NAME:ANSWER KEY GES 241 Introduction to Meteorology Quiz #1 ...
NAME:ANSWER KEY GES 241 Introduction to Meteorology Quiz #1 ...
NAME:ANSWER KEY GES 241 Introduction to Meteorology Quiz #1 ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>NAME</strong>:<strong>ANSWER</strong> <strong>KEY</strong><br />
<strong>GES</strong> <strong>241</strong> <strong>Introduction</strong> <strong>to</strong> <strong>Meteorology</strong><br />
<strong>Quiz</strong> <strong>#1</strong> (35 pts)<br />
1. (4 pts) Write down 2 greenhouse gases. (1 pt for the name, 1 pt for the chemical formula)<br />
N 2 O - Nitrous Oxide<br />
CH 4 - Methane<br />
H 2 O - Dihydrodgen Monoxide<br />
CO 2 - Carbon Dioxide<br />
O 3 - Ozone<br />
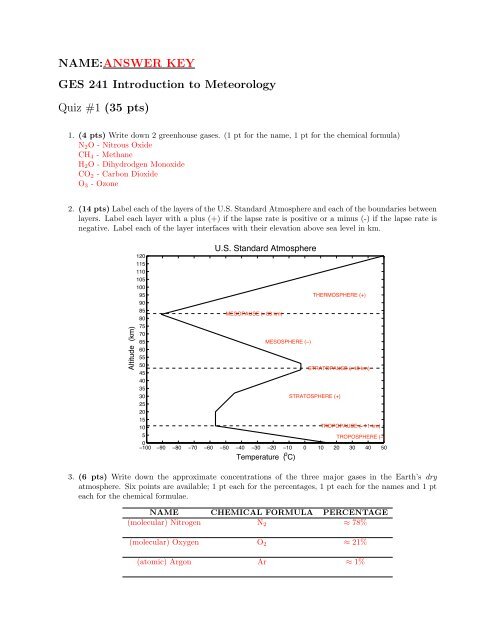
2. (14 pts) Label each of the layers of the U.S. Standard Atmosphere and each of the boundaries between<br />
layers. Label each layer with a plus (+) if the lapse rate is positive or a minus (-) if the lapse rate is<br />
negative. Label each of the layer interfaces with their elevation above sea level in km.<br />
Altitude (km)<br />
U.S. Standard Atmosphere<br />
120<br />
115<br />
110<br />
105<br />
100<br />
95<br />
THERMOSPHERE (+)<br />
90<br />
85<br />
80<br />
MESOPAUSE (! 83 km)<br />
75<br />
70<br />
65<br />
MESOSPHERE (−)<br />
60<br />
55<br />
50<br />
45<br />
STRATOPAUSE (! 48 km)<br />
40<br />
35<br />
30<br />
STRATOSPHERE (+)<br />
25<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
TROPOPAUSE (! 11 km)<br />
5<br />
TROPOSPHERE (−)<br />
0<br />
−100 −90 −80 −70 −60 −50 −40 −30 −20 −10 0 10 20 30 40 50<br />
Temperature ( o C)<br />
3. (6 pts) Write down the approximate concentrations of the three major gases in the Earth’s dry<br />
atmosphere. Six points are available; 1 pt each for the percentages, 1 pt each for the names and 1 pt<br />
each for the chemical formulae.<br />
<strong>NAME</strong> CHEMICAL FORMULA PERCENTAGE<br />
(molecular) Nitrogen N 2 ≈ 78%<br />
(molecular) Oxygen O 2 ≈ 21%<br />
(a<strong>to</strong>mic) Argon Ar ≈ 1%
4. (6 pts) Write down three ways heat can be transfered in the atmosphere.<br />
conduction<br />
convection<br />
radiation<br />
5. (1 pt) The Stefan-Boltzmann radiation law states<br />
(a) E = σT 4<br />
(b) λ max = 2890<br />
T<br />
(c) “the hotter the object is, the shorter-wave the radiation it emits”<br />
(d) “the hotter the object is, the more it radiates”<br />
(e) (a) and (c)<br />
(f) (a) and (d)<br />
6. (1 pt) Wien’s radiation law states<br />
(a) E = σT 4<br />
(b) λ max = 2890<br />
T<br />
(c) “the hotter the object is, the shorter-wave the radiation it emits”<br />
(d) “the hotter the object is, the more it radiates”<br />
(e) (a) and (c)<br />
(f) (b) and (c)<br />
7. (1 pt) If the flux of Solar radiation impinging on the planet (insolation) were <strong>to</strong> suddenly decrease,<br />
the temperature would drop until<br />
(a) the outgoing longwave radiation again equals insolation.<br />
(b) glaciers form at low latitudes.<br />
(c) all atmospheric water vapor condenses.<br />
(d) the amount of CO 2 levels off.<br />
8. (1 pt) As you ascend through the atmosphere the pressure drops. The rate of pressure decrease is<br />
about<br />
(a) half of the starting pressure for each 11.2 m of ascent.<br />
(b) half of the starting pressure for each 5.6 km of ascent.<br />
(c) 500 mb for each 11.2 km of ascent.<br />
(d) 250 mb for each 5.6 km of ascent.<br />
9. (1 pt) The average kinetic energy of the a<strong>to</strong>ms or molecules in a substance is called the<br />
(a) pressure<br />
(b) temperature<br />
(c) density<br />
(d) chemical potential