strong>in</strong>de de her yapı belirli bir kural dâhil<strong>in</strong>de işler.<br />
Örneğ<strong>in</strong> bağımsız iki cümleyi birleştirmek iç<strong>in</strong> belirli kurallar vardır ve bu kurallar<br />
oluşturulan yeni cümlen<strong>in</strong> türüne göre değişiklik gösterir.<br />
Cümle türleri;<br />
a. Time clauses “Zaman cümlecikleri”<br />
b. Adjective clauses “Sıfat cümlecikleri”<br />
c. Noun clauses “İsim cümlecikleri”<br />
d. If clauses “koşul cümlecikleri”<br />
e. Conjunctions “Anlam ilişkis<strong>in</strong>e göre Cümle kullanılan bağlaçlar”<br />
Bizim bu ünitede işleyeceğimiz cümle türü Time Clauses “Zaman Cümlecikleri”dir. Zaman<br />
cümleciği oluşturulurken göz önünde bulundurmamız gereken en önemli kural<br />
Tense Agreement “Zaman Uyuşması”dır.<br />
Bu kurala göre aralarında zaman ilişkisi bulunan iki bağımsız cümleyi herhangi bir<br />
zaman bağlacı ile bağlayarak bağımsız tek bir cümle yapmak iç<strong>in</strong>; bu iki farklı<br />
cümle arasında hem Tense hem de Aspect uyumu olmalıdır.<br />
Tense uyumu: Zaman bağlacı ile bağlanan iki bağımsız cümle aynı Tense göre<br />
çekimlenmek zorundadır. Yani bir<strong>in</strong>ci cümle Past ise ik<strong>in</strong>ci cümle de Past olmalıdır.<br />
PAST<br />
PAST<br />
Kağan went out. I entered the room.<br />
PAST<br />
PAST<br />
Bağısız cümle + bağımsız cümle = Bağımsız Tek Cümle<br />
Sentence + sentence = Clause<br />
İki cümleyi bağlamak iç<strong>in</strong> kullanılan artı işareti “+” çok önemli bir imgedir.<br />
Time Clauses “Zaman Cümlecikleri” yaparken bu artı işaret<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong> yer<strong>in</strong>e “zaman bağlaçları”<br />
kullanılır ve bu BAĞLAÇLAR ise iki cümle arasındaki Aspect uyumunu belirler.<br />
Aspect uyumu: Zaman bağlacı ile bağlanan iki bağımsız cümle arasındaki öncelik,<br />
sonralık, aynı andalık ve biri devam ederken diğer<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong> o olayı kesmesi gibi özellikleri<br />
iç<strong>in</strong>de barındırır. Bu kural ise cümleleri birleştiren bağlaca göre şekillenir.<br />
Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
Zahide was cook<strong>in</strong>g. Halil was watch<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
Simple<br />
Kağan and Ali were play<strong>in</strong>g with their toys. Ali broke one of them.<br />
Perfect<br />
Simple<br />
Yas<strong>in</strong> had gone home. Özge came to school.<br />
Simple<br />
Simple<br />
Salih kicked the ball. Nurullah cached it.<br />
Future Simple<br />
Simple<br />
Esra will be an <strong>English</strong> teacher. She graduates from university.<br />
Cümleler arasındaki<br />
Tense –Aspect<br />
ilişkis<strong>in</strong>i kavramak<br />
iç<strong>in</strong> geliştirmiş<br />
olduğumuz<br />
Tarık’s Scale adlı<br />
kavram haritamız ile<br />
bu kuralı daha etkili<br />
bir şekilde<br />
açıklamaya<br />
çalışalım.<br />
Tarık İnce 12
Tarık’s Scale<br />
Tarık’ın terazisi İngilizce zamanlar konusunda çok işimize yarayabilecek bir<br />
kavram olarak kullanılabilir. Şimdi aşağıdaki şablondan yola çıkarak tense<br />
Agreement kuralını ayrıntılı bir şekilde <strong>in</strong>celeyelim.<br />
ASPECT<br />
I. Cümle Bağlaç Cümlesi III. Cümle<br />
Simple – Cont<strong>in</strong>uous,<br />
Simple – Cont<strong>in</strong>uous,<br />
Perfect – Simple,<br />
Perfect – Simple,<br />
Perfect – Simple,<br />
Perfect- Simple,<br />
Simple,<br />
While Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
When Simple<br />
Before Simple<br />
Until Simple<br />
Till Simple<br />
By the time Simple<br />
After Perfect<br />
, Simple – Cont<strong>in</strong>uous ,<br />
, Simple - Cont<strong>in</strong>uous<br />
,Perfect – Simple<br />
, Perfect – Simple<br />
, Perfect – Simple<br />
, Perfect- Simple<br />
, Simple<br />
TENSE<br />
PAST<br />
PAST<br />
TENSE<br />
Present - Future<br />
Present<br />
Time Clauses<br />
Yukarıdaki tablodan da anlaşılacağı gibi cümleler arasında Tense uyumu olmazsa<br />
olmazdır ancak Aspect uyumu cümle içeris<strong>in</strong>deki Bağlaçlar ile ilgilidir. Eğer cümle<br />
içeris<strong>in</strong>deki eylemler<strong>in</strong> yapılış süreci önemli ise Aspect uyumu devreye girer. Bu<br />
süreç “kısalık- uzunluk, öncelik- sonralık, devam ediyorluk” vurgulanmak isteniyor ise<br />
Aspect bağlaç ilişkisi önemlidir.<br />
While<br />
Just as<br />
As<br />
bağlaçları kullanılmış oldukları cümlelerde genelde Cont<strong>in</strong>uous Aspect,<br />
When<br />
Before<br />
Until/ till<br />
By the time<br />
As soon as<br />
bağlaçları kullanılmış oldukları cümlelerde Simple Aspect,<br />
After bağlacı kendis<strong>in</strong>den sonra Perfect Aspect ister.<br />
Not: Perfect Aspect iki cümle arasında öncelik sonralık olgusuna vurgu yapmak<br />
isteniyorsa kullanılır. Eğer cümleler arasında doğal bir öncelik sonralık varsa Perfect<br />
kullanmamıza gerek yoktur.<br />
Tarık İnce 13
Adverbial Clauses of Time “Zaman Bağlaçları”<br />
1. When<br />
Cümleler arasında kronolojik bir sıralama varsa;<br />
When kısa süren eylem, kısa ya da uzun eylem.<br />
When we talk about the shared customs of a society, we are referr<strong>in</strong>g to a “culture”.<br />
I’ll pass it on to you when I’ve f<strong>in</strong>ished it.<br />
The Hittite language died out when its civilization disappeared.<br />
When you pick up someth<strong>in</strong>g that is very hot you usually drop it immediately.<br />
Berlioz’s family supported him f<strong>in</strong>ancially when he was study<strong>in</strong>g at the university.<br />
Thermal pollution occurs when factories use water from rivers to cool their mach<strong>in</strong>e<br />
The body loses large amounts of iron when red blood cells are lost through bleed<strong>in</strong>g<br />
When you next see him, you promise him you full support at the next election.<br />
As soon as kısa süren eylem,<br />
kısa ya da uzun eylem.<br />
Space camps were set up as soon as space exploration began.<br />
As soon as tourism takes place, the environment is <strong>in</strong>evitably changed or modified.<br />
As soon as Israel declared its <strong>in</strong>dependence, it was <strong>in</strong>vaded by its neighbors.<br />
Once kısa süren eylem, kısa ya da uzun eylem<br />
We will get the latest football results once the news is over.<br />
Some people f<strong>in</strong>d it impossible to th<strong>in</strong>k for themselves once they have got used to<br />
hav<strong>in</strong>g an authority dictate to them.<br />
Once Gutenberg had <strong>in</strong>vented movable letters <strong>in</strong> the 15th century, it became<br />
possible to produce read<strong>in</strong>g material quickly, cheaply and <strong>in</strong> large quantities.<br />
Share: paylaşmak<br />
Refer: atfetmek<br />
Pass on: devretmek<br />
Die out: yok olmak<br />
Disappear: kaybolma<br />
Pick up: tutmak<br />
Immediately: aniden<br />
Support: desteklemek<br />
Pollution: kirlilik<br />
Occour: olmak<br />
Lose: kaybetmek<br />
Bleed<strong>in</strong>g: kanama<br />
Promise: söz vermek<br />
Election: seçim<br />
Set up: kurmak<br />
Exploration: <strong>in</strong>celeme<br />
Inevitably: kaçınılmaz<br />
Declare: bildirmek<br />
Invade: istila etmek<br />
Result: sonuç<br />
Dictate: emretmek<br />
Invent: icat etmek<br />
Movable: hareketli<br />
Produce: üretmek<br />
Quantity: miktar<br />
The moment kısa süren eylem, kısa ya da uzun eylem<br />
Most wild animals are so shy that they run away the moment they are disturbed.<br />
The moment I see her aga<strong>in</strong>, I will ask what is her name.<br />
Feti was fa<strong>in</strong>ted the moment he came across with ghost of his death uncle.<br />
Wild: vahşi,<br />
Disturb: rahatsız etmek<br />
Run away: kaçmak<br />
Fa<strong>in</strong>t: bayılamak<br />
The last time kısa süren eylem, kısa ya da uzun eylem<br />
Mr. Nihat was so critical the last time we talked.<br />
The last time I saw my cous<strong>in</strong> he was only five years old.<br />
Esra was prepar<strong>in</strong>g university exam the last time I saw her.<br />
Whenever kısa süren eylem, kısa ya da uzun eylem<br />
Whenever solar explosions take place, there occur serious environmental problems<br />
on Earth.<br />
Whenever I hear him speak, I am impressed by his ability to conv<strong>in</strong>ce.<br />
Folktales were simply stories retold whenever a group of people with the same<br />
<strong>in</strong>terests gathered.<br />
Whenever we pick up a newspaper or turn on the TV, we are likely to be<br />
bombarded with facts and figures on such subjects as pollution, unemployment and<br />
<strong>in</strong>flation.<br />
Critical: eleştirel<br />
Prepare: hazırlanmak<br />
Explosion: patlama<br />
Solar: güneşle ilgili<br />
Impress: etkilemek<br />
Conv<strong>in</strong>ce: ikna etmek<br />
Story: hikaye<br />
Interest: ilgi<br />
Gather: toplanmak<br />
Unemployment: işsizlik<br />
Inflation: enflasyon<br />
Tarık İnce 14
2. Cümleler arasında paralel bir devam ediyorluk varsa ya da biri devam ediyorken<br />
diğeri kesiyorsa;<br />
While uzun süren eylem, kısa ya da uzun eylem.<br />
While you are <strong>in</strong> Europe, it would be easy for me to come to see you.<br />
While students were listen<strong>in</strong>g to their teacher, someone burst <strong>in</strong>to the class.<br />
Astronauts had a lot to do while they were <strong>in</strong> space.<br />
While you are <strong>in</strong> Europe, it would be easy for me to come to see you.<br />
While still <strong>in</strong> her teens, she wrote a series of sketches and tales.<br />
Burst <strong>in</strong>to: aceleyle girmek<br />
Tale: masal<br />
Just as uzun süren eylem, kısa ya da uzun eylem.<br />
Mary phoned to give me the good news just as I was leav<strong>in</strong>g the house.<br />
Richard arrived at 1 o’clock just as we were start<strong>in</strong>g to have our lunch.<br />
Just as I was leav<strong>in</strong>g the house it began to ra<strong>in</strong> heavily.<br />
I learned what had happened just as the nurse was wheel<strong>in</strong>g him <strong>in</strong>to the operat<strong>in</strong>g room.<br />
Heavily: şiddetli<br />
As uzun süren eylem, kısa ya da uzun eylem.<br />
He speaks logically as he reads books.<br />
Kağan was mak<strong>in</strong>g noise as I was try<strong>in</strong>g to concentrate on my work.<br />
As turkey was try<strong>in</strong>g to adapt European union he had to give privilege.<br />
Logically: mantıklı<br />
Adapt: uyum sağlamak<br />
Privilage: imtiyaz<br />
3. İki cümle arasında öncelik- sonralık ilişkisi varsa;<br />
Before sonra yapılan eylem, önce yapılan eylem.<br />
You had better pay that bill before the phone is cut off.<br />
Before literature was written down, people had told stories.<br />
Before pr<strong>in</strong>ted books came <strong>in</strong>, books had to be copied by hand<br />
More satellites are necessary before they can achieve accurate forecast<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Titanic was labeled “uns<strong>in</strong>kable” before her disastrous voyage <strong>in</strong> April of 1912<br />
Ch<strong>in</strong>ese found America nearly three quarters of a century before Columbus did.<br />
Ali decides upon a method before he beg<strong>in</strong>s, and may even set up rules for himself.<br />
Pay: ödemek<br />
Cut off: kesmek<br />
Pr<strong>in</strong>t: basmak<br />
Satalite: uydu<br />
Achieve: başarmak<br />
Accurate: tam, doğru<br />
Forecast: tahm<strong>in</strong><br />
Label: etiketlemek<br />
Disastorous: felaket<br />
Until sonra yapılan eylem, önce yapılan eylem.<br />
Until air fares come down, people will cont<strong>in</strong>ue to go to New York by sea.<br />
Don’t tell anyone you are leav<strong>in</strong>g until you have found another job.<br />
I didn't know myself until two or three days ago.<br />
We have to postpone go<strong>in</strong>g on holiday until she completely gets over her illness.<br />
Until about 1920 very few of the half million galaxies <strong>in</strong> space had been explored.<br />
Fare: ücret<br />
Postpone: ertelemek<br />
Completely: tamamen<br />
Get over: iyileşmek<br />
till : ……e / a kadar<br />
Till sonra yapılan eylem, önce yapılan eylem.<br />
No one told me you were ill till I came here.<br />
We really don’t need to meet at 5 o’clock. The film doesn’t start till half-past.<br />
NOT: "Until/till" bağlaçlarında öncelik sonralık zaten belli olduğu iç<strong>in</strong> Past Perfect<br />
pek fazla kullanılmaz. Ancak eylem<strong>in</strong> tamamlandığını vurgulamak istiyorsak<br />
kullanılabilir.<br />
Tarık İnce 15
By the time sonra yapılan eylem, önce yapılan eylem.<br />
By the time Brahms began to compose his symphonies, this form had been well<br />
established.<br />
By the time the construction of a dam beg<strong>in</strong>s, eng<strong>in</strong>eers must have surveyed the<br />
geological features of the proposed area.<br />
By the time the boss arrived his secretary had f<strong>in</strong>ished typ<strong>in</strong>g the report.<br />
By the time the boat had arrived half the village was there to greet it.<br />
Establish: oluşturmak<br />
Construction: yapım<br />
Survey: araştırmak<br />
Feature: özellik<br />
Proposed: önerilen<br />
Greet: karşılamak<br />
After önce yapılan eylem, sonra yapılan eylem.<br />
Coal-fired steam power quickly lost its importance for <strong>in</strong>dustry after the advantages<br />
of fossil fuels became apparent.<br />
The outcome of his resignation will only be apparent after he has stopped work<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Canary Islands were subjected to colonization soon after they were discovered by<br />
the Genoese.<br />
Unlike w<strong>in</strong>e, whisky does not change after it has been bottled.<br />
After strong w<strong>in</strong>ds started forest fires, Athens was engulfed <strong>in</strong> thick smoke<br />
After the Persian conquest of Anatolia, many of the Malaysian philosophers fled to<br />
Sicily and southern Italy.<br />
Coal-fired: kömür yakmalı<br />
Steam: buhar<br />
Importance: ömem<br />
Apparent: görünür<br />
Outcome: çıktı<br />
Resignation: istifa<br />
Discovery: keşif<br />
Unlike: aks<strong>in</strong>e<br />
Engulf: iç<strong>in</strong>de kalmak<br />
Smoke: duman<br />
Conquest: fethetmek<br />
Fled to: kaçmak<br />
No sooner…….. Than<br />
No sooner had Tarık seen his friend than he got off the bus.<br />
Tarık had no sooner seen his friend than he got off the bus.<br />
Get off: <strong>in</strong>mek<br />
Hardly<br />
Scarcely ….. When<br />
Barely<br />
Yas<strong>in</strong> had hardly/scarcely/barely come to class when his teacher called him.<br />
Hardly /scarcely/barely had Yas<strong>in</strong> come to class when his teacher called him.<br />
"No sooner ... than" "hardly/barely/scarcely ... when", bu yapılar as soon as ile aynı<br />
anlamı verirler ve cümlen<strong>in</strong> başında yer alırlarsa cümleyi devrik yaparlar.<br />
Tarık İnce 16