Saponification of Esters: Base Catalyzed Hydrolysis ... - Carbon Rules
Saponification of Esters: Base Catalyzed Hydrolysis ... - Carbon Rules
Saponification of Esters: Base Catalyzed Hydrolysis ... - Carbon Rules
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
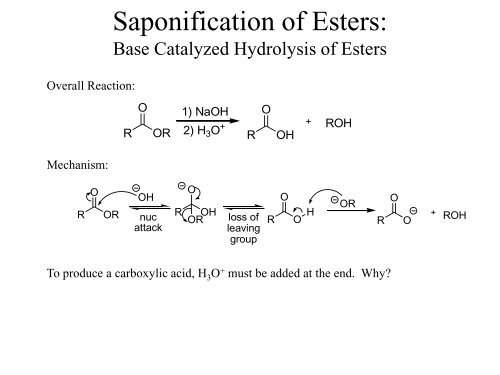
Overall Reaction:<br />
<strong>Saponification</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Esters</strong>:<br />
<strong>Base</strong> <strong>Catalyzed</strong> <strong>Hydrolysis</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Esters</strong><br />
R<br />
O<br />
OR<br />
1) NaOH<br />
2) H 3 O + R<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
ROH<br />
Mechanism:<br />
R<br />
O<br />
OR<br />
OH<br />
nuc<br />
attack<br />
R<br />
O<br />
OH<br />
OR<br />
loss <strong>of</strong><br />
leaving<br />
group<br />
R<br />
O<br />
O H<br />
OR<br />
R<br />
O<br />
O<br />
ROH<br />
To produce a carboxylic acid, H 3 O + must be added at the end. Why
How Soap Is Made<br />
O<br />
O<br />
polar group<br />
(hydrophilic)<br />
non-polar group<br />
(hydrophobic)<br />
• Soaps are compounds that contain a polar group on<br />
one end <strong>of</strong> the molecule and a non-polar group on the<br />
other end.<br />
• The hydrophobic tail surrounds oil molecules,<br />
forming a micelle.<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
NaOH<br />
OH<br />
OH<br />
OH<br />
glycerol<br />
Na<br />
Na<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
A fat molecule<br />
Na<br />
O<br />
Soap molecules<br />
<strong>Base</strong> catalyzed hydrolysis gives glycerol and 3 soap molecules.