Chapter 3.3 Notes
Chapter 3.3 Notes
Chapter 3.3 Notes
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
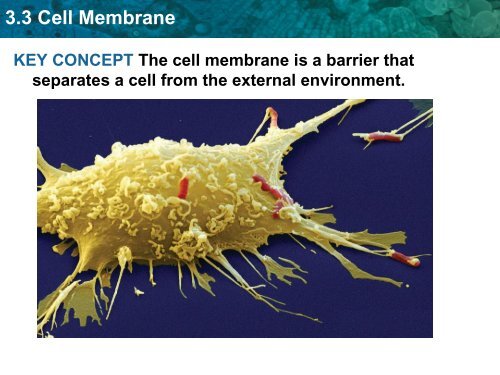
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
KEY CONCEPT The cell membrane is a barrier that<br />
separates a cell from the external environment.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
<strong>3.3</strong> Objectives<br />
Describe the structure of the cell membrane.<br />
Summarize how chemical signals are transmitted across<br />
the cell membrane.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane has two major functions.<br />
cell membrane
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane has two major functions.<br />
– forms a boundary between inside and outside of the<br />
cell<br />
cell membrane<br />
outside cell<br />
inside cell
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane has two major functions.<br />
– forms a boundary between inside and outside of the<br />
cell<br />
– controls passage of materials<br />
cell membrane<br />
outside cell<br />
inside cell
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer.<br />
cell membrane
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer.<br />
• There are other molecules embedded in the membrane.<br />
cell membrane<br />
carbohydrate<br />
chain<br />
protein<br />
cholesterol<br />
protein<br />
protein channel
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer.<br />
• There are other molecules embedded in the membrane.<br />
• The fluid mosaic model describes the membrane.<br />
cell membrane<br />
carbohydrate<br />
chain<br />
protein<br />
cholesterol<br />
protein<br />
protein channel
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane is selectively permeable.<br />
Some molecules can cross the membrane<br />
while others cannot.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid<br />
layers.<br />
• The cell membrane is selectively permeable.<br />
Some molecules can cross the membrane<br />
while others cannot.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Chemical signals are transmitted across the cell<br />
membrane.<br />
• Receptors bind with ligands and change shape.<br />
• There are two types of receptors.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Chemical signals are transmitted across the cell<br />
membrane.<br />
• Receptors bind with ligands and change shape.<br />
• There are two types of receptors.<br />
– intracellular receptor
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
Chemical signals are transmitted across the cell<br />
membrane.<br />
• Receptors bind with ligands and change shape.<br />
• There are two types of receptors.<br />
– intracellular receptor<br />
– membrane receptor
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
<strong>3.3</strong> Assessment: Hwy do phospholipids form a<br />
double layer?<br />
Phospholipids form a double layer in response to the<br />
presence of polar water molecules surrounding them.<br />
The polar heads of phospholipids interact with the water<br />
inside and outside the cell, forming transient hydrogen<br />
bonds. The nonpolar tails are repelled by water and<br />
interact with each other inside the membrane.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
<strong>3.3</strong> Assessment: Explain how membrane<br />
receptors transmit messages across the cell<br />
membrane.<br />
Membrane receptors bind to a signal molecule on the<br />
outside of a cell. Upon binding, the membrane receptor<br />
changes shape, which sends a message inside the cell.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
<strong>3.3</strong> Assessment: Describe the similarities<br />
between enzymes and receptors.<br />
Both enzymes and receptors are proteins that bind to a<br />
specific ligand or substrate, change shape in response<br />
to binding, and cause some sort of action or response.
<strong>3.3</strong> Cell Membrane<br />
<strong>3.3</strong> Assessment: If proteins were rigid, why<br />
would they make poor receptors?<br />
If proteins were rigid, they would be unable to change<br />
shape. Therefore, they could not effectively transmit a<br />
message to the cell interior.