Final Review Packet -- APES 2010-2011 UNIT 1 - Raleigh Charter ...
Final Review Packet -- APES 2010-2011 UNIT 1 - Raleigh Charter ...
Final Review Packet -- APES 2010-2011 UNIT 1 - Raleigh Charter ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Final</strong> <strong>Review</strong> <strong>Packet</strong> -- <strong>APES</strong> <strong>2010</strong>-<strong>2011</strong><br />
<strong>UNIT</strong> 1 – Introduction and History<br />
1. What is the significance of the agricultural revolution in environmental history<br />
2. What are the four major environmental eras of U.S. Environmental History Briefly describe each era.<br />
3. How would you describe the environmental sentiment of each decade from the 1960’s to the 1990’s<br />
4. What environmental disasters from the 1940’s through 1980’s focused attention on the environment<br />
a. Oil disasters include…<br />
b. Air pollution disasters include…<br />
c. Toxic chemical disasters include…<br />
d. Nuclear accidents include…<br />
5. What is the tragedy of the commons What real life resources end up as “tragedies”<br />
6. What are possible solutions to the tragedy of the commons<br />
7. Describe methods of ocean fishing, including dredging, harpooning, longlining, trapping, trolling, gillnetting,<br />
trawling, and purse seining.<br />
<strong>UNIT</strong> 2 – Ecology<br />
1. What are the two laws of thermodynamics, and which plays a greater role in trophic exchanges Explain.<br />
2. What is synergy What are positive and negative feedback loops What effect do they have on systems<br />
3. Why do energy pyramids always have the same general shape<br />
4. What is the equation for photosynthesis What is the equation for respiration<br />
5. Be able to calculate NPP, GPP, and respiration given light/dark bottle data (and know what they are!).<br />
6. What is the difference between a population and a community<br />
7. What are the characteristics of a good indicator species<br />
8. What is a niche Be able to give multiple definitions for this term.<br />
9. What is an ecotone Give an example.<br />
10. How does the environment play a role in evolution<br />
11. What is the competitive exclusion principle How does it relate to niches How does it relate to succession<br />
12. What is the Rule of 70 Be able to use it to estimate doubling time or percent growth rate.<br />
I. Understand these major CATEGORIES/CLASSIFICATIONS:<br />
1. Biotic Factors vs. Abiotic Factors<br />
2. R-selected species vs. K selected species<br />
3. Exponential Growth vs. Logistic Growth<br />
4. Fundamental Niche vs. Realized Niche<br />
5. Generalist Species vs. Specialist Species<br />
6. Competition, Mutualism, Commensalism, Predation, Parasitism, Herbivory, Amensalism<br />
7. Ecological Roles—Carnivore, Herbivore, Primary Consumer, Detritovore, etc.<br />
<strong>UNIT</strong> 3 – Ecosystems/Biomes/Biodiversity<br />
1) List three direct causes of species extinction. What are the main underlying causes Describe as many specific causes<br />
of species extinction as you can.<br />
2) Primary vs. Secondary Succession and Facilitation vs. Inhibition vs. Tolerance in successional environments<br />
3) What is the theory of island biogeography Explain how it might be a useful theory for species preservation in the<br />
contemporary world.<br />
4) Be able to list 5-10 ecosystem services. Be able to discuss why biodiversity is important, and in general terms, how it<br />
can be measured and sustained.<br />
5) What is the ESA What is CITES How does each protect endangered species<br />
6) <strong>Review</strong> characteristics of grasslands, rainforests, tundra, taiga, temperate deciduous forests, chaparral. Think in<br />
particular about temperature, precipitation, and special adaptations for each.
<strong>UNIT</strong> 4 – Nutrient Cycling<br />
1. Be able to draw, with reasonable detail, the water, carbon and nitrogen cycles. You need to be able to name the<br />
various processes in each.<br />
2. Have a general sense of how phosphorous and sulfur cycle in the environment.<br />
3. For all five cycles, know the largest reservoir.<br />
4. In addition, some main ideas include carbon sources/sinks, human-caused influences, such as eutrophication within<br />
the nitrogen and phosphorous cycles, combustion, wet/dry deposition.<br />
<strong>UNIT</strong> 5 - Earth, Soil<br />
1. What are the four eras of earth history What are the defining moments of each era<br />
2. What is a mass extinction What is an adaptive radiation How are these two things related<br />
3. What are the mechanical layers of the earth Why are these layers useful divisions of the earth for the study of plate<br />
tectonics<br />
4. What things do seafloor magnetic stripes tell us about plate movement around the mid-ocean ridge How<br />
5. What are the three types of plate boundaries Where is new rock created Where is old rock destroyed<br />
6. What is an igneous rock Metamorphic Sedimentary<br />
7. What is the rock cycle KNOW all processes that change rock from one form to another! Be able to draw the entire<br />
cycle and understand it.<br />
8. What is soil What four things compose soil Why is soil important<br />
9. What three factors control the formation of soil<br />
10. What is physical weathering Chemical weathering<br />
11. What is soil texture How is it measured What properties of soil are influenced by soil texture (The BEST way to<br />
think about this is to compare a pure sand with a pure clay)<br />
12. What is a loam Where does a loam fit on the soil texture triangle Why is loam special<br />
13. How does pH influence soil<br />
14. What is the difference between porosity and permeability<br />
15. Where in the soil do plants get their nutrients<br />
16. What is deep (subsurface/underground) mining What is surface mining What are the advantages and disadvantages<br />
of each What is in-situ leaching<br />
<strong>UNIT</strong> 6 – Water Basics<br />
1. Where is the majority of the Earth’s water stored Where is the majority of freshwater stored How much is where<br />
2. Be able to draw/explain the changes in a river as you move from the source zone to the floodplain.<br />
3. How are lakes described by depth in the lake What two layers (and one transition layer) are part of a lake What are<br />
the abiotic properties of each of these layers (nutrients, DO, temperature) How do these layers mix<br />
4. What are the four life zones in a lake<br />
5. What is a watershed How does a watershed relate to pollution<br />
6. What are the two main life zones in the oceans Which one is more productive and why<br />
7. What is an estuary What causes temperature and salinity variation in an estuary over time<br />
8. Why are coral reefs important What organisms cooperate to form the coral structure<br />
9. What is groundwater What is an aquifer What is an aquitard Which can contain water<br />
10. What is a recharge zone How does the recharge zone play a role in aquifer pollution<br />
11. What is the zone of aeration What is the zone of saturation What is the water table
<strong>UNIT</strong> 7 – Circulation<br />
Atmosphere Basics<br />
1. What are the main components (gases) of the atmosphere<br />
2. How is the atmosphere divided into layers What are the four layers Where is the ozone layer Where is the most<br />
mass<br />
3. How is the atmosphere heated<br />
Weather and Global Winds<br />
4. What kind of weather would you expect in a low pressure center What about a high pressure center<br />
5. How do we name winds<br />
6. What is the Hadley cell Polar Cell Ferrel cell Why do these cells form<br />
7. What is the “rain shadow” effect What causes it<br />
Ocean Circulation<br />
8. What type of water sinks<br />
9. What is thermohaline circulation What is deep water formation Upwelling<br />
El Niño and Amigos<br />
10. What are “normal” conditions in the eastern equatorial Pacific Describe sea surface height, water temperature,<br />
precipitation patterns, and nutrient level.<br />
11. Define El Niño-Southern Oscillation. What are the effects of El Niño (think upwelling/fisheries/guano)<br />
12. What is La Niña What are the effects of La Niña How does El Niño cause flooding in Southern California or a dry<br />
spell in Alabama<br />
13. Name two BIOTIC and ABIOTIC effects of an El Niño/La Niña.<br />
Global Warmth and Global Warming<br />
14. What causes the seasons Why are polar latitudes cooler than equatorial latitudes<br />
15. What is UV radiation Longwave/IR radiation Which does the sun emit Which does the earth “emit”<br />
16. What three main gases absorb incoming radiation What three main gases absorb outgoing radiation (+ others)<br />
17. What is albedo How can albedo vary on the Earth’s surface<br />
18. What is the “greenhouse effect” What are “greenhouse gases” Put in other terms, why isn’t the earth’s average<br />
temperature -18ºC<br />
19. What is “global warming” or more accurately, global climate destabilization<br />
Ozone<br />
20. What is stratospheric ozone depletion and how serious is this problem What types of chemicals cause ozone<br />
depletion How do these chemicals cause such depletion<br />
21. Explain how seasonal ozone thinning occurs each year over the earth’s poles<br />
22. Why is it good to have ozone in the stratosphere, but bad to have it in the troposphere<br />
<strong>UNIT</strong> 8 – Human Population<br />
1) You should be able to calculate the natural rate of increase (R-value) from CBR and CDR (and<br />
immigration/emigration). Know what they are, including units.<br />
2) You should be able to calculate the natural rate of increase (R) or doubling time using the rule of 70. Be careful about<br />
units.<br />
3) What are the three basic types of population age structures Be able to interpret and analyze population age structures<br />
(pyramids).<br />
4) Why is replacement-level fertility a slightly higher number in LDC’s than MDC’s<br />
5) Why is the world’s rate of growth slowing What do measures such as IMR, LE, TFR say about how a<br />
country/population is doing<br />
6) Why is there a time lag (“population momentum”) for ZPG
7) What are the four stages of demographic transition Briefly explain what is occurring during each stage, especially<br />
specifics about growth rate and public health. Be able to analyze a graph of birth and death rates for demographic<br />
transition.<br />
8) What is an ecological footprint What contributes to the size of a person/city/nation’s footprint<br />
9) Which nations have the largest ecological footprints Which nations have the smallest<br />
10) What is the current world population The U.S. population China’s India’s<br />
11) Describe briefly the (a) population age structure, (b) unique challenges, and (c) solutions to these challenges for:<br />
a. INDIA b. KENYA c. JAPAN<br />
12) Three specific examples of disease vectors and the diseases they transmit.<br />
13) How might poverty harm the environment<br />
<strong>UNIT</strong> 9 – Environmental Economics<br />
1. Understand full-cost accounting, the difference between internal and external costs, and the concept of internalization<br />
of costs.<br />
2. Understand the general types of environmental regulations (command vs. market), and be able to develop a list of<br />
economic methods/government incentives to improve environmental quality.<br />
3. Know the difference between GDP and GNP, and understand their shortcomings (and know alternatives) in describing<br />
the overall well-being of a country.<br />
<strong>UNIT</strong> 10 – Resource Use and Abuse<br />
1) What are the three top crops produced for human consumption (excluding sugar)<br />
2) What is the difference between the green revolution and the agricultural revolution<br />
3) What is the difference between monoculture and polyculture What are the pros and cons of each<br />
4) Describe the benefits of each of the following sustainable agriculture methods: (a) conservation tillage, (b) terracing,<br />
(c) contour farming, (d) intercropping, (e) agroforestry, and (f) crop rotation.<br />
5) What are “green” fertilizer options (i.e. not inorganic chemical fertilizers)<br />
6) Define the following agricultural problems: eutrophication, salinization, overgrazing, overcultivation, desertification.<br />
7) How does erosion result in coarse soils with poor nutrient quality<br />
8) What is the difference between malnutrition and undernutrition<br />
9) What is IPM Explain.<br />
10) What are the three R’s What are the differences between them Which is the best environmental option Which is<br />
the best economic option<br />
11) Be able to discuss low waste approaches/solutions, especially closed-loop solutions.<br />
12) Be able to diagram a sanitary landfill and explain how it works.<br />
13) Describe how incineration works. What are the pros and cons of using incineration as a waste disposal method<br />
14) What is hazardous waste What is RCRA Be able to describe the pros and cons of EACH of the six methods we<br />
discussed in class: surface waste lagoons, deep well injection, hazardous waste landfills, aboveground bunkers,<br />
incineration and export.
<strong>UNIT</strong> 11 - TOXICOLOGY<br />
1. Explain this statement: “The dose makes the poison.” Are all individuals in a population equally sensitive to the same<br />
dose<br />
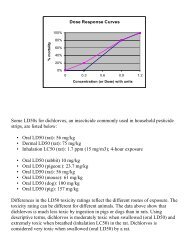
2. Define the terms DOSE and RESPONSE. Which of these is the independent variable in a toxicological study Which<br />
is the dependent variable What does a dose-response curve show How can you determine LD-50 and LC-50 from a<br />
graph<br />
3. What is the difference between LC-50/LD-50 values and threshold values<br />
4. What are the three main pathways that toxicants can enter your body Describe a situation where each of these intake<br />
pathways would be the primary means of exposure.<br />
5. What is the difference between hydrophilic and lipophilic/hydrophobic chemicals<br />
6. Compare and contrast bioaccumulation and biomagnification.<br />
7. How do chemical interactions affect the toxicity of a substance<br />
8. Define the following terms: teratogen, carcinogen, mutagen, endocrine disruptor.<br />
9. List at least three possible fates for a chemical. Is a chemical ever really gone<br />
10. What is cancer What are possible risk factors for developing cancer<br />
11. What is the endocrine system What is a hormone How do endocrine disruptors work<br />
<strong>UNIT</strong> 12 – Water Resources and Pollution<br />
1) List at least THREE PROS and THREE CONS of dam construction.<br />
2) Know the locations and brief descriptions of each of the following: Glen Canyon, California Water Project, Aswan<br />
High Dam, Aral Sea water transfer, Three Gorges Dam, James Bay, Ogallala Aquifer.<br />
3) Why are floodplains important<br />
4) What is DO BOD Describe.<br />
5) What is an oxygen sag curve Where would you expect to see an oxygen sag curve in nature<br />
6) What is cultural eutrophication Describe the process IN DETAIL!!! What nutrients are involved in cultural<br />
eutrophication<br />
7) Why is heat classified as a type of water pollutant<br />
8) How is water cleaned at a water treatment plant Be able to describe the process in detail.<br />
9) How is wastewater cleaned at a wastewater treatment plant Be able to describe the process in detail. Divide the<br />
process into primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment.<br />
10) Where is BOD highest relative to a wastewater effluent pipe Where is DO level highest<br />
<strong>UNIT</strong> 13 - Energy<br />
1. Know the main reserves of the four fossil fuels, and the advantages and disadvantages of each.<br />
2. Understand how nuclear energy works to generate electricity. Know what is meant by “half-life” and how to use it in<br />
calculations.<br />
3. Be familiar with various alternative energy sources, how they work and the advantages and disadvantages of each.<br />
4. Understand the concept of net energy, particularly as it concerns transitioning to lower supplies of the big three fossil<br />
fuels and alternative energy sources, particularly corn ethanol.<br />
5. Why would burning biodiesel fuel have a different impact on atmospheric CO 2 concentrations than does burning<br />
fossil fuels (What does it mean to be carbon-neutral)<br />
6. Be ready for math problems with energy concepts!<br />
7. Know efficiencies for 5-6 familiar “energy conversion devices” (light bulbs, cars, power plants, etc.)
<strong>UNIT</strong> 14 – Air Pollution (+ Laws)<br />
1) Explain, chemically, how each of the following primary pollutants are produced in the combustion process:<br />
a. Nitric oxide<br />
c. Carbon dioxide<br />
b. Carbon monoxide<br />
d. Sulfur dioxide<br />
2) What is the difference between mobile and stationary pollution Between primary and secondary pollutants<br />
3) Explain, chemically, how tropospheric ozone is produced.<br />
4) Explain, chemically, how nitric acid and sulfuric acid deposition is formed in the atmosphere.<br />
5) What is the difference between industrial-air smog and photochemical smog<br />
6) How do carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone concentration vary with time in an urban area<br />
7) What is acid deposition What are the different types of acid deposition What are the effects of acid deposition Be<br />
able to list at least four specific effects of acid deposition.<br />
8) What are some indoor air pollutants Is indoor air pollution regulated the same way as outdoor air pollution Explain.<br />
9) Explain how noise can be pollution.<br />
10) Explain the “urban heat island” effect.<br />
11) What are NAAQS What law governs their establishment<br />
12) Be familiar with the four main types of control equipment used on industrial sources.<br />
13) Explain what a temperature inversion is, and how it relates to air pollution.<br />
14) <strong>Review</strong> the laws on the handout from class<br />
15) Be familiar with the following indoor air pollutants:<br />
a. Radon<br />
c. Carbon Monoxide<br />
b. Asbestos<br />
d. Nitrogen Oxides<br />
e. Formaldehyde<br />
f. Cigarette Smoke