Earth Layers Powerpoint
Earth Layers Powerpoint
Earth Layers Powerpoint
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
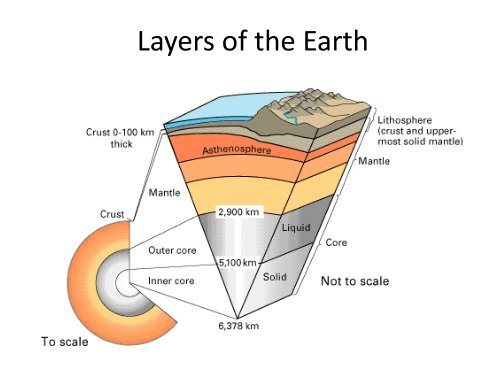
<strong>Layers</strong> of the <strong>Earth</strong>
• Seismic Waves<br />
Exploring the <strong>Layers</strong><br />
– When waves change we<br />
know the layers are<br />
different
Exploring the <strong>Layers</strong> Continued<br />
• Drilling & Mining<br />
– Furthest Drill = 15 km<br />
– Furthest Mine = 3.8 km<br />
• Future Goals<br />
– 2020 – Drill to Mantle
• Composition<br />
<strong>Earth</strong><br />
– Different mixtures of elements<br />
make up the layers<br />
– Broken into 3 <strong>Layers</strong><br />
• Physical Properties<br />
– Characteristics of the <strong>Layers</strong><br />
– Includes: Temperature, Density<br />
& Ability to Flow<br />
– Broken into 5 <strong>Layers</strong>
Composition & Physical Properties<br />
• Composition<br />
– Broken into 3 <strong>Layers</strong><br />
• Crust<br />
• Mantle<br />
• Core<br />
• Physical Properties<br />
– Broken into 5 <strong>Layers</strong><br />
• Lithosphere<br />
• Asthenosphere<br />
• Mesosphere<br />
• Inner Core<br />
• Outer Core
• Thin, Outer Layer<br />
– Layer we live on<br />
Composition - Crust<br />
• Made of Light Elements<br />
– Less than 1% of <strong>Earth</strong>’s Mass<br />
• Generally 30-100 km thick<br />
• Broken into 2 different types<br />
– Oceanic<br />
– Continental
Composition - Crust<br />
• Oceanic<br />
– Under Oceans<br />
– Thinner<br />
– Denser<br />
• Continental<br />
– Under Continents<br />
– Thicker<br />
– Less Dense
Composition - Mantle<br />
• Layer beneath the crust<br />
• Thickest layer<br />
– 64% of mass<br />
– 2,900 km thick<br />
• Made of Iron and<br />
Magnesium
Physical Properties - Lithosphere<br />
• “Rock Sphere”<br />
• Part of Crust and Mantle<br />
• Outer Layer<br />
• Cool, Rigid, Solid<br />
• 15 – 300 km thick<br />
• Divided into Tectonic Plates
Physical Properties - Asthenosphere<br />
• “Middle Mantle”<br />
• Soft, Plastic Layer<br />
made of rock<br />
• 250 km thick<br />
• Flows slowly<br />
– Allows tectonic plates<br />
to move<br />
– Compresses and<br />
Stretches
Physical Properties - Mesosphere<br />
• Solid Rock<br />
• Lowest portion of Mantle<br />
• 2,250 km thick<br />
• Convection Occurs Here
• Allows the mantle to move<br />
• Hot material rises<br />
• As it rises it gets cooler and<br />
sinks<br />
Convection Currents
Convection Currents<br />
• When you take a pot, and boil<br />
some water into it, what do you<br />
notice?<br />
• Hopefully you will notice<br />
movement of the liquid. That is<br />
the convection currents moving<br />
it around.<br />
• When the convection currents<br />
flow in the asthenosphere layer,<br />
they also move the crust. The<br />
crust gets a free ride with these<br />
currents<br />
• The cork in the picture is the<br />
crust
Composition - Core<br />
• Hot & Dense<br />
– 4,000-5,000°C<br />
• Made of Nickel and Iron<br />
• 3,480 km thick<br />
• 1/3 of the <strong>Earth</strong>’s Mass<br />
• Broken into 2 sections<br />
– Due to Physical Properties<br />
• Inner Core<br />
• Outer Core
Physical Properties – Outer Core<br />
• Liquid Layer<br />
• 2,300 km Thick<br />
• Made of Iron & Nickel<br />
• Creates <strong>Earth</strong>’s<br />
Magnetic Field<br />
• Cooler than inner<br />
core
Physical Properties – Inner Core<br />
• Solid Metal Layer<br />
• 1,200 km Thick<br />
• Iron and Nickel<br />
• Extreme Pressure