Depo-Provera: comparison with some other ... - epgonline.org
Depo-Provera: comparison with some other ... - epgonline.org
Depo-Provera: comparison with some other ... - epgonline.org
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong>: <strong>comparison</strong> <strong>with</strong> <strong>some</strong> <strong>other</strong><br />
contraceptive methods<br />
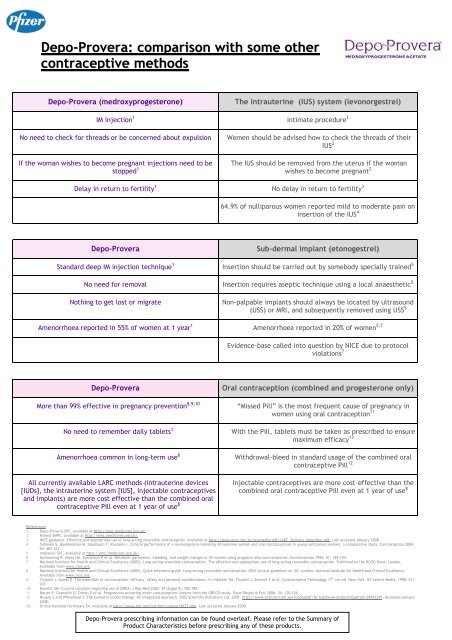
<strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong> (medroxyprogesterone)<br />
The Intrauterine (IUS) system (levon<strong>org</strong>estrel)<br />
IM injection 1 Intimate procedure 2<br />
No need to check for threads or be concerned about expulsion<br />
If the woman wishes to become pregnant injections need to be<br />
stopped 1<br />
Women should be advised how to check the threads of their<br />
IUS 2<br />
The IUS should be removed from the uterus if the woman<br />
wishes to become pregnant 2<br />
Delay in return to fertility 1 No delay in return to fertility 3<br />
64.9% of nulliparous women reported mild to moderate pain on<br />
insertion of the IUS 4<br />
<strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong><br />
Sub-dermal implant (etonogestrel)<br />
Standard deep IM injection technique 1 Insertion should be carried out by <strong>some</strong>body specially trained 5<br />
No need for removal Insertion requires aseptic technique using a local anaesthetic 5<br />
Nothing to get lost or migrate<br />
Non-palpable implants should always be located by ultrasound<br />
(USS) or MRI, and subsequently removed using USS 5<br />
Amenorrhoea reported in 55% of women at 1 year 1 Amenorrhoea reported in 20% of women 5,7<br />
Evidence-base called into question by NICE due to protocol<br />
violations 7<br />
<strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong><br />
More than 99% effective in pregnancy prevention 8,9,10<br />
No need to remember daily tablets 1<br />
Amenorrhoea common in long-term use 6<br />
All currently available LARC methods (intrauterine devices<br />
[IUDs], the intrauterine system [IUS], injectable contraceptives<br />
and implants) are more cost effective than the combined oral<br />
contraceptive Pill even at 1 year of use 8<br />
Oral contraception (combined and progesterone only)<br />
“Missed Pill” is the most frequent cause of pregnancy in<br />
women using oral contraception 11<br />
With the Pill, tablets must be taken as prescribed to ensure<br />
maximum efficacy 13<br />
Withdrawal-bleed in standard usage of the combined oral<br />
contraceptive Pill 12<br />
Injectable contraceptives are more cost-effective than the<br />
combined oral contraceptive Pill even at 1 year of use 8<br />
References:<br />
1. <strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong> SPC, available at http://emc.medicines.<strong>org</strong>.uk/.<br />
2. Mirena SMPC, available at http://emc.medicines.<strong>org</strong>.uk/.<br />
3. NICE guidance. Effective and appropriate use of long-acting reversible contraception. Available at http://www.nice.<strong>org</strong>.uk/nicemedia/pdf/LARC_2ndcons_algorithm.pdf. Last accessed January 2008.<br />
4. Suhonen S, Haukkkamaa M, Jakobsson T, Rauramo I. Clinical performance of a levon<strong>org</strong>estrel-releasing intrauterine system and oral contraceptives in young nulliparous women: a comparative study. Contraception 2004;<br />
69: 407-412.<br />
5. Implanon SPC, available at http://emc.medicines.<strong>org</strong>.uk/.<br />
6. Mainwaring R, Hales HA, Stevenson K et al. Metabolic parameter, bleeding, and weight changes in US women using progestin only contraceptives. Contraception 1995; 51: 149-153.<br />
7. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (2005). Long-acting reversible contraception. The effective and appropriate use of long-acting reversible contraception. Published by the RCOG Press, London.<br />
Available from www.nice.<strong>org</strong>.<br />
8. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (2005). Quick reference guide. Long-acting reversible contraception. NICE clinical guideline no. 30. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence.<br />
Available from www.nice.<strong>org</strong>.<br />
9. Trussell J, Kowal D. The essentials of contraception: efficacy, safety and personal considerations. In: Hatcher RA, Trussell J, Stewart F et al. Contraceptive Technology 17 th rev ed. New York, NY Ardent Media; 1998: 211-<br />
247.<br />
10. Kaunitz AM. Current concepts regarding use of DMPA. J Rep Med 2002: 47 (Suppl 9); 785-789.<br />
11. Barjot P, Graesslin O, Cohen D et al. Pregnancies occurring under contraception: lessons from the GRECO study. Gyne Obstet & Fert 2006: 34; 120-126.<br />
12. Nussey S and Whitehead S. The Gonad in Endocrinology: An Integrated Approach. BIOS Scientific Publishers Ltd, 2001. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=endocrin&partid=29#A1245. Accessed January<br />
2008.<br />
13. British National Formulary 54. Available at http://www.bnf.<strong>org</strong>/bnf/bnf/current/4573.htm. Last accessed January 2008.<br />
<strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong> prescribing information can be found overleaf. Please refer to the Summary of<br />
Product Characteristics before prescribing any of these products.
Prescribing information:<br />
<strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong> 150 mg/ml (medroxyprogesterone acetate)<br />
ABBREVIATED PRESCRIBING INFORMATION (UK)<br />
(ALL CLAIMS)<br />
Please refer to the SmPC before prescribing <strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong> 150 mg/ml.<br />
Presentation: 1 ml Disposable syringe, containing 150 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate in a Sterile suspension for injection.<br />
Indication: Long-term contraceptive agent, in women who have been counselled concerning the likelihood of menstrual disturbance,<br />
potential delay in return to full fertility and risks of bone mineral density losses. Short-term contraception for the following (i) For<br />
partners of men undergoing vasectomy, until the vasectomy becomes effective, (ii) In women who are being immunised against rubella<br />
(iii) In women awaiting sterilisation. Dosage: First injection: 150mg intramuscular injection during the first 5 days of a normal<br />
menstrual cycle. Post Partum: Within 5 days post partum (if not breast-feeding). Women in puerperium can experience prolonged and<br />
heavy bleeding, therefore caution is required, and women should be advised accordingly. If the puerperal woman will breast-feed, the<br />
initial injection should be no sooner than 6 weeks post partum. Further doses: These should be given at 12 week intervals, however as<br />
long as the injection is given no later than 5 days after the 12 week interval, no additional contraception measures are required. For<br />
partners of men undergoing vasectomy, a second injection 12 weeks after the first may be necessary in a small proportion of patients<br />
where the partner's sperm count has not fallen to zero. If the dose repeat interval is greater than 89 days (12 weeks and 5 days) for any<br />
reason, then pregnancy should be excluded before the next injection is given and the patient should use additional contraceptive<br />
measures (e.g. barrier) for fourteen days after this subsequent injection. Elderly: Not appropriate. Children: <strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong> is not<br />
indicated before menarche (Refer to the Summary of Product Characteristics section 4.2 Posology and method of administration) Data<br />
in adolescent females (12-18 years) is available (see section 4.4 Special Warnings and Special Precautions for Use). Other than<br />
concerns about loss of BMD, the safety and effectiveness of <strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong> is expected to be the same for adolescents after menarche<br />
and adult females. Administration: By deep intramuscular injection. The sterile aqueous suspension should be vigorously shaken just<br />
before use to ensure the dose being given represents a uniform suspension. Contraindications: Known sensitivity to<br />
medroxyprogesterone acetate or any of its ingredients. Pregnancy, either for diagnosis or therapy. Known or suspected hormonedependent<br />
malignancy of breast or genital <strong>org</strong>ans. Patients <strong>with</strong> abnormal uterine bleeding, whether administered alone or in<br />
combination <strong>with</strong> oestrogen until a definite diagnosis has been established and the possibility of genital tract malignancy eliminated.<br />
Special Warnings and Precautions: Loss of bone mineral density, increasing <strong>with</strong> length of use. A risk: benefit assessment should be<br />
performed, especially in young or adolescent women and if use is anticipated to be long term (ie 2 years or longer). In adolescents and<br />
women <strong>with</strong> significant lifestyle and/or medical risk factors for osteoporosis, <strong>other</strong> methods of contraception should be considered<br />
before using <strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong>. Women should be counselled that there is a potential for delay in return to full fertility following use of<br />
the method, regardless of the duration of use. Disruption of normal menstrual cycle. Small increase in the risk of being diagnosed <strong>with</strong><br />
breast cancer, compared <strong>with</strong> non-users. Considered among the risk factors for osteoporosis. Weight Gain. Very few reports of<br />
anaphylactoid reactions. Pulmonary embolism, cerebrovascular disease or retinal thrombosis. Rare cases of thrombo-embolism have<br />
been reported. History of endogenous depression, including premenstrual-type depression, should be carefully monitored. Migraine or<br />
unusually severe headaches, acute visual disturbances of any kind, pathological changes in liver function and hormone levels. Patients<br />
<strong>with</strong> thromboembolic or coronary vascular disease should be carefully evaluated before treatment. Decreased glucose tolerance.<br />
Diabetic patients should be carefully monitored while receiving therapy. Increased and decreased in total cholesterol, triglycerides and<br />
low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Associated <strong>with</strong> a 15-20% reduction in serum high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol<br />
levels. Potential for an increased risk of coronary disease should be considered prior to use. Patients <strong>with</strong> recent trophoblastic disease,<br />
exhibiting abnormal chorionic gonadotrophin levels. Pathologists should be informed of the patient's use of <strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong> if<br />
endometrial or endocervical tissue is submitted for examination. Results of certain laboratory tests may be affected. Refer to the<br />
Summary of Product Characteristics for more detailed information on Special Warnings and Precautions. Drug interactions:<br />
Aminoglutethimide administered concurrently may significantly depress bioavailability. The possibility of interaction (including oral<br />
anticoagulants) should be borne in mind in patients receiving concurrent treatment <strong>with</strong> <strong>other</strong> drugs. Pregnancy and Lactation:<br />
Check for pregnancy before initial injection, and also if administration of subsequent injection is delayed beyond 89 days (12 weeks<br />
and 5 days). Side-effects: Common: Menstrual irregularities (bleeding and/or amenorrhoea), weight changes, headache, nervousness,<br />
abdominal pain or discomfort, dizziness, asthenia (weakness or fatigue), decreased libido or an<strong>org</strong>asmia, backache, leg cramps,<br />
depression, nausea, insomnia, leucorrhoea, acne, vaginitis, pelvic pain, breast pain, no hair growth or alopecia, bloating, rash, oedema,<br />
hot flushes. Uncommon: (fewer than 1 % of subjects) galactorrhoea, melasma, chloasma, convulsions, changes in appetite,<br />
gastrointestinal disturbances, jaundice, genitourinary infections, vaginal cysts, dyspareunia, paraesthesia, chest pain, pulmonary<br />
embolus, allergic reactions, anaemia, syncope, dyspnoea, thirst, hoarseness, somnolence, decreased glucose tolerance, hirsutism,<br />
pruritus, arthralgia, pyrexia, pain at injection site, injection site abscess, blood dyscrasia, rectal bleeding, changes in breast size, breast<br />
lumps or nipple bleeding, axillary swelling, prevention of lactation, sensation of pregnancy, lack of return to fertility, paralysis, facial<br />
palsy, scleroderma, osteoporosis, uterine hyperplasia, varicose veins, dysmenorrhoea, thrombophlebitis, deep vein thrombosis. In postmarketing<br />
surveillance rare cases of osteoporosis including osteoporotic fractures have been reported in patients taking <strong>Depo</strong>-<strong>Provera</strong>.<br />
Package Quantities and Basic NHS Cost: Single 1ml Syringe pack: £6.01. Legal Category: POM. Marketing Authorisation<br />
Number and Holder: PL 00032/0082, Pharmacia Limited, Ramsgate Road, Sandwich, CT13 9NJ, UK. Last Revised: August 2007.<br />
Further information is available on request from: Medical Information at Pfizer Limited, Walton Oaks, Dorking Road, Tadworth,<br />
Surrey, KT20 7NS, UK. Tel: +44 (0) 1304 616161<br />
Adverse events should be reported to Pfizer Medical Information on 01304 616161<br />
Information about adverse event reporting can also be found at www.yellowcard.gov.uk<br />
Ref: DP 4_0<br />
Date of preparation January 2008<br />
DPR-056-08