Mitosis and Meiosis Test Review - WhippleHill
Mitosis and Meiosis Test Review - WhippleHill
Mitosis and Meiosis Test Review - WhippleHill
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Mitosis</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Meiosis</strong> <strong>Test</strong> <strong>Review</strong><br />
Vocabulary (Nerdy Words)<br />
Cell Cycle Chromatid Centromere<br />
Chromosome Asexual Reproduction Prophase<br />
Metaphase<br />
Interphase<br />
Anaphase<br />
Sexual Reproduction<br />
Telophase<br />
Synthesis<br />
Egg Fertilization Zygote<br />
Diploid Cell Haploid Cell <strong>Meiosis</strong><br />
Sex Cells Cytokinesis <strong>Mitosis</strong><br />
Gap 1 Gap 2<br />
Important Concepts<br />
Section One (<strong>Mitosis</strong>)<br />
1. What are the phases of the cell cycle?<br />
2. What are the three stages of interphase? What happens to the DNA during<br />
interphase? Why must this happen to the DNA?<br />
3. What part of the cell cycle do cells spend the most time in? Why?<br />
4. What are the four steps of <strong>Mitosis</strong>?<br />
5. What does a cell look like during each step of <strong>Mitosis</strong>?<br />
6. What important events are going on during each step of <strong>Mitosis</strong>?<br />
7. What is cytokinesis?<br />
8. Are there any differences between the parent cell’s DNA <strong>and</strong> the two new cells<br />
produced DNA (produced by <strong>Mitosis</strong>)?<br />
9. Why is <strong>Mitosis</strong> important?<br />
10. Why wouldn’t a prokaryote go through <strong>Mitosis</strong>?<br />
11. What is meant by asexual reproduction? What type of offspring result from<br />
asexual reproduction? Genetically, are they similar or different from the parent?<br />
12. What is budding? What is regeneration?<br />
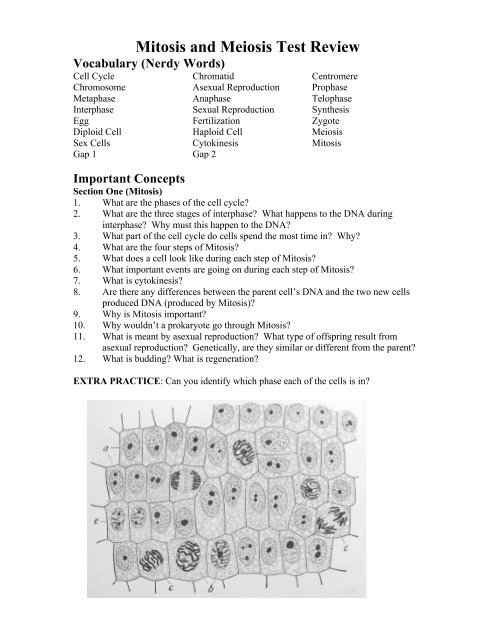
EXTRA PRACTICE: Can you identify which phase each of the cells is in?
Section II (<strong>Meiosis</strong>)<br />
1. What is sexual reproduction <strong>and</strong> how is it different from asexual reproduction?<br />
2. What are male <strong>and</strong> female human sex cells called?<br />
3. What is the difference between a somatic cell <strong>and</strong> a sex cell?<br />
4. What is the difference between a diploid cell <strong>and</strong> a haploid cell?<br />
5. What percent of an organism’s hereditary material would a diploid cell have?<br />
What about a haploid cell?<br />
6. What is the process of meiosis?<br />
7. Why is meiosis necessary?<br />
8. What type of cell is produced when two haploid cells (such as sperm <strong>and</strong> egg)<br />
combine?<br />
9. How many sex cells are produced after <strong>Meiosis</strong> I <strong>and</strong> <strong>Meiosis</strong> II?<br />
10. A human body cell has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs), how many chromosomes<br />
would an egg cell have?<br />
11. A cat has 38 chromosomes, a gorilla 48, a dog 78, <strong>and</strong> a rabbit 44. Why are all of<br />
these numbers even?<br />
12. Which is more similar to <strong>Mitosis</strong>, <strong>Meiosis</strong> I or II?<br />
13. Can you order the 8 steps of <strong>Meiosis</strong> I <strong>and</strong> II by sight?<br />
14. What does the cell look like during each stage of <strong>Meiosis</strong> I <strong>and</strong> II?