Reduced Intrusion-Related Gold System - GSINET | Geological ...
Reduced Intrusion-Related Gold System - GSINET | Geological ...
Reduced Intrusion-Related Gold System - GSINET | Geological ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
C.J.R. Hart<br />
Temperature °C<br />
550°<br />
500°<br />
450°<br />
400°<br />
350°<br />
300°<br />
250°<br />
to 650°C<br />
Anhydrous<br />
W skarn<br />
Hydrous<br />
Au skarn<br />
BRITTLE<br />
T FAILURE<br />
Qtz-ksp-scheelite veins<br />
W<br />
Qtz-py±po±aspy veins<br />
Au-Bi-Te<br />
Qtz-aspy-py<br />
As<br />
Qtz-stibnite<br />
Sb<br />
Carbonate-base metal veins Pb-Zn-Ag<br />
Time<br />
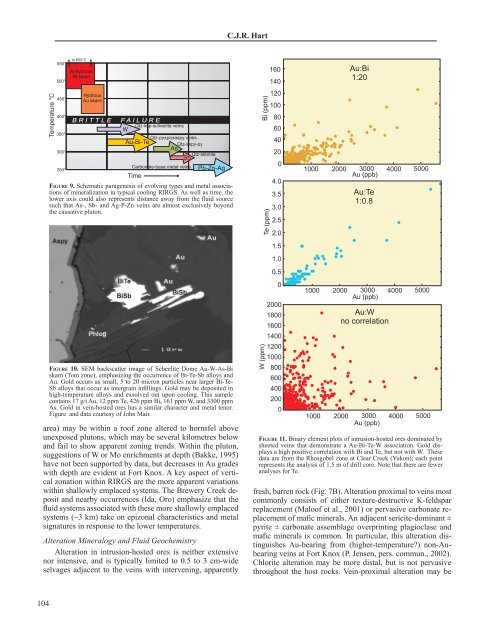
FIGURE 9. Schematic paragenesis of evolving types and metal associations<br />
of mineralization in typical cooling RIRGS. As well as time, the<br />
lower axis could also represents distance away from the fluid source<br />
such that As-, Sb- and Ag-P-Zn veins are almost exclusively beyond<br />
the causative pluton.<br />
FIGURE 10. SEM backscatter image of Scheelite Dome Au-W-As-Bi<br />
skarn (Tom zone), emphasizing the occurrence of Bi-Te-Sb alloys and<br />
Au. <strong>Gold</strong> occurs as small, 5 to 20 micron particles near larger Bi-Te-<br />
Sb alloys that occur as intergrain infillings. <strong>Gold</strong> may be deposited in<br />
high-temperature alloys and exsolved out upon cooling. This sample<br />
contains 17 g/t Au, 12 ppm Te, 426 ppm Bi, 161 ppm W, and 3300 ppm<br />
As. <strong>Gold</strong> in vein-hosted ores has a similar character and metal tenor.<br />
Figure and data courtesy of John Mair.<br />
area) may be within a roof zone altered to hornsfel above<br />
unexposed plutons, which may be several kilometres below<br />
and fail to show apparent zoning trends. Within the pluton,<br />
suggestions of W or Mo enrichments at depth (Bakke, 1995)<br />
have not been supported by data, but decreases in Au grades<br />
with depth are evident at Fort Knox. A key aspect of vertical<br />
zonation within RIRGS are the more apparent variations<br />
within shallowly emplaced systems. The Brewery Creek deposit<br />
and nearby occurrences (Ida, Oro) emphasize that the<br />
fluid systems associated with these more shallowly emplaced<br />
systems (~3 km) take on epizonal characteristics and metal<br />
signatures in response to the lower temperatures.<br />
Alteration Mineralogy and Fluid Geochemistry<br />
Alteration in intrusion-hosted ores is neither extensive<br />
nor intensive, and is typically limited to 0.5 to 3 cm-wide<br />
selvages adjacent to the veins with intervening, apparently<br />
Bi (ppm)<br />
Te (ppm)<br />
W (ppm)<br />
160<br />
140<br />
120<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
4.0<br />
3.5<br />
3.0<br />
2.5<br />
2.0<br />
1.5<br />
1.0<br />
0.5<br />
0<br />
2000<br />
1800<br />
1600<br />
1400<br />
1200<br />
1000<br />
800<br />
600<br />
400<br />
200<br />
0<br />
1000<br />
1000<br />
1000<br />
2000<br />
3000<br />
Au (ppb)<br />
2000 3000<br />
Au (ppb)<br />
2000<br />
Au:Bi<br />
1:20<br />
Au:Te<br />
1:0.8<br />
Au:W<br />
no correlation<br />
3000<br />
Au (ppb)<br />
4000<br />
4000<br />
4000<br />
5000<br />
5000<br />
5000<br />
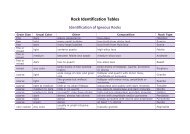
FIGURE 11. Binary element plots of intrusion-hosted ores dominated by<br />
sheeted veins that demonstrate a Au-Bi-Te-W association. <strong>Gold</strong> displays<br />
a high positive correlation with Bi and Te, but not with W. These<br />
data are from the Rhosgobel zone at Clear Creek (Yukon); each point<br />
represents the analysis of 1.5 m of drill core. Note that there are fewer<br />
analyses for Te.<br />
fresh, barren rock (Fig. 7B). Alteration proximal to veins most<br />
commonly consists of either texture-destructive K-feldspar<br />
replacement (Maloof et al., 2001) or pervasive carbonate replacement<br />
of mafic minerals. An adjacent sericite-dominant ±<br />
pyrite ± carbonate assemblage overprinting plagioclase and<br />
mafic minerals is common. In particular, this alteration distinguishes<br />
Au-bearing from (higher-temperature) non-Aubearing<br />
veins at Fort Knox (P. Jensen, pers. commun., 2002).<br />
Chlorite alteration may be more distal, but is not pervasive<br />
throughout the host rocks. Vein-proximal alteration may be<br />
104