Chapter 3.3 Notes
Chapter 3.3 Notes
Chapter 3.3 Notes
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
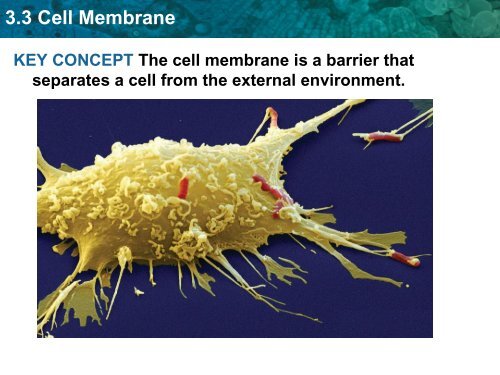
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
KEY CONCEPT The cell membrane is a barrier that<br />
separates a cell from the external environment.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
<strong>3.3</strong> Objectives<br />
Describe the structure of the cell membrane.<br />
Summarize how chemical signals are transmitted across<br />
the cell membrane.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane has two major functions.<br />
cell membrane
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane has two major functions.<br />
– forms a boundary between inside and outside of the<br />
cell<br />
cell membrane<br />
outside cell<br />
inside cell
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane has two major functions.<br />
– forms a boundary between inside and outside of the<br />
cell<br />
– controls passage of materials<br />
cell membrane<br />
outside cell<br />
inside cell
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer.<br />
cell membrane
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer.<br />
• There are other molecules embedded in the membrane.<br />
cell membrane<br />
carbohydrate<br />
chain<br />
protein<br />
cholesterol<br />
protein<br />
protein channel
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer.<br />
• There are other molecules embedded in the membrane.<br />
• The fluid mosaic model describes the membrane.<br />
cell membrane<br />
carbohydrate<br />
chain<br />
protein<br />
cholesterol<br />
protein<br />
protein channel
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
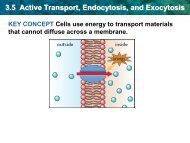
• The cell membrane is selectively permeable.<br />
Some molecules can cross the membrane<br />
while others cannot.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane is selectively permeable.<br />
Some molecules can cross the membrane<br />
while others cannot.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Chemical signals are transmitted across the cell<br />
membrane.<br />
• Receptors bind with ligands and change shape.<br />
• There are two types of receptors.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Chemical signals are transmitted across the cell<br />
membrane.<br />
• Receptors bind with ligands and change shape.<br />
• There are two types of receptors.<br />
– intracellular receptor
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Chemical signals are transmitted across the cell<br />
membrane.<br />
• Receptors bind with ligands and change shape.<br />
• There are two types of receptors.<br />
– intracellular receptor<br />
– membrane receptor
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
<strong>3.3</strong> Assessment: Hwy do phospholipids form a<br />
double layer?<br />
Phospholipids form a double layer in response to the<br />
presence of polar water molecules surrounding them.<br />
The polar heads of phospholipids interact with the water<br />
inside and outside the cell, forming transient hydrogen<br />
bonds. The nonpolar tails are repelled by water and<br />
interact with each other inside the membrane.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
<strong>3.3</strong> Assessment: Explain how membrane<br />
receptors transmit messages across the cell<br />
membrane.<br />
Membrane receptors bind to a signal molecule on the<br />
outside of a cell. Upon binding, the membrane receptor<br />
changes shape, which sends a message inside the cell.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
<strong>3.3</strong> Assessment: Describe the similarities<br />
between enzymes and receptors.<br />
Both enzymes and receptors are proteins that bind to a<br />
specific ligand or substrate, change shape in response<br />
to binding, and cause some sort of action or response.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
<strong>3.3</strong> Assessment: If proteins were rigid, why<br />
would they make poor receptors?<br />
If proteins were rigid, they would be unable to change<br />
shape. Therefore, they could not effectively transmit a<br />
message to the cell interior.