Proceedings of a Workshop on - The Havemeyer Foundation
Proceedings of a Workshop on - The Havemeyer Foundation
Proceedings of a Workshop on - The Havemeyer Foundation
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Havemeyer</strong> Foundati<strong>on</strong> M<strong>on</strong>ograph Series No. 11<br />
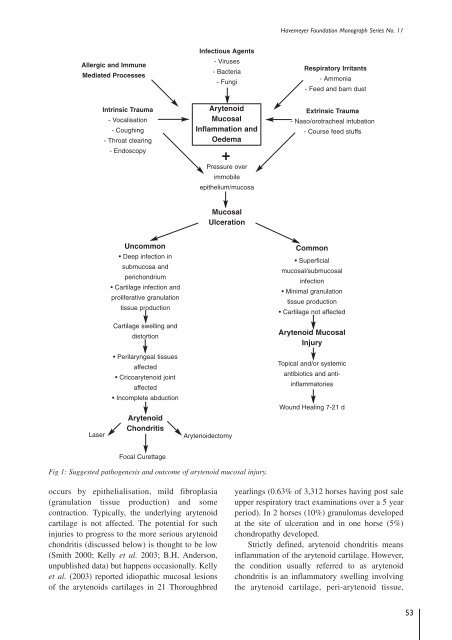
Allergic and Immune<br />
Mediated Processes<br />
Infectious Agents<br />
- Viruses<br />
- Bacteria<br />
- Fungi<br />
Respiratory Irritants<br />
- Amm<strong>on</strong>ia<br />
- Feed and barn dust<br />
Intrinsic Trauma<br />
- Vocalisati<strong>on</strong><br />
- Coughing<br />
- Throat clearing<br />
- Endoscopy<br />
Arytenoid<br />
Mucosal<br />
Inflammati<strong>on</strong> and<br />
Oedema<br />
+<br />
Pressure over<br />
immobile<br />
epithelium/mucosa<br />
Extrinsic Trauma<br />
- Naso/orotracheal intubati<strong>on</strong><br />
- Course feed stuffs<br />
Mucosal<br />
Ulcerati<strong>on</strong><br />
Uncomm<strong>on</strong><br />
• Deep infecti<strong>on</strong> in<br />
submucosa and<br />
perich<strong>on</strong>drium<br />
• Cartilage infecti<strong>on</strong> and<br />
proliferative granulati<strong>on</strong><br />
tissue producti<strong>on</strong><br />
Cartilage swelling and<br />
distorti<strong>on</strong><br />
Comm<strong>on</strong><br />
• Superficial<br />
mucosal/submucosal<br />
infecti<strong>on</strong><br />
• Minimal granulati<strong>on</strong><br />
tissue producti<strong>on</strong><br />
• Cartilage not affected<br />
Arytenoid Mucosal<br />
Injury<br />
Laser<br />
• Perilaryngeal tissues<br />
affected<br />
• Cricoarytenoid joint<br />
affected<br />
• Incomplete abducti<strong>on</strong><br />
Arytenoid<br />
Ch<strong>on</strong>dritis<br />
Arytenoidectomy<br />
Topical and/or systemic<br />
antibiotics and antiinflammatories<br />
Wound Healing 7-21 d<br />
Focal Curettage<br />
Fig 1: Suggested pathogenesis and outcome <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> arytenoid mucosal injury.<br />
occurs by epithelialisati<strong>on</strong>, mild fibroplasia<br />
(granulati<strong>on</strong> tissue producti<strong>on</strong>) and some<br />
c<strong>on</strong>tracti<strong>on</strong>. Typically, the underlying arytenoid<br />
cartilage is not affected. <strong>The</strong> potential for such<br />
injuries to progress to the more serious arytenoid<br />
ch<strong>on</strong>dritis (discussed below) is thought to be low<br />
(Smith 2000; Kelly et al. 2003; B.H. Anders<strong>on</strong>,<br />
unpublished data) but happens occasi<strong>on</strong>ally. Kelly<br />
et al. (2003) reported idiopathic mucosal lesi<strong>on</strong>s<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the arytenoids cartilages in 21 Thoroughbred<br />
yearlings (0.63% <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> 3,312 horses having post sale<br />
upper respiratory tract examinati<strong>on</strong>s over a 5 year<br />
period). In 2 horses (10%) granulomas developed<br />
at the site <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> ulcerati<strong>on</strong> and in <strong>on</strong>e horse (5%)<br />
ch<strong>on</strong>dropathy developed.<br />
Strictly defined, arytenoid ch<strong>on</strong>dritis means<br />
inflammati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the arytenoid cartilage. However,<br />
the c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong> usually referred to as arytenoid<br />
ch<strong>on</strong>dritis is an inflammatory swelling involving<br />
the arytenoid cartilage, peri-arytenoid tissue,<br />
53