Photosynthesis Details - Lake Central High School
Photosynthesis Details - Lake Central High School
Photosynthesis Details - Lake Central High School
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
5.2 Notes…continued<br />
• Analyze the function of electron transport chains in<br />
the second stage of photosynthesis.<br />
• Relate the Calvin cycle to carbon dioxide fixation in<br />
the third stage of photosynthesis.<br />
• Identify three environmental factors that affect the<br />
rate of photosynthesis.<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
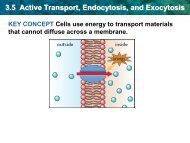
Stage Two: Conversion of Light Energy<br />
• The absorbed light energy in electrons is used to<br />
make three different products…<br />
– __________ ATP<br />
– __________ NADPH<br />
O 2<br />
– __________<br />
• Since these substances need light to be produced,<br />
stage two is referred to as the ____________ light<br />
_________________ dependent reactions<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
• First an excited electron _______ jumps to a nearby<br />
molecule in the thylakoid membrane.<br />
• Then the electron is passed down a series of<br />
molecules along the membrane called an<br />
_____________ electron _______________<br />
transport<br />
____________ chain (ETC)<br />
• As electrons move down the molecules, they<br />
release ____________…<br />
energy<br />
– Similar to how a bucket brigade loses water<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
Electron Transport Chains of <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
The first<br />
electron<br />
transport chain<br />
lies between<br />
the two green<br />
___________ clusters<br />
of pigment<br />
molecules<br />
• The first pigment cluster is called _________________<br />
Photosystem II<br />
(PSII) because it was the second one discovered<br />
– It absorbs energy and releases an excited<br />
____________ electron<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
The excited<br />
electron jumps<br />
to the next<br />
molecule in the<br />
electron<br />
transport<br />
chain,<br />
releasing<br />
____________ energy<br />
• This energy is used by a membrane pump that pumps<br />
___________________ hydrogen ions _______ into the thylakoid<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
This creates a<br />
__________ build<br />
____ up of<br />
hydrogen ions<br />
inside the<br />
thylakoid<br />
This concentration gradient causes hydrogen ions to<br />
________________ diffuse through a transport protein _____ out of<br />
the thylakoid into the ___________ stroma<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
The flow of<br />
hydrogen ions<br />
causes the<br />
transport<br />
protein to<br />
__________ spin<br />
• The spinning action creates a __________ force that binds a<br />
phosphate group to ADP, producing _______ ATP<br />
• Since this transport protein produces ATP, it is called<br />
_____________________<br />
ATP synthetase<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
The energy<br />
released from<br />
the electrons<br />
also allows an<br />
enzyme to split<br />
a ______ water<br />
molecule into<br />
hydrogen atoms<br />
and the gas ___<br />
O 2<br />
• Chlorophyll molecules replace their excited electrons<br />
by taking an electron from hydrogen atoms, leaving<br />
them as _______. ions This allows light energy to excite<br />
___________ another electron in PSII<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
The second<br />
cluster of<br />
pigments is called<br />
______________<br />
Photosystem I<br />
(PSI) because it<br />
was the first one<br />
discovered<br />
• The original excited electron from ______ PSII is<br />
eventually passed to PSI, where chlorophyll<br />
molecules will absorb light energy and __________ excite<br />
the electron again<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
These excited<br />
electrons move<br />
down a ________ second<br />
electron transport<br />
chain, releasing<br />
energy<br />
• The released energy is used to bind a ___________<br />
hydrogen<br />
ion to NADP + , which forms ___________ NADPH<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
• NADPH is an electron ___________ carrier that provides the<br />
high-energy electrons needed to make ___________ sugar<br />
in the third stage of photosynthesis<br />
• Review…<br />
– What three products are made during the lightdependent<br />
reactions?<br />
ATP<br />
O 2<br />
NADPH<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
Stage Three: Formation of Organic Compounds<br />
• In the third (final) stage of photosynthesis, carbon<br />
atoms from _________________ carbon dioxide in the atmosphere<br />
are used to make organic compounds, such as<br />
______________, glucose in which chemical energy is stored.<br />
• The transfer of carbon dioxide to organic compounds<br />
is called carbon dioxide _______________<br />
fixation<br />
• These reactions do not require light energy, so<br />
stage three is referred to as the light<br />
____________________or independent<br />
_____ dark reactions<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
Sugars are<br />
formed in the<br />
______________<br />
Calvin<br />
_________, cycle<br />
which is named<br />
after __________ Melvin<br />
__________, Calvin the<br />
scientist who<br />
discovered it<br />
***Occurs in the<br />
____________ stroma<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
First ____ 3 CO 2<br />
molecules are<br />
added to ____ 3<br />
5-carbon<br />
compounds<br />
called<br />
____________<br />
ribulose<br />
____________<br />
biphosphate<br />
(_______) RuBP<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
These form 3<br />
unstable<br />
___-carbon 6<br />
compounds<br />
that<br />
immediately<br />
split into ____ 6<br />
3-carbon<br />
compounds<br />
called<br />
phosphoglyceric<br />
____________<br />
____________<br />
acid (PGA)<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
Next, the ATP<br />
and NADPH<br />
made during<br />
the _________ light<br />
reactions<br />
supply<br />
_______ energy for<br />
___ 6 3-carbon<br />
sugars, called<br />
phosphoglycer-<br />
____________<br />
aldehyde ___________, (PGAL)<br />
to be made<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
One PGAL is<br />
used by the<br />
plant to<br />
synthesize<br />
___________, sugars<br />
while the<br />
others<br />
regenerate<br />
RuBP, which<br />
began the<br />
cycle<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
As shown in<br />
the diagram,<br />
RuBP needs<br />
another<br />
phosphate<br />
before the<br />
cycle can begin<br />
again… where<br />
does it come<br />
from?<br />
ATP<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
What organic<br />
compound does a<br />
plant need to<br />
make for itself?<br />
glucose<br />
What is its<br />
formula?<br />
C 6 H 12 O 6<br />
How many carbon<br />
atoms does it<br />
contain?<br />
6<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
How many<br />
carbons are in<br />
the initial sugar<br />
produced?<br />
3<br />
So while this<br />
diagram shows<br />
3 CO 2<br />
molecules,<br />
photosynthesis<br />
really needs<br />
_____ 6<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
• Fill in the coefficients in the equation for<br />
photosynthesis below…<br />
__ 6 CO 2 + __ 6<br />
light<br />
H 2 0 ------------ > C 6 H 12 0 6 + __ 6 O 2<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5<br />
Section 2 <strong>Photosynthesis</strong><br />
• <strong>Photosynthesis</strong> is directly affected by various<br />
environmental factors such as…<br />
– _____________________<br />
Light intensity<br />
– _____________________<br />
CO 2 concentration<br />
– _____________________<br />
temperature<br />
• The rate of photosynthesis will increase with light<br />
intensity and CO 2 concentration, until all of the<br />
_____________ pigments are being used or the _________ Calvin<br />
cycle cannot process CO 2 any faster<br />
• Because photosynthesis involves ___________, enzymes it is<br />
most ___________ efficient within a specific temperature range<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Question 1<br />
• In what part of the chloroplast are the electron<br />
transport chains located?<br />
In the thylakoid membranes<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Question 2<br />
• Which of the following is not a product of the lightdependent<br />
reactions?<br />
A. O 2<br />
B. glucose<br />
C. ATP<br />
D. NADPH<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Question 3<br />
• Which molecule is necessary to start the Calvin<br />
cycle?<br />
A. O 2<br />
B. glucose<br />
C. CO 2<br />
D. ADP<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Question 4<br />
• What two other names are used to describe the<br />
Calvin cycle?<br />
Light independent reactions<br />
Dark reactions<br />
Chapter menu<br />
Resources<br />
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.