Rate Law worksheet - Head-Royce
Rate Law worksheet - Head-Royce
Rate Law worksheet - Head-Royce
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
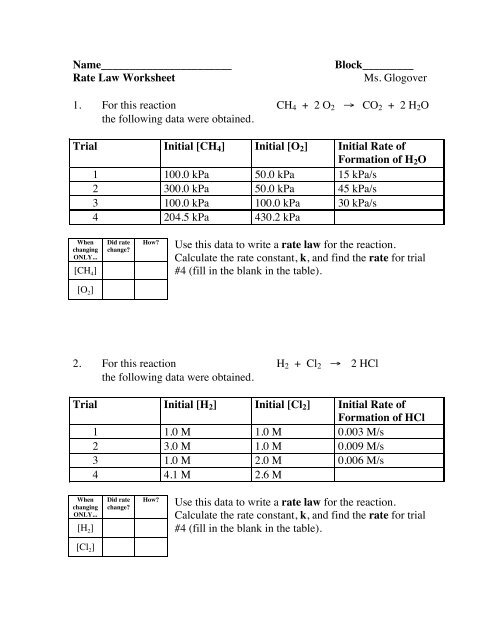
Name_______________________<br />
<strong>Rate</strong> <strong>Law</strong> Worksheet<br />
Block_________<br />
Ms. Glogover<br />
1. For this reaction CH 4 + 2 O 2 → CO 2 + 2 H 2 O<br />
the following data were obtained.<br />
Trial Initial [CH 4 ] Initial [O 2 ] Initial <strong>Rate</strong> of<br />
Formation of H 2 O<br />
1 100.0 kPa 50.0 kPa 15 kPa/s<br />
2 300.0 kPa 50.0 kPa 45 kPa/s<br />
3 100.0 kPa 100.0 kPa 30 kPa/s<br />
4 204.5 kPa 430.2 kPa<br />
When<br />
changing<br />
ONLY...<br />
[CH 4 ]<br />
Did rate<br />
change?<br />
How?<br />
Use this data to write a rate law for the reaction.<br />
Calculate the rate constant, k, and find the rate for trial<br />
#4 (fill in the blank in the table).<br />
[O 2 ]<br />
2. For this reaction H 2 + Cl 2 → 2 HCl<br />
the following data were obtained.<br />
Trial Initial [H 2 ] Initial [Cl 2 ] Initial <strong>Rate</strong> of<br />
Formation of HCl<br />
1 1.0 M 1.0 M 0.003 M/s<br />
2 3.0 M 1.0 M 0.009 M/s<br />
3 1.0 M 2.0 M 0.006 M/s<br />
4 4.1 M 2.6 M<br />
When<br />
changing<br />
ONLY...<br />
[H 2 ]<br />
Did rate<br />
change?<br />
How?<br />
Use this data to write a rate law for the reaction.<br />
Calculate the rate constant, k, and find the rate for trial<br />
#4 (fill in the blank in the table).<br />
[Cl 2 ]
3. For this reaction Ag + (aq) + Cl - (aq) → AgCl (cr)<br />
the following data were obtained.<br />
Trial Initial [Ag + ] Initial [Cl - ] Initial <strong>Rate</strong> of<br />
Disappearance of Cl -<br />
1 0.1 M 0.5 M 0.05 M/s<br />
2 0.01 M 0.5 M 0.005 M/s<br />
3 0.1 M 1.0 M 0.10 M/s<br />
4 0.35 M 0.50 M<br />
When<br />
changing<br />
ONLY...<br />
[Ag + ]<br />
Did rate<br />
change?<br />
How?<br />
Use this data to write a rate law for the reaction.<br />
Calculate the rate constant, k, and find the rate for trial<br />
#4 (fill in the blank in the table).<br />
[Cl – ]<br />
4. For this reaction Na + (aq) + Cl - (aq) → NaCl (cr)<br />
the following data were obtained.<br />
Trial Initial [Na + ] Initial [Cl - ] Initial <strong>Rate</strong> of<br />
Disappearance of Cl -<br />
1 1.0 M 0.5 M 0.005 M/s<br />
2 2.0 M 0.5 M 0.010 M/s<br />
3 1.0 M 1.0 M 0.010 M/s<br />
4 4.6 M 2.0 M<br />
When<br />
changing<br />
ONLY...<br />
[Na + ]<br />
Did rate<br />
change?<br />
How?<br />
Use this data to write a rate law for the reaction.<br />
Calculate the rate constant, k, and find the rate for trial<br />
#4 (fill in the blank in the table).<br />
[Cl – ]
5. For this reaction A + 2 B → C + 2 D<br />
the following data were obtained.<br />
Trial Initial [A] Initial [B] Initial <strong>Rate</strong> of<br />
Appearance of C<br />
1 1.0 M 0.050 M 0.10 M/s<br />
2 2.0 M 0.050 M 0.10 M/s<br />
3 1.0 M 0.100 M 0.40 M/s<br />
4 3.6 M 0.390 M<br />
When<br />
changing<br />
ONLY...<br />
[A]<br />
Did rate<br />
change?<br />
How?<br />
Use this data to write a rate law for the reaction.<br />
Calculate the rate constant, k, and find the rate for trial<br />
#4 (fill in the blank in the table).<br />
[B]<br />
6. For this reaction Q + R → Z<br />
the following data were obtained.<br />
Trial Initial [Q] Initial [R] Initial <strong>Rate</strong> of<br />
Formation of Z<br />
1 0.50 M 1.0 M 0.0030 M/s<br />
2 0.25 M 1.0 M 0.0015 M/s<br />
3 0.50 M 2.0 M 0.0060 M/s<br />
4 0.00034 M 0.18 M<br />
When<br />
changing<br />
ONLY...<br />
[Q]<br />
Did rate<br />
change?<br />
How?<br />
Use this data to write a rate law for the reaction.<br />
Calculate the rate constant, k, and find the rate for trial<br />
#4 (fill in the blank in the table).<br />
[R]
7. For this reaction L (aq) + M (aq) → T (ppt)<br />
the following data were obtained.<br />
Trial Initial [L] Initial [M] Initial <strong>Rate</strong> of<br />
Disappearance of M<br />
1 0.20 M 0.50 M 0.050 M/s<br />
2 0.020 M 0.50 M 0.0050 M/s<br />
3 0.20 M 1.5 M 0.15 M/s<br />
4 0.35 M 0.50 M<br />
When<br />
changing<br />
ONLY...<br />
[L]<br />
Did rate<br />
change?<br />
How?<br />
Use this data to write a rate law for the reaction.<br />
Calculate the rate constant, k, and find the rate for trial<br />
#4 (fill in the blank in the table).<br />
[M]<br />
8. For this reaction E + 2 G → H + J<br />
the following data were obtained.<br />
Trial Initial [E] Initial [G] Initial <strong>Rate</strong> of<br />
Disappearance of E<br />
1 1.0 M 0.5 M 0.35 M/s<br />
2 2.0 M 0.5 M 0.35 M/s<br />
3 1.0 M 1.0 M 1.40 M/s<br />
4 0.75 M 0.56 M<br />
When<br />
changing<br />
ONLY...<br />
[E]<br />
Did rate<br />
change?<br />
How?<br />
Use this data to write a rate law for the reaction.<br />
Calculate the rate constant, k, and find the rate for trial<br />
#4 (fill in the blank in the table).<br />
[G]