Fourth Year Syllabus 2011-12(Civil) - Malnad College of Engineering
Fourth Year Syllabus 2011-12(Civil) - Malnad College of Engineering
Fourth Year Syllabus 2011-12(Civil) - Malnad College of Engineering
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
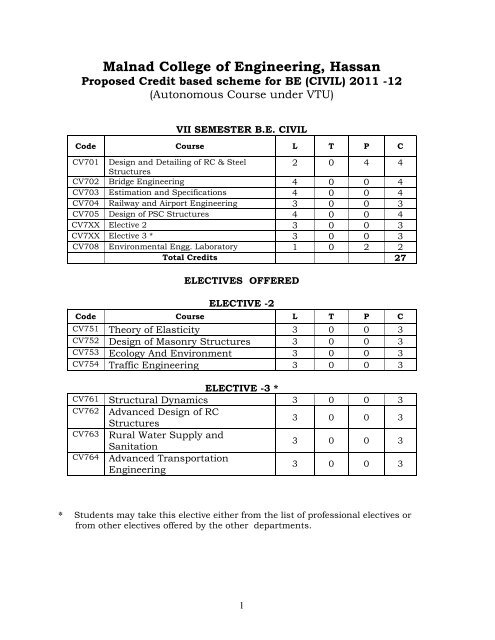
<strong>Malnad</strong> <strong>College</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Engineering</strong>, Hassan<br />
Proposed Credit based scheme for BE (CIVIL) <strong>2011</strong> -<strong>12</strong><br />
(Autonomous Course under VTU)<br />
VII SEMESTER B.E. CIVIL<br />
Code Course L T P C<br />
CV701 Design and Detailing <strong>of</strong> RC & Steel<br />
2 0 4 4<br />
Structures<br />
CV702 Bridge <strong>Engineering</strong> 4 0 0 4<br />
CV703 Estimation and Specifications 4 0 0 4<br />
CV704 Railway and Airport <strong>Engineering</strong> 3 0 0 3<br />
CV705 Design <strong>of</strong> PSC Structures 4 0 0 4<br />
CV7XX Elective 2 3 0 0 3<br />
CV7XX Elective 3 * 3 0 0 3<br />
CV708 Environmental Engg. Laboratory 1 0 2 2<br />
Total Credits 27<br />
ELECTIVES OFFERED<br />
ELECTIVE -2<br />
Code Course L T P C<br />
CV751 Theory <strong>of</strong> Elasticity 3 0 0 3<br />
CV752 Design <strong>of</strong> Masonry Structures 3 0 0 3<br />
CV753 Ecology And Environment 3 0 0 3<br />
CV754 Traffic <strong>Engineering</strong> 3 0 0 3<br />
ELECTIVE -3 *<br />
CV761 Structural Dynamics 3 0 0 3<br />
CV762 Advanced Design <strong>of</strong> RC<br />
Structures<br />
3 0 0 3<br />
CV763 Rural Water Supply and<br />
Sanitation<br />
3 0 0 3<br />
CV764 Advanced Transportation<br />
<strong>Engineering</strong><br />
3 0 0 3<br />
* Students may take this elective either from the list <strong>of</strong> pr<strong>of</strong>essional electives or<br />
from other electives <strong>of</strong>fered by the other departments.<br />
1
VIII SEMESTER B.E. CIVIL<br />
Code Course L T P C<br />
CV801 Construction Planning & Management 3 0 0 3<br />
CV8XX Elective 4 3 0 0 3<br />
CV8XX Elective 5 * 3 0 0 3<br />
CV805 Seminar 0 0 2 2<br />
CV806 Project Work 0 0 18 9<br />
Total Credits 20<br />
ELECTIVES OFFERED<br />
ELECTIVE -4<br />
Code Course L T P C<br />
CV851 Finite Element Analysis 3 0 0 3<br />
CV852 Advanced Design <strong>of</strong> Steel<br />
Structures<br />
3 0 0 3<br />
CV853 Environment Impact Assessment 3 0 0 3<br />
CV854 Advanced Foundation Design 3 0 0 3<br />
CV855 Water Resources <strong>Engineering</strong> 3 0 0 3<br />
CV856 Urban And Rural Planning 3 0 0 3<br />
ELECTIVE -5*<br />
CV861 Earthquake Resistant Design <strong>of</strong><br />
Structures<br />
3 0 0 3<br />
CV862 Advanced Prestressed Concrete<br />
Structures<br />
3 0 0 3<br />
CV863 Solid Waste Management 3 0 0 3<br />
CV864 Design And Drawing <strong>of</strong> Irrigation<br />
Structures<br />
1 0 4 3<br />
CV865 Highway Pavement Design 3 0 0 3<br />
* Students may take this elective either from the list <strong>of</strong> pr<strong>of</strong>essional electives or<br />
from other electives <strong>of</strong>fered by the other departments.<br />
2
CV701 DESIGN AND DETAILING OF STEEL AND RC STRUCTURES<br />
(2-0-4)4<br />
PART –A - Steel Structures:<br />
Design and Detailing <strong>of</strong><br />
1 Plate girder<br />
2. Ro<strong>of</strong> Trusses<br />
3. Gantry girder 20 Hrs<br />
The connections in all the above structures shall be welded connections<br />
only.<br />
PART – B : Reinforced Concrete Structures:<br />
Design and Detailing <strong>of</strong><br />
1. Circular and Rectangular water tanks resting on ground with fixed<br />
base and without top cover<br />
2. Cantilever retaining walls (without surcharge)<br />
3. Combined footing (rectangular) slab and beam type only 32 Hrs<br />
Water tanks shall be designed as per IS 3370 part IV. The design <strong>of</strong><br />
cantilever retaining wall and combined footings shall be by the limit state<br />
method.<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Ramamrutham.S “ Design <strong>of</strong> Reinforced Concrete Structures” Dhanpath<br />
Rai & Sons – 2009<br />
2. B.C.Punmia “Reinforced Concrete Structures” Vol IO & 2 Laxmi<br />
Publication Pvt. Ltd.. 2001<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Clyder T Morris “ Designing and Detailing <strong>of</strong> Simple Steel Structures”<br />
Little field press USA 2008 (Part 1)<br />
2. Krishnamurthy – Structural Design and Drawing (Concrete Structures)<br />
CBS publishers, New Delhi 1985 (Part -2)<br />
3. Krishna Raj.N “ Structural Design and Drawing Reinforced Concrete and<br />
Steel” Universities Press, Hyderabad 2009<br />
4. IS 3370 (part 4) 1967, IS 456 -2000, IS 800-2007, SP 16, BIS New Delhi<br />
3
Question Paper Pattern :<br />
Two questions from Part-A <strong>of</strong> 40 Marks (15 marks for Design and 25 marks<br />
for Detailing) each, two questions from Part-B <strong>of</strong> 60 Marks (25 marks for<br />
Design and 35 marks for Detailing) each shall be set. The student has to<br />
answer one question from each part.<br />
SEE : Duration 04 hrs.<br />
4
CV 702 BRIDGE ENGINEERING (4-0-0) 4<br />
1. Introduction: Definition <strong>of</strong> a bridge - Components <strong>of</strong> a bridge-<br />
Classification <strong>of</strong> bridges - Requirements <strong>of</strong> an ideal bridge- Forces to be<br />
considered for the design <strong>of</strong> bridges- IRC loading standards- Impact effect.<br />
04 Hrs<br />
2. Hydraulic Design: Design discharge- Afflux, Natural waterway- Linear<br />
waterway- Economic span.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
3. Substructures: Abutments, Piers- Wing walls- Forces on substructures-<br />
Stability considerations -Empirical design.<br />
03 Hrs<br />
4. Foundations: Depth <strong>of</strong> foundation-Pile and well foundation- Depth <strong>of</strong><br />
scour.<br />
04 Hrs<br />
5. RC Slab Culverts: Design <strong>of</strong> superstructure for IRC class AA loading,<br />
10 Hrs<br />
6. Pipe Culverts: Design for both shallow and deep embankment for IRC<br />
class AA wheel loading.<br />
07 Hrs<br />
7. RC T Beam Bridge: Design <strong>of</strong> slab by using Pigeaud’s curves- Design <strong>of</strong><br />
longitudinal girders by Morice Little method for IRC class AA loading.<br />
10 Hrs<br />
8. Composite Bridge: Design <strong>of</strong> RC slab and steel girder for equivalent<br />
loading- Design <strong>of</strong> shear connectors.<br />
08 Hrs<br />
(Drawings <strong>of</strong> bridges providing all details shall be given as assignment)<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. Jhonson Victor. “Essentials <strong>of</strong> Bridge <strong>Engineering</strong>” Oxford IBH<br />
Publication 2008 (Ch 1, 4, 5 & 7)<br />
2. Bindra S.P. “Principles and Practice <strong>of</strong> Bridge <strong>Engineering</strong>” Dhanapat<br />
Rai Publications 2008(Ch 2, 3, 6 & 8)<br />
Reference Books:<br />
1. Krishna Raju N. “Design <strong>of</strong> Bridges” Oxford IBH Publication 2008<br />
2. Jagadeesh.T.R. & Jayaram.M.A “ Design <strong>of</strong> Bridge Structure” II Edn.<br />
PHI Learning Pvt.Ltd., 2009<br />
3. IRC 21 !987 (Revised)<br />
Relevant Design charts to be supplied in SEE<br />
5
CV 703 ESTIMATION AND SPECIFICATION (4-0-0) 4<br />
1. Introduction - Different type <strong>of</strong> estimates ― Study <strong>of</strong> various<br />
drawings attached with estimates- important terms, units <strong>of</strong> measurement<br />
― abstract ― approximate methods <strong>of</strong> estimating cost <strong>of</strong> buildings 03 Hrs<br />
2. Estimating - Methods <strong>of</strong> taking out quantities and cost ― center line<br />
method ― Long and short wall method or crossing method ― Preparation<br />
<strong>of</strong> detailed and abstract estimates for the following <strong>Civil</strong> <strong>Engineering</strong> works:<br />
Buildings, framed structures with flat or sloped RCC slabs and Masonry<br />
structures<br />
08 Hrs<br />
3. Estimating (Contd…);Building components: Beams ―Columns, Column<br />
Footings, stair cases and retaining walls<br />
08 Hrs<br />
4. Estimating (Contd…);- Steel trusses, A.C.Sheet and G.I.Sheet ro<strong>of</strong>s,<br />
RCC slab culverts, pipe culverts, metalled roads, C.C. trackway, premix<br />
carpeting, stabilized soil roads, manholes and septic tanks 09 Hrs<br />
5.Rate Analysis - Definition and purpose ― Working out quantities and<br />
rates for the following standard items <strong>of</strong> work: earthwork in different<br />
types <strong>of</strong> soils ― cement concrete <strong>of</strong> different mixes, brick and stone<br />
masonry, flooring ― plastering― RCC works, painting, white washing and<br />
distempering<br />
08 Hrs<br />
6. Computation <strong>of</strong> Earthwork in cuttings and embankments for Roads<br />
and canals - Methods <strong>of</strong> computation <strong>of</strong> earthwork ― cross sections ― mid<br />
section formula ― trapezoidal or average end area or mean sectional<br />
area formula ― prismoidal formula- for different terrains.<br />
07 Hrs<br />
7. Specifications: Definition <strong>of</strong> specifications ― objective <strong>of</strong> writing<br />
specifications ― essentials <strong>of</strong> specifications ― general and detailed<br />
specifications <strong>of</strong> various items <strong>of</strong> work in buildings.<br />
04 Hrs<br />
8. Contracts - Types <strong>of</strong> contract ― essentials <strong>of</strong> contract agreement-legal<br />
aspects- penal provisions on breach <strong>of</strong> contract ― Definition <strong>of</strong> the terms<br />
― Tender ― earnest money deposit― security deposit ― tender<br />
forms―documents and types― Comparative statements ― acceptance <strong>of</strong><br />
contract documents and issue <strong>of</strong> work orders- Duties and liabilitiestermination<br />
<strong>of</strong> contract― completion certificate- quality control― rights <strong>of</strong><br />
contractor― refund <strong>of</strong> deposit― Administrative approval ― Technical<br />
sanction― Nominal muster roll― measurement books ― procedure for<br />
recording and checking measurements ― preparation <strong>of</strong> bills. 05 Hrs<br />
6
Text Books:<br />
1. Datta.B.N. “Estimating and Costing in <strong>Civil</strong> <strong>Engineering</strong>” UBS<br />
Publications 7 th Reprint - twenty sixth revised edition 2009<br />
2. Chakraborti.N, “Estimating, Costing, Specification and Valuation”,<br />
published by the author, ninth edition. 1987<br />
Reference Books:<br />
1. Bhasin.P.L. “Quantity Surveying” S.Chand & Co., New Delhi. 2006<br />
2. Kohli.D.D. and Kohli. R.C. A text book on “Estimating, Costing and<br />
Accounts” - S.Chand Co., New Delhi. 2008<br />
Examination Question Pattern :<br />
PART – A [Compulsory]<br />
One Question for 40 marks shall be set from topic no. 2 and 3.<br />
PART – B<br />
Six Questions carrying 15 marks each shall be set from topics 1, 4, 5, 6, 7<br />
and 8. Students shall be asked to answer any four questions from part B.<br />
7
CV704 RAILWAY AND AIRPORT ENGINEERING (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Railway : Role <strong>of</strong> railways in transportation – Historical developments<br />
<strong>of</strong> railways in India - Selection <strong>of</strong> routes- preliminary and locations<br />
surveys.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
2. Permanentway : Gauges in railways – railway track – cross sections,<br />
coning <strong>of</strong> wheels– rails, rail section– ballast– sleepers– wear on rails, rail<br />
joints – welding <strong>of</strong> rails –creep <strong>of</strong> rails– rail fixtures – calculation <strong>of</strong><br />
quantity <strong>of</strong> materials needed for laying <strong>of</strong> tracks. Traction and tractive<br />
resistances – tractive power – Hauling capacity<br />
06 Hrs<br />
3. Geometric Design <strong>of</strong> Track : grade– ruling grade– minimum gradient<br />
pusher grade– speed <strong>of</strong> train– superelevation– cant deficiency– negative<br />
cant.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
4. Points and Crossing : turnout– design <strong>of</strong> turnout stations and yards–<br />
signaling and interlocking – defects in tracks – maintenance <strong>of</strong><br />
permanent way– track maintenance– level crossings– Indian railway<br />
standards.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
5. Airport Planning : Site selection – Aircraft characteristics- Regional<br />
planning – A brief description <strong>of</strong> visibility, wind characteristics and noise<br />
nuisance- runway maintenance and drainage.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
6. Runway Design : Analysis <strong>of</strong> wind data by wind rose diagram to find<br />
out the best direction <strong>of</strong> runway - Basic patterns <strong>of</strong> runway - Length <strong>of</strong><br />
runway – Correction to runway length by ICAO and FAA specifications.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
7. Taxiway Design : Factors affecting layout – taxiway – Geometric<br />
design <strong>of</strong> Taxiway, turning radius <strong>of</strong> taxiways as per ICAO. Design <strong>of</strong> exit<br />
taxiways.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
8. Airport Marking : lighting and ILS & VLS 05 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Saxena and Arora “ Railway <strong>Engineering</strong> “ Dhanpath Rai and Sons,<br />
2005 (Ch. 1,2,3,4)<br />
2. Khanna, Arora and Jain “Airport Planning and Design” Nemchand<br />
and Bros, Roorkee, 2006 (Ch.5,6,7,8)<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Agarwal M.M “ Indian Railway Track” Jaico publications, Bombay –<br />
2003<br />
2. Kadayali and Chopra “Highway and Airport <strong>Engineering</strong>” Nemchand<br />
and Bros. – Roorkee -2005<br />
8
CV 705 DESIGN OF PRE - STRESSED CONCRETE STRUCTURES<br />
(4-0-0) 4<br />
1. Materials – High Strength materials : Necessity ― Properties ― Stress<br />
strain characteristics. I.S. Specifications ― Mix design for high<br />
strength concrete.<br />
07 Hrs<br />
2. Basic Principles <strong>of</strong> Prestressing – Fundamentals– Definition ― Types<br />
<strong>of</strong> Prestressing ― Pre tensioning and Post tensioning systems ―<br />
Analysis <strong>of</strong> pre-stress ― resultant stress concept ― pressure line<br />
concept ― load balancing concept.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
3. Analysis <strong>of</strong> Sections for Flexure ― Stresses in concrete due to<br />
prestress, Self weight and imposed loads ― working loads ― Variation<br />
<strong>of</strong> stress in steel in bonded and unbonded beams ― Cracking<br />
moment.<br />
Composite construction: types <strong>of</strong> composite construction – Analysis for<br />
stresses ― Differential shrinkage ― Deflection <strong>of</strong> composite members.<br />
08 Hrs<br />
4. Losses <strong>of</strong> Prestress – Types <strong>of</strong> losses in pre tensioning and post<br />
tensioning. Determination <strong>of</strong> losses due to various causes. 05 Hrs<br />
5. Deflection <strong>of</strong> Prestressed Members – Short term and long term<br />
deflections ― deflections at transfer <strong>of</strong> loads and due to cable pr<strong>of</strong>iles,<br />
Codal limitations.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
6. Flexural Strength and Shear Capacity – IS recommendations<br />
―Ultimate flexural strength ― Ultimate shear resistance (bonded) ―<br />
Shear reinforcement as per IS Codal provisions.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
7. Design <strong>of</strong> PSC Beams - Elastic Design ― Permissible stresses ―<br />
Design <strong>of</strong> symmetrical and unsymmetrical sections ― limiting zone.<br />
Limit State Design ― Limit state <strong>of</strong> serviceability and collapse ― Design<br />
<strong>of</strong> sections for limit state <strong>of</strong> collapse in flexure. Design <strong>of</strong> sections for<br />
axial tension. Design <strong>of</strong> reinforcement to resist shear. Design <strong>of</strong><br />
composite sections.<br />
11 Hrs<br />
8. Anchorage Zone and End Blocks – Transmission <strong>of</strong> prestress in<br />
pretensioning systems ― Transmission length ― Anchorage stresses in<br />
post tensioning systems – End blocks, Design <strong>of</strong> end block by IS<br />
Method<br />
06 Hrs<br />
9
Text Books :<br />
1. Sinha.N.C. & Roy.S.K. “Fundamentals <strong>of</strong> Prestressed Concrete” S<br />
Chand. Co New Delhi. 1997 [ Ch.1,2]<br />
2. Krishnaraju.N “Prestressed Concrete” Tata McGraw Hill, New<br />
Delhi.2007 [Ch.1 to 14) Ninth reprint 2010.<br />
Reference Books:<br />
1. Dayaratnam.P “ Prestressed Concrete Structures” oxford – IBH<br />
publishers - 1996<br />
2. LiN .T.Y, Margy Burns ‘Design <strong>of</strong> Prestressed Concrete Structures.<br />
John Willey & Sons - 1981<br />
3. IS 1343- 1980 “Design <strong>of</strong> Prestressed Concrete Structure”, BIS New<br />
Delhi.<br />
CV 751 THEORY OF ELASTICITY (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Introduction to Mathematical theory <strong>of</strong> elasticity – Definition <strong>of</strong><br />
Continuum – Stress and strain at a point – Constitutive laws –<br />
Generalised Hooke’s law – Strain-displacement relations.<br />
04 Hrs<br />
2. Analysis <strong>of</strong> Stress : Introduction – differential equations <strong>of</strong> equilibrium –<br />
Boundary conditions – Principal stresses and principal Planes – Mohr’s<br />
Circle.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
3. Analysis <strong>of</strong> Strain : Introduction - Plane stress and Plane strain –<br />
Principal planes – measurement <strong>of</strong> surface strains – Strain rossetes –<br />
Compatibility concept – need and physical significance – Compatibility<br />
equation in terms <strong>of</strong> strains – compatibility equations for plane stress<br />
and plane strain cases – Airy’s stress function – Polynominal stress<br />
functions<br />
07 Hrs<br />
4. Two-dimensional Problems in Rectangular Coordinates – Bending <strong>of</strong> a<br />
cantilever beam subjected to end load and u.d.l – Simply supported beam<br />
subjected to UDL – Displacements in Cantilever and S.S.Beams 05 Hrs<br />
5. Two dimensional problems in polar coordinates : Strain-displacement<br />
relations – Equations <strong>of</strong> equilibrium – Compatibility equation – Stress<br />
function<br />
05 Hrs<br />
6. Stress Distribution Symmetrical About an Axis – Thick disc cylinders –<br />
Rotating discs and cylinders<br />
04 Hrs<br />
10
7. Effect <strong>of</strong> Circular Holes on Stress Distribution in Plates- Subjected to<br />
Tension, compression and shear – Stress concentration factor 05 Hrs<br />
8. Stresses Due to a Knife Edge Load on the straight edge <strong>of</strong> a semiinfinite<br />
plate : Boussiness’s problem – Problems <strong>of</strong> wedges subjected<br />
to different load conditions<br />
07 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Timonshenko S P and Goodier.J.N. “ Theory <strong>of</strong> Elasticity” International<br />
Students’ Education McGraw Hill Book Co Inc. New Delhi, Third edition<br />
2007 [Ch.1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]<br />
2. Sadhu Singh “Theory <strong>of</strong> Elasticity”. Khanna Publishers,New Delhi, 2007<br />
[ Ch.2,3,4,5,6,7)<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Valliappan.C “ Continuum Mechanics Fundamentals” Oxford and IBH<br />
Publishing Co.Ltd, New Delhi - 2003<br />
2. Srinath.L.S. “ Advanced Mechanics <strong>of</strong> Solids” Tata McGraw Hill<br />
Publications Co., Ltd., New Delhi- Third edition- third reprint 2009<br />
CV 752 DESIGN OF MASONRY STRUCTURES (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Introduction: Types <strong>of</strong> masonry units – properties – suitability and<br />
applications-classification and properties <strong>of</strong> mortars-description <strong>of</strong> types <strong>of</strong><br />
mortar as per IS 1905.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
2. Masonry Construction: Defects and errors in masonry constructions –<br />
causes <strong>of</strong> cracks in masonry-methods <strong>of</strong> controlling and prevention <strong>of</strong> cracks<br />
in masonry.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
3. Strength <strong>of</strong> Masonry: Factors affecting strength <strong>of</strong> masonry – unit<br />
strength, joint thickness – rate <strong>of</strong> absorption, effects <strong>of</strong> curing etc. – stresses<br />
in masonry under direct compressive force- derivation <strong>of</strong> formulae. 05 Hrs<br />
4. Permissible Stresses: Permissible basic compressive stress in masonrystress<br />
reduction factor – area reduction factor – shape modification factorincrease<br />
in permissible stresses for eccentric – vertical and lateral loadspermissible<br />
tensile stress and shear stress.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
5. Design Considerations: Effective height <strong>of</strong> walls and columns-different<br />
cases-effective length- different design cases-effective thickness-slenderness<br />
ratio-eccentricity-load dispersion in masonry- arching action-lintels – design<br />
<strong>of</strong> lintels for different design situations.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
6. Design <strong>of</strong> Structural Masonry- 1 : Design <strong>of</strong> walls subjected to axial load<br />
& eccentric load.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
11
7. Design <strong>of</strong> Structural Masonry- 2 : Design <strong>of</strong> walls with openings in<br />
different positions-free standing wall-design <strong>of</strong> load bearing masonry<br />
buildings up to 3 storeys as per provisions <strong>of</strong> IS 1905 and SP 20. 05 Hrs<br />
8. Reinforced Masonry: Applications –methods <strong>of</strong> placement <strong>of</strong><br />
reinforcement in masonry- flexural and compression elements- design <strong>of</strong><br />
reinforced masonry lintels and slabs.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. Hendry A.W. Structural Masonry, Mac Milan Education Ltd., 1990<br />
(Ch 1 – 6)<br />
2. P.Dayaratham- Brick and Reinforced Brick Structures – Oxford and<br />
IBH, 1987 ( Ch – 1 -8)<br />
Reference Books:<br />
1. SP21 Summary <strong>of</strong> IS codes on Building Materials – BIS New Delhi<br />
2. SP20 Hand book on Masonry design and Construction BIS New<br />
Delhi<br />
3. IS 1905 Code <strong>of</strong> Practice for use <strong>of</strong> un-reinforced Masonry – BIS<br />
New Delhi<br />
4. Sinha B.P., Davies S.R. “ Design <strong>of</strong> Masonry Structures” E& FN<br />
spon – 1997<br />
<strong>12</strong>
CV753 ECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Introduction : Environment – Definition– Components <strong>of</strong> Environment<br />
and their interaction – Ecology – Definition – Sub divisions <strong>of</strong> Ecology<br />
04 Hrs<br />
2. Concepts <strong>of</strong> Ecosystem : Structural and functional characteristics <strong>of</strong><br />
an ecosystem – Balanced ecosystem, Biological control – Production and<br />
decomposition in nature<br />
06 Hrs<br />
3. Principles and Concepts Pertaining to Energy in Ecological System:<br />
Fundamental principles related to energy – Energy environment – Laws<br />
<strong>of</strong> thermodynamics – Energy system – Pathways <strong>of</strong> energy in the<br />
biosphere – Concept <strong>of</strong> productivity – its measurement – Food chains/<br />
food webs – trophic levels – trophic structure<br />
08 Hrs<br />
4. Bio-Chemical Cycles : Concept <strong>of</strong> bio-geo-chemical cycles – significance<br />
– pathways <strong>of</strong> matter in the biosphere – C, N, S and P cycles 05 Hrs<br />
5. Freshwater Ecology : Fresh water environment types and limiting<br />
factors – classification <strong>of</strong> freshwater organisms – Fresh water biota<br />
(Flora & Founa) Zonation in streams – Eutrophication <strong>of</strong> lakes 06 Hrs<br />
6. Marine Ecology : Marine environment, Marine biota, Zonaton in the<br />
area ( Case study) Estuarine ecology<br />
03 Hrs<br />
7. Pollution and Environmental Health : Types <strong>of</strong> pollution- Effect on<br />
human health – Effects on aquatic and terrestrial systems 04 Hrs<br />
8. Global Environmental Problems : Acid rain – Ozone layer depletion –<br />
Green house effect – Global warming<br />
06 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Sharma.P.D. “Ecology and Environment” Rastogi Publications,<br />
2009 (Ch.1,2,3,4,7,8)<br />
2. Odum.E.P “Ecology” I.B.M.Limited,2008 (Ch.1,2,3,4,5)<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1 Kormondy “Concept <strong>of</strong> Ecology”4 th Edition Dorling Kindersteng (India)<br />
Pvt.ltd. 2007<br />
2 Garg.S.K. “Environmental <strong>Engineering</strong> – Vol II”<br />
3 Kotpal and Bali “Concepts <strong>of</strong> Ecology” Visahi Publications, Jalandhar<br />
13
CV 754 TRAFFIC ENGINEERING (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Scope <strong>of</strong> Traffic <strong>Engineering</strong> : Definition <strong>of</strong> Traffic engineering – Road<br />
user & Vehicular characteristics Power and performance <strong>of</strong> vehicle –<br />
Rolling resistance – Air resistance – Grade resistance – Acceleration and<br />
retardation – Transmission losses – Power requirements with numerical<br />
examples – Dynamic characteristics – static characteristics viz., weight <strong>of</strong><br />
vehicle – Power <strong>of</strong> the vehicle – speed and breaking characteristics with<br />
numerical examples – Off tracking <strong>of</strong> vehicles.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
2. Traffic Parameter Studies and Analysis : Speed – Types <strong>of</strong> speeds viz.,<br />
spot speed – running speed. Overall speed – Time mean speed – Space<br />
mean speed – Uses – Methods – Presentation <strong>of</strong> speed study data with<br />
numerical examples – Relationship between time mean speed and space<br />
mean speed – Variance – Speed and Delay studies – uses – methods –<br />
Advantages - numerical examples Traffic volume Analysis<br />
06 Hrs<br />
3. Traffic Flow Characteristics : Traffic capacity studies. Traffic volume –<br />
Traffic density – Traffic capacity – Basic capacity – possible capacity.<br />
Determination <strong>of</strong> theoretical capacity <strong>of</strong> a single lane – Relationship<br />
between speed and maximum capacity – Factors affecting practical<br />
capacity. Relationship between design capacity and level <strong>of</strong> service with<br />
numerical applications.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
4. Accident Studies: Objectives – causes – records – preparation <strong>of</strong> accident<br />
report – Condition diagram – Collision diagram – Accident investigations.<br />
Analysis <strong>of</strong> individual traffic accidents – Analysis <strong>of</strong> speed from skid<br />
resistance – Collision <strong>of</strong> moving vehicle with parked vehicle – Two vehicles<br />
approaching at right angles collide – Measures for reduction in accident<br />
rates. Numerical examples.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
5. Traffic Flow Theories: Definition – relationship between speed, flow and<br />
concentration – Fundamental diagram <strong>of</strong> traffic flow – Green shield theory –<br />
Lighthill and Whitham’s theory – Applications with numerical examples.<br />
Queuing theory – applications- Arrival pattern – service facility<br />
characteristics, Queuing discipline – order <strong>of</strong> service – Assumptions<br />
numerical examples. Car following theory.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
6. Probability Distributions: Normal distribution – Application – Poisson’s<br />
distribution, Significance test for observed traffic data – Chi-square test –<br />
Goodness <strong>of</strong> fit – correlation - regression analysis (linear only) for relevant<br />
problems. Sample size traffic forecast simulation technique.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
14
7. Traffic Regulation and Control: Vehicle, Driver and Road Control – Traffic<br />
Regulation – One way traffic signs – Traffic markings.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
8. Traffic Signals : Vehicle actuated and synchronized signals. Signal<br />
coordination. Webster method <strong>of</strong> Design <strong>of</strong> signal and IRC method with<br />
numerical examples. Traffic rotary elements, design guidelines with<br />
numerical examples. Design <strong>of</strong> street lighting – road side arboriculture.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Khanna & Justo, “ Highway <strong>Engineering</strong>” Nemchand Bros ,2008<br />
(Ch.1,2,4)<br />
2. Kadiyali.L.R “ Traffic <strong>Engineering</strong> and Transport Planning” Khanna<br />
Publishers 7 th edition 2005 (Ch.2,3,5, 6,7,8)<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Pignataro “ Traffic <strong>Engineering</strong>” Printice Hall<br />
2. Edward K Morlok “ Introduction to Transportation <strong>Engineering</strong> and<br />
Planning” McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
15
CV 761 STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Introduction; Definition <strong>of</strong> vibration – Parts <strong>of</strong> a vibrating system –<br />
Degrees <strong>of</strong> freedom – Undamped and damped free vibration <strong>of</strong> a single<br />
degree <strong>of</strong> freedom system – Logarithmic decrement.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
2. Forced Vibration; Undamped and damped forced vibration <strong>of</strong> a single<br />
degree <strong>of</strong> freedom system – response to harmonic loading – rotational and<br />
reciprocating unbalance<br />
05 Hrs<br />
3. General System <strong>of</strong> Loading; Duhamel’ Integral – dynamic load factor –<br />
response spectrum – SDOF system subjected to harmonic base excitation<br />
– vibration measuring instruments –vibration isolation. 06 Hrs<br />
4. MDOF Systems: Free vibration – natural frequencies – Orthoganality<br />
principle – eigen values and eigen vectors<br />
05 Hrs<br />
5. MDOF System(Contd…) : Shear buildings modeled as MDOF systems –<br />
Free vibrations.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
6. MDOF System(Contd…); Forced undamped vibration <strong>of</strong> shear buildings<br />
– Modal superposition method – Response to harmonic excitation.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
7. MDOF System(Contd…); Forced damped vibration <strong>of</strong> shear buildings –<br />
Decoupling <strong>of</strong> equation <strong>of</strong> motion.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
8. Continuous Systems; Analysis <strong>of</strong> continuous systems like axial vibration<br />
<strong>of</strong> rods and flexural vibration <strong>of</strong> beams.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
Text Books:<br />
1.Mukhopadhya M. “Vibrations, Dynamics and Structural Systems”<br />
Oxford IBH Publications, 2000 (Ch. 1, 2, & 8)<br />
2. Mario Paz. “Structural Dynamics” CBS Publishers, 2004 (Ch. 3, 4, 5, 6<br />
& 7)<br />
Reference Books:<br />
1. Clough & Penzen. “Dynamics <strong>of</strong> Structures” McGraw Hill Publishers<br />
2004<br />
2. Anil K Chopra. “Dynamics <strong>of</strong> Structures” PHI Publishers 2006<br />
16
CV 762 ADVANCED DESIGN OF RC STRUCTURES (3-0-0)3<br />
1. Design <strong>of</strong> RC overhead circular and rectangular water tanks with<br />
supporting towers<br />
06 Hrs<br />
2. Design <strong>of</strong> silos and bunkers using Janssen’s Theory 06 Hrs<br />
3. Introduction to shell and folded plate ro<strong>of</strong>s – their forms and structural<br />
behaviour<br />
10 Hrs<br />
4. Yield line analysis <strong>of</strong> slabs with equilibrium method and virtual work<br />
method<br />
10 Hrs<br />
5. Design <strong>of</strong> Grid Floors by approximate method 05 Hrs<br />
6. Design <strong>of</strong> flat slabs by Direct Design Method (with and without drops)<br />
05 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Devadas Menon and Unnikrishnan.P “Reinforced Concrete Structures”<br />
2 Varghese.P.C. “Limit State Design <strong>of</strong> Reinforced Concrete Vol.II” Prentice<br />
Hall <strong>of</strong> India (P) ltd, New Delhi<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Jai Krishna and Jain “Plain and Reinforced Concrete Vol.II” Nem Chand<br />
Bros. Roorkee<br />
2. Varghese P.C “ Advanced Reinforced Concrete Design” Prentice Hall <strong>of</strong><br />
India - 2007<br />
17
CV763 RURAL WATER SUPPLY AND SANITATION (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Introduction : Importance <strong>of</strong> Village community in India – Need for<br />
a protected water supply – Traditional sources <strong>of</strong> water in rural areas –<br />
Investigation and selection <strong>of</strong> water sources<br />
04 Hrs<br />
2. Rural Water Supply: Waterborne diseases – protection <strong>of</strong> well waters –<br />
Drinking water quality standards – Water lifting arrangements – Water<br />
supply system – BWS, MWS, PWS.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
3. Water Treatment Methods: Treatment methods - Disinfection,<br />
Deflouridation – Hardness and iron removal – water quality surveillance<br />
06 Hrs<br />
4 Rural Sanitation: Public latrine – night soil-collection and disposal –<br />
trenching and composting methods – Two pit latrines, aqua privy, W.C,<br />
septic tank – soak pit – Drainage Systems – Storm water and sullage<br />
disposal.<br />
08 Hrs<br />
5. Rain Water Harvesting: Different methods <strong>of</strong> harvesting and<br />
precautions to be taken.<br />
04 Hrs<br />
6. Refuse Collection & Disposal: Garbage, ash, rubbish – collection<br />
methods – Transportation – Disposal – Composting– Dung Disposal–<br />
Bio-gas plant<br />
06 Hrs<br />
7. Communicable Diseases And Insect Control: Terminology –<br />
classifications – modes <strong>of</strong> communication – general methods <strong>of</strong> control –<br />
house fly and mosquito – life cycle – disease transmission and control<br />
measures . 04 Hrs<br />
8. Milk Sanitation: Essential tests for milk quality – pasteurization –<br />
quality control – cattle borne disease – planning for a cow shed 04 Hrs<br />
Text Books:<br />
1 Salveto “Environmental Sanitation” Mc Graw Hill, II Edition, 1970<br />
2 Steel.E.W. “Water Supply and Sewerage.” Mc Graw Hill, V Edition, 1985<br />
Reference Books:<br />
1. Gourishekar Gosh “ Water Supply in Rural India : Policy and Programme”<br />
APH Publishing Corporation- 2006<br />
2. Allan Greenwell “ Rural Water Supply” Bibliolife publishers<br />
18
CV 764 ADVANCED TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Highway Capacity: General – Importance <strong>of</strong> capacity in highway<br />
transportation studies – capacity for uninterrupted flow condition (HCM)<br />
– level <strong>of</strong> service factor affecting level <strong>of</strong> service. Capacity <strong>of</strong> two lane<br />
rural highway without access control – Capacity <strong>of</strong> urban street.<br />
Capacity <strong>of</strong> Rotary intersection – U.K. practice. Capacity <strong>of</strong> weaving<br />
section – manual approach. Multi weaving sections. Problems on the<br />
above. Norman method <strong>of</strong> determining signalized intersection capacity<br />
06 Hrs<br />
2. Vehicle Arrivals, Headways and Gaps: Probabilistic aspects <strong>of</strong> traffic<br />
flow-Spacing and headway characteristics. Study <strong>of</strong> vehicle arrivals.<br />
Poission’s distribution with numerical examples. Limitation <strong>of</strong> Poission’s<br />
distribution. Gap and headway distribution. Shifted exponential<br />
distribution- Erlang distribution- with numerical examples. Pearson type<br />
– III distribution; Gap acceptance – Gap and lag – Gap acceptance study<br />
techniques, critical lag distribution <strong>of</strong> gap acceptance.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
3. Simulation <strong>of</strong> Traffic – Advantages – Steps in simulation Techniques.<br />
Model validation<br />
05 Hrs<br />
4. Transport Planning Process – Inter-dependence <strong>of</strong> the land use and<br />
traffic. Systems approach to transportation planning. Stages in<br />
transportation planning. Survey and analysis <strong>of</strong> existing conditions.<br />
Forecast, Analysis <strong>of</strong> future conditions and plan Synthesis, evaluation.<br />
Programme adoption and Implementation<br />
05 Hrs<br />
5. Trip Generation – Trip purpose – Factors governing Trip generation and<br />
Attraction on routes Multiple linear regression analysis – Assumptions<br />
validity in trip generation studies. Aggregated and Disaggregated<br />
analysis. Criteria for evaluation <strong>of</strong> Regression equations, category<br />
analysis – Assumptions. Critical appraisal <strong>of</strong> category analysis<br />
techniques.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
6. Trip Distribution : Method <strong>of</strong> trip distribution, Uniform factor method,<br />
Average factor method – Fratar method. Furness method, criticism <strong>of</strong><br />
growth factor method, Gravity model, Calibration <strong>of</strong> gravity model,<br />
Tanner’s model, Opportunity model with relevant numerical problems<br />
05 Hrs<br />
7. Traffic Assignment : General principles – Assignment techniques – All or<br />
nothing assignment – Multiple route assignment – capacity resistant<br />
assignment – Smock method –Diversion curve with numerical examples<br />
05 Hrs<br />
19
8. Modal Split - Factors affecting modal split – Modal split in transportation<br />
planning process.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Kadiyali.L.R. “Transport Planning” 7 th edition, Khanna Publishers,<br />
2006 (Ch.1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8)<br />
2. Black John, “ Urban Transport planning”, Croom Helm ltd, Landon<br />
3 rd edition, 2005 (Ch.3,5,7)<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Hutchison A G ‘ Urban and Regional models in Geography and<br />
Planning John Wiley and sons, London, 5 th edition, 2002<br />
2. Drew and Thomson “Traffic <strong>Engineering</strong> and Planning”, Croom Helm<br />
ltd, London 5 th edition<br />
20
CV 708 ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY (1-0-2) 2<br />
1. Determination <strong>of</strong> Solids in Sewage : Total Solids- Suspended Solids-<br />
Dissolved Solids- Volatile Solids- Fixed Solids – Settleable Solids<br />
2. Determination <strong>of</strong> Chlorides and Sulphates.<br />
3. Determination <strong>of</strong> Alkalinity, Acidity and pH.<br />
4. Determination <strong>of</strong> Calcium, Magnesium and Total Hardness.<br />
5. Determination <strong>of</strong> Dissolved Oxygen and Determination <strong>of</strong> BOD<br />
6. Determination <strong>of</strong> COD.<br />
7. Determination <strong>of</strong> percentage <strong>of</strong> available chlorine in bleaching powder,<br />
Residual Chlorine and Chlorine Demand.<br />
8. Jar Test for Optimum Dosage <strong>of</strong> Alum – Turbidity determination by<br />
Nephelometer.<br />
9. Determination <strong>of</strong> Iron – Phenanthroline method.<br />
10.Determination <strong>of</strong> Fluorides SPANDS Method.<br />
11.MPN Determination.<br />
<strong>12</strong>.Determination <strong>of</strong> Nitrates by spectrophotometer.<br />
13.Determination <strong>of</strong> sodium and potassium by flame photometer.<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Manual <strong>of</strong> Water and Wastewater Analysis – NEERI Publication<br />
2. Standard Methods for Examination <strong>of</strong> Water and Wastewater<br />
(1995). ARHA – Water Pollution Control Federation – American<br />
Water Works Association – Washington DC.<br />
3. IS Standards – 2490-1974, 3360-1974, 3307-1974.<br />
4. Sawyer.C.N. Mccarty P.L & Parkin.G.F “ Chemistry for<br />
Environmental <strong>Engineering</strong> & Science” , Tata Mc.Graw Hill-<br />
2009<br />
21
CV 801 CONSTRUCTION PLANNING AND MANAGEMENT (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Introduction to <strong>Engineering</strong> Economics – Basic concepts <strong>of</strong> economic<br />
analysis – Micro and Macro analysis – project feasibility – economic and<br />
financial feasibility.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
2. <strong>Engineering</strong> Planning Methods : Benefit cost ratio – interest formulae –<br />
present worth – future worth Annual equivalent – basis for comparison <strong>of</strong><br />
alternatives – rate <strong>of</strong> return method – break even analysis – planning<br />
methods – problems on the above<br />
05 Hrs<br />
3. Linear Programming : Standard form <strong>of</strong> a linear programming – problem<br />
formulation – graphical solution – simplex method – maximization<br />
and minimization.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
4. Construction Industry and Management : Introduction – value<br />
engineering time management – labour and material management – contract<br />
and contractor – organization and administration – industrial financial<br />
management<br />
05 Hrs<br />
5. Construction Planning : Introduction – time estimates – planning<br />
methods <strong>of</strong> projects – Bar and Milestone charts – PERT and CPM network<br />
analysis – project feasibility – cost model – direct cost – indirect cost – total<br />
cost – optimum cost – optimum duration <strong>of</strong> project – problems – Line <strong>of</strong><br />
Balance Technique – resource allocation and updating<br />
07 Hrs<br />
6. Construction Equipment : Introduction – various earth moving<br />
equipments – hoisting equipments – trenching machines equipment for<br />
highway construction – factors for selecting equipment – concrete mixers and<br />
plants – conveyors and rollers – special equipments – economic life <strong>of</strong><br />
equipments<br />
. 07 Hrs<br />
7. Work Study in Construction, safety measures – Project control during<br />
construction – Project supervision<br />
02 Hrs<br />
8. Transportation Problems : Introduction – Mathematical formulation –<br />
optimal solution <strong>of</strong> transportation problems – methods for initial basic<br />
feasible solution – summary <strong>of</strong> methods <strong>of</strong> initial BFS – North west corner<br />
method – Lowest cost entry method – Vogel’s approximation method –<br />
optimality test – Degeneracy in Transportation Problems – Unbalanced –<br />
Transportation problems<br />
06 Hrs<br />
22
Text Books :<br />
1. Subramaniam.K “Construction Management” , Anuradha Publishers,<br />
Madras, 1989 (Ch. 1 – 5)<br />
2. Peurifoy, R L “Construction Planning equipments and methods”<br />
McGraw Hill Publications 3 rd edition,1985 (Ch.6,7 & )<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Mahesh Varma “Construction Planning and Management” Metropolitan<br />
Book Co. Delhi 1982<br />
2. Sharma.S.D. “Operation Research” Khanna Publishers, New Delhi 1980<br />
23
CV 851 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS (3-0-0) 3<br />
Prerequisite : CV 751 Theory <strong>of</strong> Elasticity<br />
1. Introduction: Basic concepts and background review – stress-strain<br />
relations and strain displacement relations – matrix displacement<br />
formulation – energy concepts – equilibrium and energy methods for<br />
analyzing the structures – Rayleigh-Ritz and Gaelrkin’s methods – simple<br />
applications in structural analysis.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
2. Fundamentals <strong>of</strong> Finite Element Method: Introduction, Finite Element<br />
Modeling - Displacement functions – element coordinates - Global coordinates<br />
– Displacement functions for 1-D element and simple problems<br />
06 Hrs<br />
3. Analysis <strong>of</strong> Pin Jointed Frames : 2-D truss element and its application<br />
to simple truss problems<br />
04 Hrs<br />
4. Continuous Beams and Stiff Jointed Frames : Euler – Bernouli beam<br />
element – Hermitian interpolation function – generation <strong>of</strong> stiffness matrix<br />
and nodal load vector – Analysis <strong>of</strong> Continuous beams<br />
06 Hrs<br />
5. 2 D Frame Element : 2 D Frame Element - Solution <strong>of</strong> simple stiff<br />
jointed frames (maximum <strong>of</strong> three kinematic degrees <strong>of</strong> freedom) 04 Hrs<br />
6. Analysis <strong>of</strong> 2-Dimensional Plane stress / Plane Strain Problems :<br />
Introduction – finite element modeling – different types <strong>of</strong> triangle and<br />
quadrilateral elements, their characteristics and suitability for applications –<br />
polynomial shape functions – Lagrange’s interpolation - compatibility and<br />
convergence requirements <strong>of</strong> shape functions – element strains and stresses<br />
– element stiffness matrices, nodal load vector - application <strong>of</strong> CST, LST and<br />
quadrilateral elements for some simple problems<br />
06 Hrs<br />
7..Isoparametric Elements, Numerical Integration and Higher Order<br />
Elements : Isoparametric, superparametric and subparametric elements –<br />
necessity – description <strong>of</strong> solution process using Isoparametric elements –<br />
characteristics <strong>of</strong> Isoparametric quadrilateral elements – computation <strong>of</strong><br />
stiffness matrix – numerical integration – convergence criteria for<br />
Isoparametric elements.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
8. Axi – Symmetric Elements : Introduction – Axis – Symmetric Elements<br />
and formulation <strong>of</strong> axis symmetric triangular toroidal elements.<br />
Introduction to 3 D finite elements<br />
04 Hrs<br />
24
Text Books :<br />
1. Krishnamoorthy.C.S “Finite Element Analysis”, Theory and<br />
Programming II Edition, 1994<br />
2. Rajashekaran, “Finite Element Analysis in <strong>Engineering</strong> Design”,<br />
Wheeler publisher -2008.<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Chandru Patla.T.R, Belegundu. A.D., “Introduction to FEM”, 3 rd edition,<br />
Prentice Hall -2009.<br />
2. Mukhopadyaya. M “Matrix, Finite Element, Structural Analysis”, Oxford &<br />
IBH.Publishers<br />
3. Robert D. Cook “ Concept and Applications <strong>of</strong> Finite Element Analysis”<br />
John Wiley & Sons inc<br />
25
CV 852 ADVANCED DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Introduction , Basic principles <strong>of</strong> design – Stress strain relationship for<br />
mild steel – evaluation <strong>of</strong> fully plastic moment for mild steel beams – Plastic<br />
hinges – Shape factors and plastic moment – fixed and simply supported<br />
beams – effect <strong>of</strong> partial fixity – Rectangular portal frames – gable frames –<br />
Invariance <strong>of</strong> collapse load.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
2. Statement <strong>of</strong> Theorems: Application <strong>of</strong> principle <strong>of</strong> virtual work –<br />
Partial and over complete collapse – Trial and error method – Method <strong>of</strong><br />
combined mechanisms – plastic moment distribution method and other<br />
methods <strong>of</strong> determining plastic collapse load – estimation <strong>of</strong> deflection –<br />
factors affecting fully plastic moment<br />
06 Hrs<br />
3. Minimum Weight Design Theories. Application <strong>of</strong> theorems and<br />
methods <strong>of</strong> solution – Plastic analysis applied to the design <strong>of</strong> fixed and<br />
continuous beams – portal and gable frames.<br />
04 Hrs<br />
4. Design <strong>of</strong> Laterally Unsupported Beams: Design <strong>of</strong> built up beams.<br />
Design <strong>of</strong> encased beams.<br />
03 Hrs<br />
5. Design <strong>of</strong> Open Web Structures, Advantages, Design Methods, Design <strong>of</strong><br />
open web beams.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
6. Moment Resistant Connections large moment resistant connections –<br />
semi – rigid connections and behavior <strong>of</strong> semi – rigid connections – beam line<br />
method – modified slope deflection method – modified moment distribution<br />
method.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
7. Non Symmetrical Bending : Principal Axes <strong>of</strong> a Section – stress due to<br />
unsymmetrical bending – deflection <strong>of</strong> beams under unsymmetrical bending<br />
– design <strong>of</strong> purlins subjected to unsymmetrical bending 06 Hrs<br />
8. Tubular Structures – Introduction – permissible stresses – Tube columns<br />
and compression members – Tube tension members – design <strong>of</strong> members <strong>of</strong><br />
tubular ro<strong>of</strong> truss for given member forces and their combinations – joints in<br />
tubular trusses – design <strong>of</strong> tubular beams and purlins<br />
06 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Subramanyan.N “ Design <strong>of</strong> Steel Structures” Oxford University<br />
Press, USA, 2003 ( Ch. 1 to 6 )-<br />
2. Duggal.S.K. “ Design <strong>of</strong> Steel Structures” IIIrd Edn. Tata Mc Graw<br />
Hill, 2008 (Ch. 5 - 8 )<br />
26
Reference Books :<br />
1 Segui. “Design <strong>of</strong> Steel Structures” Thomson Publishers- 2009<br />
2. Negi.L.S, “Design <strong>of</strong> Steel Structures” Tata Mc Graw Hill -2008<br />
3. IS 800- 2007, BIS, New Delhi<br />
27
CV 853 ENVIRONMENT IMPACT ASSESSMENT (3-0-0) 3<br />
1 Sustainable development and ecological factors EIA – EIS – FONSI – Need<br />
for EIA Studies – Baseline Information.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
2. Step-by-step procedures for conducting El A, Limitations <strong>of</strong> EIA 05 Hrs<br />
3 Frame work Impact Assessment – Developmental projects –<br />
environmental setting – objectives and Scope <strong>of</strong> EIA – Contents <strong>of</strong> EIA –<br />
methodologies – techniques <strong>of</strong> EIA.<br />
08 Hrs<br />
4 Assessment and prediction <strong>of</strong> impacts on attributes : Air – Water – Noise<br />
–Land Ecology – Soil – Cultural and Socio-economic Environment<br />
05 Hrs<br />
5 EIA guidelines for developmental projects, Rapid and comprehensive EIA<br />
05 Hrs<br />
6 Public Participation in Environmental Decision making – Practical<br />
Considerations in preparing Environmental Impact Assessment and<br />
Statements.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
7 Simple methods for impact identification : Matrices – networks and check<br />
lists<br />
04 Hrs<br />
8 EIA for water resource developmental projects, highway projects:<br />
Nuclear power plant projects – mining projects (Coal, Iron ore)<br />
05 Hrs<br />
Text Books:<br />
1 Jain, R.K., Urban.L.V Staceyers “Environmental Impact Assessment”, Mc<br />
Graw Hill, New York, 1993 (Ch.1,2,3,4,5,7,8)<br />
2. Anjaneyalu, Y., ‘Environment Impact Assessment Métrologies’<br />
B.S. Publications Hyderabad,2007 (Ch.4,5,6,7,8)<br />
Reference Books:<br />
1. Guidelines for EIA <strong>of</strong> developmental Projects Ministry <strong>of</strong> Environment<br />
and Forests, GOI. 2002<br />
2. Canter,L.W., “Environment Impact Assessment” - McGraw Hill<br />
Publication 2008<br />
28
CV854 ADVANCED FOUNDATION DESIGN (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Shallow Foundations :<br />
Presumptive bearing capacity according to BIS – Factors affecting bearing<br />
capacity and settlement – Factors influencing selection <strong>of</strong> depth <strong>of</strong><br />
foundation – Problems on settlement<br />
05 Hrs<br />
2. Shallow Foundation (Contd..) :<br />
Principles <strong>of</strong> design <strong>of</strong> footings _ Design <strong>of</strong> Isolated footing – Combined<br />
footing – Strap footing – Strip footing and raft ( proportioning only) 06 Hrs<br />
3. Pile Foundation :<br />
Pile groups – Number <strong>of</strong> piles and spacing – group capacity <strong>of</strong> piles –<br />
group efficiency <strong>of</strong> piles – settlement <strong>of</strong> piles – negative skin friction and<br />
under reamed piles.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
4. Drilled Piers :<br />
Introduction – Construction – Advantages and disadvantages <strong>of</strong> drilled<br />
piers<br />
05 Hrs<br />
5. Caissons :<br />
Introduction – Types <strong>of</strong> Caissons – Design aspects <strong>of</strong> caissons –<br />
Construction <strong>of</strong> open, pneumatic and floating caissons – their advantages<br />
and disadvantages – Stability <strong>of</strong> floating caissons<br />
05 Hrs<br />
6. Well Foundation : Shapes <strong>of</strong> wells – components <strong>of</strong> well foundation and<br />
their design aspects – forces acting on a well foundation – Sinking <strong>of</strong> wells<br />
– causes and remedies <strong>of</strong> tilts and shifts 05 Hrs<br />
7. Foundations on Expansive Soils :<br />
Introduction – definition – Mineral structure – identification <strong>of</strong> expansive<br />
soils – foundation treatment for structures on expansive soils 05 Hrs<br />
8. Machine Foundations :<br />
Introduction – Types <strong>of</strong> machine foundations –Basic definitions – Degrees<br />
<strong>of</strong> freedom <strong>of</strong> a block foundation – general criteria for design<br />
<strong>of</strong> machine foundation - free and forced vibrations – vibration analysis <strong>of</strong> a<br />
machine foundation – Determination <strong>of</strong> natural frequency - vibration<br />
isolation and control<br />
06 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Arora.K.R. “ Soil Mechanics and Foundation <strong>Engineering</strong>” Standard<br />
Publishers Distributors, Delhi, Fifth edition 2001 ( Ch.1,2,3,4,5,6,8)<br />
2. Gopal Ranjan & Rao. A.S.R “ Basic and Applied Soil Mechanics” New<br />
Age International Publishers, 2 nd edition 2006 ( Ch.1,2,3,6,7,8)<br />
29
Reference Books :<br />
1. Punmia.B.C, Ashok Kumar Jain, Arun Kumar Jain “ Soil Mechanics<br />
and Foundations” Laxmi Publications (P) ltd, 16 th edition Oct. 2008<br />
(Ch.1,2,3,6,8)<br />
2. Venkataramaiah.C “ Geotechnical <strong>Engineering</strong>” New Age International<br />
Publishers, 3 rd edition 2006 (ch.1,2,3,5,6,8)<br />
30
CV855 WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Introduction : Fields <strong>of</strong> water resources engineering – Economics in<br />
Water resource planning – Social aspects – Planning <strong>of</strong> water resources<br />
surveys – Water resources <strong>of</strong> the world – Water resources in India – Water<br />
demand for various purpose – Need for conserving water resources 05 Hrs<br />
2. Water Law : Riparian right – Appropriative rights – Permit system –<br />
Water codes – Ground water laws- Inter state problems – International<br />
problems<br />
04 Hrs<br />
3. Floods : Importance <strong>of</strong> flood studies – Definition <strong>of</strong> flood – Causes <strong>of</strong><br />
floods – Factors affecting flood flow – Estimating the magnitude and<br />
frequency <strong>of</strong> floods – Empirical formulae – Rational method – Envelope<br />
curve – Unit hydrograph method and probability methods – Design floods<br />
– Standard project flood and probable maximum flood. 06 Hrs<br />
4. <strong>Engineering</strong> Economy in Water Resources Projects : Introduction –<br />
Steps involved in economy study – Economics <strong>of</strong> combined flood projects<br />
and multi purpose projects – Principle <strong>of</strong> Optimization in planning –<br />
Capital budgeting<br />
05 Hrs<br />
5. Planning for Water Resources Development : Definition <strong>of</strong> Planning –<br />
Levels <strong>of</strong> planning – Phases <strong>of</strong> planning – Objectives <strong>of</strong> Planning – Project<br />
formulation – Project evaluation – Environmental aspects in planning –<br />
System analysis – Pitfalls in Planning<br />
06 Hrs<br />
6. Multipurpose Projects : Functional requirements – Compatibility <strong>of</strong><br />
multipurpose uses – Cost Allocation to various uses in multipurpose<br />
projects planning – Component parts <strong>of</strong> a multipurpose river basin<br />
development – Operation <strong>of</strong> multi purpose reservoirs – Water shed<br />
management – Small dams v/s big dams – Economic height <strong>of</strong> a dam<br />
05 Hrs<br />
7. Integrated Water Resource Development : Main Objectives – Secondary<br />
objectives like reclamation <strong>of</strong> water logged areas – Control <strong>of</strong> overdraft <strong>of</strong><br />
ground water – Salt water intrusion etc – Aspects <strong>of</strong> integrated and<br />
conjunctive use <strong>of</strong> water and their constraints – A brief description <strong>of</strong><br />
perspective water resources development <strong>of</strong> Himalayan and Peninsular<br />
rivers <strong>of</strong> India<br />
06 Hrs<br />
31
8. Organisation <strong>of</strong> Water Resources Development : Present<br />
administrative structures – problems involved therein – Organizational<br />
setup for execution <strong>of</strong> water resources development and river basin<br />
development<br />
05 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1 Subramanya.K “ <strong>Engineering</strong> Hydrology” Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing<br />
Company Ltd., New York, 2008.<br />
2 Linsley.K and Frozini.J.B “ Water Resources <strong>Engineering</strong>’ International<br />
Students Edition, McGraw Hill Kogakusha Ltd.,<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Garg. S.K “ Hydrology and Water Resources Engg” Khanna<br />
Publishers, New Delhi, India<br />
2 Gupta.B.L & Amith Gupta “Water Resources Systems and<br />
Management” Standard Publishers & Distributors, Delhi<br />
32
CV 856 URBAN AND RURAL PLANNING (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. History and Development <strong>of</strong> Settlement Planning – Introduction –<br />
Early civilizations – Egyptian cities – Greek cities – Roman cities –<br />
Medieval cities – Renaissance cities<br />
04 Hrs<br />
2. Planning in Ancient India : Indus Valley <strong>Civil</strong>ization – The Buddhist<br />
period – Mauryan period and the Gupta period – India during the<br />
medieval and Renaissance period<br />
03 Hrs<br />
3. The Industrial Revolution and Urban Planning : The Garden city<br />
concept – Satellite Towns – Philosophy <strong>of</strong> Patrick Geddes – Le Carbusier<br />
– C.A. Doxiades – Evolution <strong>of</strong> cities 05 Hrs<br />
4. Principles and Processes <strong>of</strong> Planning : Introduction – Types <strong>of</strong><br />
planning – Types <strong>of</strong> surveys – Concept and objectives <strong>of</strong> Zoning<br />
05 Hrs<br />
5. Planning Theory : Land use theories – Descriptives – Exploratory and<br />
Speculative theories – Master Plan and land uses<br />
06 Hrs<br />
6. Transportation Planning : Classification and hierarchy –<br />
Recommendations for design <strong>of</strong> roads – Traffic flow characteristics<br />
- Transport Surveys and Parking Surveys 06 Hrs<br />
7. Rural Planning : Definition – Surveys – Development plan for a village –<br />
Problems <strong>of</strong> rural housing – Areas <strong>of</strong> development – Socio Economic<br />
aspects <strong>of</strong> housing<br />
07 Hrs<br />
8. Legislation in Planning : Objectives <strong>of</strong> Development Controls – Technical<br />
considerations for formation <strong>of</strong> Building Bye-laws – Urban local bodies –<br />
Public health and sanitation – Public works and public utilities –<br />
Education and Social Welfare Development – Administrative and General<br />
Functions – Obligatory and Discretionary functions<br />
06 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Abir Bandyapadhyay “ Text Book <strong>of</strong> Town Planning” Books and Allied (P)<br />
ltd, Calcutta, India 2000 ( Ch.1,2,3,4,5,6,8)<br />
2. Rame Gowda. K.S “ Urban and Regional Planning”, Prasaranga,<br />
University <strong>of</strong> Mysore, Mysore, 1986 ( Ch.7)<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Arthur.B.Gallion Simon Eisner “ The Urban Pattern” CBS Publishers and<br />
Distributors, New Delhi, 1998<br />
2. Rangawala.S.C., Rangawala P.S & Rangawala.K.S “ Town Planning”<br />
Charotar Publishing House, Anand, India, 1987<br />
33
CV 861 EARTHQUAKE RESISTANT DESIGN OF STRUCTURES<br />
(3-0-0) 3<br />
Prerequisite : CV 752 Structural Dynamics<br />
1. Seismic Hazard Assessment<br />
<strong>Engineering</strong> Seismology- definitions – introduction to seismic hazard –<br />
earthquake phenomenon- seismotectonics and seismic zoning <strong>of</strong> India<br />
04 Hrs<br />
2. Earthquake Parameters :<br />
Earthquake monitoring and seismic instrumentation- characteristics <strong>of</strong><br />
strong earthquake motion – estimation <strong>of</strong> earthquake parameters –<br />
microzonation.<br />
04 Hrs<br />
3. Earthquake Effects on Structures<br />
Response to ground acceleration – response analysis by mode superposition<br />
– torsional response <strong>of</strong> buildings. 04 Hrs<br />
4. Analysis <strong>of</strong> Earthquake Forces :<br />
Response spectrum analysis – selection <strong>of</strong> design earthquake – ductility<br />
demand – evaluation <strong>of</strong> earthquake forces – lessons learnt from past<br />
earthquakes<br />
04 Hrs<br />
5. Geotechnical Earthquake <strong>Engineering</strong><br />
Failure <strong>of</strong> foundations during earthquake – liquefaction – remedial<br />
measures.<br />
03 Hrs<br />
6. Concepts <strong>of</strong> Earthquake Resistant Design<br />
Causes <strong>of</strong> damage – planning and architectural consideration and concept –<br />
philosophy and principles <strong>of</strong> earthquake resistant design –guidelines 07 Hrs<br />
7. Earthquake Resistant Design <strong>of</strong> Masonry Buildings<br />
Strength and structural properties <strong>of</strong> masonry – lateral load design<br />
considerations.<br />
08 Hrs<br />
8. Earthquake Resistant Design <strong>of</strong> RC Buildings<br />
Material properties – lateral load analysis – design and detailing.<br />
08 Hrs<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. Chopra A.K, “Dynamics <strong>of</strong> Structures”, Prentice Hall, India, 2003<br />
(Ch 1-3 )<br />
2 Ghosh S.K, “Earthquake Resistant Design <strong>of</strong> Concrete Structures”,<br />
SDCPL-R&D center, New Delhi, 2005 (Ch. 1 -5)<br />
34
Reference Books:<br />
1. Pouley and Priestly, “Earthquake Resistant Design <strong>of</strong> RC structures,<br />
John Wiley. 2004<br />
2. Stratta. J.L., “Manual <strong>of</strong> Seismic Design”. Pearson education, India.<br />
3. Kramer “Geotechnical Earthquake <strong>Engineering</strong>” Pearson education,<br />
India.<br />
4. IS:1893-2002, IS:4326-1993, IS:13920-1993<br />
35
CV 862 ADVANCED PRESTRESSED CONCRETE STRUCTURES (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Prestressed Indeterminate Structures<br />
Continuous beams – Analysis for secondary moments – Linear<br />
transformation and concordant cable pr<strong>of</strong>ile – Guyon’s theory 05 Hrs<br />
2 Anchorage Zone Stresses in Post Tensioned Members<br />
Introduction – stress distribution in end block – anchorage zone stresses –<br />
Magnel’s and Guyon’s methods – comparative analysis –anchorage zone<br />
reinforcement.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
3 Shear and Torsional Resistance<br />
Shear and principal stresses – ultimate shear resistance – design <strong>of</strong> shear<br />
reinforcement – torsion – design <strong>of</strong> torsional reinforcement – combined shear<br />
and bending.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
4 Composite Beams<br />
Introduction – composite structural members – types <strong>of</strong> composite<br />
constructions – analysis <strong>of</strong> stresses – differential shrinkage – deflection –<br />
serviceability limit states – deflection and cracking - flexural strength – shear<br />
strength.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
5 Tension Members<br />
Introduction – ties – pressure pipes – fabrication – analysis and design<br />
procedure for cylindrical containers and design specifications <strong>of</strong> ring beams.<br />
05 Hrs<br />
6 Compression Members<br />
Introduction – columns – short and long columns – biaxially loaded columns<br />
– design procedure. 05 Hrs<br />
7 Slab and Grid Floors<br />
Floor slab types – design <strong>of</strong> one way and two way slabs – flat slabs as per IS<br />
specifications – Design <strong>of</strong> grid floors<br />
06 Hrs<br />
8 Pre Cast Elements<br />
PSC poles – manufacturing – shape and sectional properties – design loads<br />
and principles <strong>of</strong> design – railway sleepers – manufacturing – design loads<br />
and principles <strong>of</strong> design – PSC pavements – slab and wall panels 06 Hrs<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. Lin T.Y and Burns.H, “Design <strong>of</strong> Prestressed Concrete Structures”, John<br />
Wiley and Sons, 2000 (Ch. 1,2)<br />
2. Krishnaraju.N, “Prestressed Concrete”, Tata McGraw-Hill, 2007 (Ch.1 to 8)<br />
36
Reference Books:<br />
1. Dayaratnam.P, “Prestressed Concrete Structures”, Oxford and IBH<br />
Publishers – 2004 edition<br />
2. Pandit.G.S and Gupta.S.P, “Prestressed Concrete”, CBS publishers-2000<br />
3 IS 1343- 1980 Design <strong>of</strong> Prestressed Concrete Structure, BIS New Delhi.<br />
37
CV 863 SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT (3-0-0) 3<br />
1. Introduction : Definition – Land Pollution – Scope and importance <strong>of</strong><br />
solid waste management – Functional elements <strong>of</strong> solid waste<br />
management – Sources, Classification and characteristics – Municipal,<br />
commercial and industrial methods <strong>of</strong> quantification<br />
08 Hrs<br />
2. Collection and Transportation : Systems <strong>of</strong> collection – Collection<br />
equipment – Garbage chutes – Transfer stations – Baling and compacting,<br />
route optimization techniques and problems<br />
06 Hrs<br />
3. Treatment / Processing Techniques : Components separation – Volume<br />
reduction – Size reduction – Chemical reduction and biological processing<br />
problems<br />
06 Hrs<br />
4. Incineration : Process – 3 T’s factors affecting incineration process –<br />
Incinerators – Types – Prevention <strong>of</strong> air pollution – Pyrolysis – Design<br />
criteria for incineration<br />
06 Hrs<br />
5. Composing : Aerobic and anaerobic composting – Factors affecting<br />
composting – Indore and Bangalore processes – Mechanical and semi<br />
mechanical composting processes – Vermicomposting<br />
05 Hrs<br />
6. Sanitary Land Filling : Different types – Trench area – Ramp and pit<br />
method – Site selection – Basic steps involved – Cell design – Prevention <strong>of</strong><br />
site pollution – Leachate and gas collection and control methods –<br />
Geosynthetic fabrics in sanitary landfills<br />
05 Hrs<br />
7. Disposal Methods : Open dumping – Selection <strong>of</strong> site – Ocean disposal –<br />
feeding to hogs – Biomedical wastes and disposal<br />
02 Hrs<br />
8. Recycle and Reuse : Material and energy recovery operations – Reuse in<br />
other industries – Plastic wastes – Environmental significance <strong>of</strong> reuse<br />
04 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Integrated Solid Waste Management : Tchobanoglous : Mc. Graw Hill,<br />
1970, I Edition<br />
2. Sasi Kumar.K, Sanoop Gopikrishna “Solid Waste Management” PHI<br />
Learning Pvt.ltd, 2009.<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Pavoni J.L “Hand book on Solid Waste Disposal” - 1973<br />
2. Peavy and Tchobanoglous “Environmental <strong>Engineering</strong>” 1985<br />
3. Biomedical waste handling rules – 1998<br />
38
CV 864 DESIGN AND DRAWING OF IRRIGATION STRUCTURES (1-0-4) 3<br />
PART – A<br />
14 Hrs<br />
Preparation <strong>of</strong> Drawings for given design details <strong>of</strong> : Overflow<br />
Section <strong>of</strong> Gravity Dams – Sections <strong>of</strong> earth dams <strong>of</strong> Homogeneous fill –<br />
zonal embankment – Diaphragm types with drainage plans – Sections <strong>of</strong><br />
Canals – different conditions, in cutting, in banking and partly in<br />
cutting and partly in banking<br />
PART – B<br />
28 Hrs<br />
Designs and Drawings for : Surplus Weir with stepped type <strong>of</strong> aprons<br />
– Tank Sluice – Direct Sluice – Head Regulator – Cross regulator – Canal<br />
Drop (Notch type) – Cross drainage works.<br />
Question Paper Pattern :<br />
In the examination two questions are to be set from PART-A for 20 marks<br />
and two questions from PART-B <strong>of</strong> 80 marks. PART-B includes 20 marks<br />
for design and 60 marks for drawing. Student is expected to answer<br />
selecting one question from each part. The duration <strong>of</strong> SEE is 04 hrs.<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Murthy C.S. “ Design <strong>of</strong> Minor Irrigation and Canal Structures” Wiley<br />
Eastern ltd, New Delhi (Part A) 2000 edition [Ch. Part A, Part B)<br />
2. Leliavasky.S “ Design Text Book in <strong>Civil</strong> <strong>Engineering</strong> ‘ Oxford and IBH<br />
Publishing co., Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi (Part B) 1996 edition<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Sehgal P.P. “ Design <strong>of</strong> Irrigation Structures” Khanna Publishers, New<br />
Delhi. 1998<br />
2. Varshney “ Hydraulic Structures:, Nem Chand and Bros, Roorkee, 1999<br />
39
CV 865 HIGHWAY PAVEMENT DESIGN (3-0-0) 3<br />
1 Pavement Design:<br />
Desirable characteristics – Basic difference between highway and Airfield<br />
pavement – Design process and strategies – Functions <strong>of</strong> sub base, base<br />
and surface course – Comparison between flexible and rigid pavements.<br />
07 Hrs<br />
2 Types <strong>of</strong> Distress:<br />
Structural and functional causes. Relationship between serviceability<br />
and age. Principles <strong>of</strong> optimization <strong>of</strong> design. Factors affecting design<br />
viz., Design life reliability – Traffic factors – Climatic factors – Sub grade<br />
strength and drainage<br />
08 Hrs<br />
3. Stresses in Homogeneous Mass:<br />
Assumptions – Boussinesq’s theory – limitations. Burmister’s theory-<br />
Assumptions – limitations. Three layer analysis, Assumptions, design<br />
procedure with relevant numerical examples.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
4. Wheel Load:<br />
Design wheel loads - Relationship between wheel load on vertical stress<br />
– Contact pressure – Tyre pressure. ESWL concept – Determination<br />
based on stress and deflection criteria – Repetitions <strong>of</strong> load and concept<br />
<strong>of</strong> EWL – McLeod method – Damaging effect <strong>of</strong> axle load, numerical<br />
examples<br />
06 Hrs<br />
5. Flexible Pavement Design Methods for Air Field and Highway<br />
Pavement :<br />
Fundamental assumptions – Mcleod method – Development – principles<br />
and design steps with numerical example.<br />
06 Hrs<br />
6. Kansas Method :<br />
Kansas method and design steps with numerical examples – California<br />
Resistance value method – principles – Design procedure with numerical<br />
examples – CBR method <strong>of</strong> design ( IRC37 – 2001), numerical examples<br />
limitations <strong>of</strong> CBR method<br />
06 Hrs<br />
7 Design <strong>of</strong> Rigid Pavement : Design principles – Factors affecting the<br />
design – Wheel load and repetition – Properties <strong>of</strong> sub grade – Properties<br />
<strong>of</strong> concrete – External conditions – Joints – Reinforcement – Analysis <strong>of</strong><br />
stresses – Westergard’s Analysis – Modified Westergaurd, Tellar &<br />
Sutherland equations – estimation <strong>of</strong> critical stresses through charts –<br />
Load, temperature stresses – combination <strong>of</strong> stresses. IRC 58 – 2002<br />
method <strong>of</strong> design – design steps – numerical examples<br />
06 Hrs<br />
40
8 Joints in Pavement Slabs : Design <strong>of</strong> reinforcement – Design <strong>of</strong> joints<br />
Requirements <strong>of</strong> joints – Types <strong>of</strong> joints – Expansion joint – Contraction<br />
joint – Warping joint – Construction joint – Longitudinal joint – Spacing<br />
<strong>of</strong> joints – Design <strong>of</strong> Dowel bars – numerical examples<br />
07 Hrs<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Khanna & Justo “ Highway <strong>Engineering</strong> “ Nemchand Bros. 2007<br />
(Ch.1,2,3,4,5)<br />
2. Kadiyali and Dr.Lal N.B. “Highway <strong>Engineering</strong>” Khanna Publications<br />
Delhi 6 7 th edition 2004. (Ch.6,7,8)<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Yoder E J & Witezack, “ Principles <strong>of</strong> Pavement Design”, 2 nd edition,<br />
John Wiley and Sons. 2000 edition.<br />
2. IRC : 37 – 2001, Design <strong>of</strong> Flexible Pavement<br />
3. IRC : 38 – 2002, Design <strong>of</strong> Rigid Pavement<br />
41
CV 805 SEMINAR<br />
Course Code : CV 805 CIE : 50<br />
No. <strong>of</strong> Project Hours / Week : 2<br />
Seminar on current topics <strong>of</strong> <strong>Civil</strong> <strong>Engineering</strong> shall be presented before a<br />
committee comprising the faculty constituted by the HOD. The seminar<br />
marks shall be awarded by the committee. Students shall submit the<br />
seminar report in the prescribed standard format, one week before<br />
presentation.<br />
CV 806 PROJECT WORK<br />
Course Code : CV 806 CIE : 100<br />
No. <strong>of</strong> Project Hours / Week : 18 Exam Hours : 03<br />
SEE : 100<br />
The Project report shall be presented in the following form :<br />
1. Definition <strong>of</strong> the problem<br />
2. Exhaustive literature survey<br />
3. Experimental work / Analysis / Design, based on the type <strong>of</strong> the<br />
problem<br />
4. Results and discussion<br />
5. Conclusions, scope for further work<br />
6. References.<br />
The Project Report in four copies shall be submitted in the prescribed<br />
standard format to the HOD, after certification by the concerned guide and<br />
HOD. CIE marks shall be awarded by the committee headed by HOD and<br />
members comprising the Guide and one subject expert after conducting the<br />
viva-voce examination.<br />
42