Thermocouple Catalog (North America) - English - Pyrotek
Thermocouple Catalog (North America) - English - Pyrotek
Thermocouple Catalog (North America) - English - Pyrotek
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
GENERAL TECHNICAL REFERENCES AND TABLES<br />
LETTER OF CALIBRATION<br />
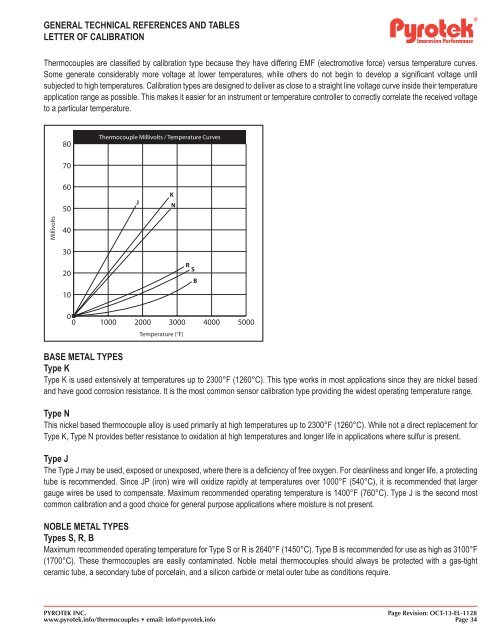
<strong>Thermocouple</strong>s are classified by calibration type because they have differing EMF (electromotive force) versus temperature curves.<br />
Some generate considerably more voltage at lower temperatures, while others do not begin to develop a significant voltage until<br />
subjected to high temperatures. Calibration types are designed to deliver as close to a straight line voltage curve inside their temperature<br />
application range as possible. This makes it easier for an instrument or temperature controller to correctly correlate the received voltage<br />
to a particular temperature.<br />
80<br />
<strong>Thermocouple</strong> Millivolts / Temperature Curves<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
J<br />
K<br />
N<br />
Millivolts<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
R<br />
S<br />
B<br />
10<br />
0<br />
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000<br />
Temperature (°F)<br />
BASE METAL TYPES<br />
Type K<br />
Type K is used extensively at temperatures up to 2300°F (1260°C). This type works in most applications since they are nickel based<br />
and have good corrosion resistance. It is the most common sensor calibration type providing the widest operating temperature range.<br />
Type N<br />
This nickel based thermocouple alloy is used primarily at high temperatures up to 2300°F (1260°C). While not a direct replacement for<br />
Type K, Type N provides better resistance to oxidation at high temperatures and longer life in applications where sulfur is present.<br />
Type J<br />
The Type J may be used, exposed or unexposed, where there is a deficiency of free oxygen. For cleanliness and longer life, a protecting<br />
tube is recommended. Since JP (iron) wire will oxidize rapidly at temperatures over 1000°F (540°C), it is recommended that larger<br />
gauge wires be used to compensate. Maximum recommended operating temperature is 1400°F (760°C). Type J is the second most<br />
common calibration and a good choice for general purpose applications where moisture is not present.<br />
NOBLE METAL TYPES<br />
Types S, R, B<br />
Maximum recommended operating temperature for Type S or R is 2640°F (1450°C). Type B is recommended for use as high as 3100°F<br />
(1700°C). These thermocouples are easily contaminated. Noble metal thermocouples should always be protected with a gas-tight<br />
ceramic tube, a secondary tube of porcelain, and a silicon carbide or metal outer tube as conditions require.<br />
PYROTEK INC.<br />
Page Revision: OCT-13-EL-1128<br />
www.pyrotek.info/thermocouples • email: info@pyrotek.info Page 34