Blood culture - GLOBE Network
Blood culture - GLOBE Network
Blood culture - GLOBE Network
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
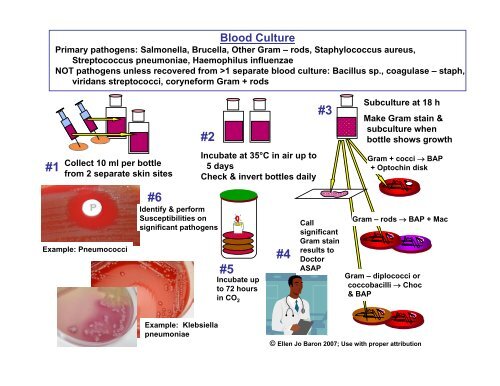
<strong>Blood</strong> Culture<br />
Primary pathogens: Salmonella, Brucella, Other Gram – rods, Staphylococcus aureus,<br />
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae<br />
NOT pathogens unless recovered from >1 separate blood <strong>culture</strong>: Bacillus sp., coagulase – staph,<br />
viridans streptococci, coryneform Gram + rods<br />
#2<br />
#3<br />
Sub<strong>culture</strong> at 18 h<br />
Make Gram stain &<br />
sub<strong>culture</strong> when<br />
bottle shows growth<br />
#1<br />
Collect 10 ml per bottle<br />
from 2 separate skin sites<br />
Incubate at 35°C in air up to<br />
5 days<br />
Check & invert bottles daily<br />
Gram + cocci → BAP<br />
+ Optochin disk<br />
Example: Pneumococci<br />
#6<br />
Identify & perform<br />
Susceptibilities on<br />
significant pathogens<br />
#5<br />
Incubate up<br />
to 72 hours<br />
in CO 2<br />
#4<br />
Call<br />
significant<br />
Gram stain<br />
results to<br />
Doctor<br />
ASAP<br />
Gram – rods → BAP + Mac<br />
Gram – diplococci or<br />
coccobacilli → Choc<br />
& BAP<br />
Example: Klebsiella<br />
pneumoniae<br />
© Ellen Jo Baron 2007; Use with proper attribution
# 1<br />
Doctor collects<br />
CSF via sterile<br />
skin puncture<br />
(lumbar<br />
puncture) into<br />
sterile tubes.<br />
Tube #2 or #3 is<br />
for Microbiology<br />
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Culture<br />
Primary pathogens: Grp. B Beta streptococcus (newborns),<br />
Haemophilus influenzae (2 months – 2 years old),<br />
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis<br />
1 mL minimum;<br />
>5 mL best<br />
# 7<br />
Place round drop of<br />
sediment on slide.<br />
Do NOT spread out<br />
drop. Let dry & Gram<br />
stain. If many PMNs,<br />
infection more likely.<br />
# 2<br />
Centrifuge 15<br />
min at 1500 x g<br />
(if possible)<br />
# 3<br />
Remove supernatant<br />
with pipette down to<br />
1 cc CSF sediment<br />
# 6<br />
Incubate<br />
up to 72<br />
hours in<br />
CO 2<br />
# 5<br />
Place 1 drop sediment<br />
onto chocolate &<br />
blood agar plates<br />
© Ellen Jo Baron 2007; Use with proper attribution<br />
Note: Do NOT pour off<br />
# 4<br />
Pipette up &<br />
down 10 X to<br />
mix sediment
Stool (Feces) Culture<br />
Important pathogens: Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, Vibrio cholera, Vibrio<br />
parahemolyticus, Toxigenic E. coli & Clostridium difficile (may not be detected in basic labs)<br />
#1<br />
Culture feces within 30<br />
minutes of collection or<br />
place into Cary-Blair<br />
transport medium<br />
#6<br />
#2<br />
Choose areas with<br />
blood or pus to plate<br />
Plate onto Campy agar – or use filter<br />
paper method. Incubate in reduced<br />
oxygen at 37-42° C up to 72 h<br />
#3<br />
Plate onto BAP, MacConkey,<br />
Hektoen or DCA, & TCBS if Vibrio.<br />
Incubate at 37° C in air up to 48 h<br />
#4<br />
Lactose neg GNRs on Mac,<br />
HEK, or DCA need workup.<br />
Campy agar<br />
Gram stain shows curved<br />
or spiral shaped rods<br />
Campylobacter sp.<br />
Oxidase +, moist,<br />
beige colonies<br />
#5<br />
Oxidase + GNRs on BAP need<br />
additional workup.<br />
© Ellen Jo Baron 2007; Use with proper attribution<br />
Plate to TCBS & grow in broth<br />
with salt concentrations 0-6%.
Genital Culture<br />
Primary pathogens: Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Trichomonas, Yeast & Bacterial Vaginosis<br />
syndrome in females, Group B Beta streptococcal carriage in pregnant females<br />
A. Cervical, anal swab from female<br />
B. Urethral swab from male<br />
# 1<br />
BAP & Thayer-Martin<br />
# 1 Thayer-Martin & Gram stain<br />
Yeast on BAP<br />
C. Vaginal & anal swab from<br />
female 35-37 wks pregnant<br />
# 2<br />
Incubate up to 48 hours in CO 2<br />
GC on T-M<br />
Incubate up to 72 hours in CO 2<br />
Look for N. gonorrhoeae on T-M<br />
Look for yeast on BAP<br />
# 1<br />
# 2<br />
Incubate overnight in<br />
enrichment broth<br />
Sub<strong>culture</strong> to BAP to look for<br />
group B strep<br />
D. Vaginal swab from female<br />
# 1<br />
BAP for yeast<br />
T-M for GC<br />
# 1<br />
Gram stain for BV<br />
NOT PATHOGENS<br />
Staphylococcus aureus<br />
Any Gram negative rods,<br />
including E. coli, Proteus<br />
Beta streptococcus group B (GBS)<br />
Report for pregnant women only !<br />
© Ellen Jo Baron 2007; Use with proper attribution<br />
# 2<br />
Swab in 0.5 ml saline to examine<br />
for Trichomonas within 30 min<br />
Roll swab on slide to<br />
make smear 1 cell<br />
layer thick; look for<br />
“clue cells”
Pus, Aspirate, or Tissue Specimen<br />
Primary pathogens: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, other beta<br />
streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, other Gram negative rods<br />
NOT pathogens: Coagulase neg staphylococci, small numbers of coryneform Gram + rods<br />
#1<br />
•Cleanse skin around wound<br />
with alcohol<br />
•Aspirate or tissue is best<br />
•Swab worst<br />
#2<br />
•Inoculate BAP & Mac<br />
•If aspirate or tissue, make<br />
Gram stain & call Doctor<br />
with significant results<br />
#3<br />
Incubate up<br />
to 48 hours<br />
in CO 2<br />
#5<br />
When 3 or more pathogens, report as “mixed<br />
flora” and list Pseudo, S. aureus, Proteus,<br />
Enteric GNRs descriptively if present<br />
Klebsiella<br />
pneumoniae<br />
#4<br />
Identify & perform<br />
susceptibilities on 1 or 2<br />
significant pathogens<br />
Beta streptococci<br />
Staph aureus<br />
predominant<br />
Mixed enteric Gram neg rods -<br />
2 types: report both; full workup<br />
Pseudomonas<br />
aeruginosa<br />
© Ellen Jo Baron 2007; Use with proper attribution
Sputum Specimen<br />
Primary pathogens: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella species, Haemophilus<br />
influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa<br />
NOT pathogens: Yeast, viridans streptococci, coagulase negative staphylococci<br />
#1<br />
Patient should rinse mouth<br />
with water, cough from<br />
deep in lung, do not spit<br />
Strep. pneumo<br />
#2<br />
• Make Gram stain to screen if<br />
acceptable for <strong>culture</strong><br />
• Call significant Gram stain<br />
results to Doctor ASAP<br />
Reject: Many<br />
squamous<br />
epithelial cells<br />
Good: Rare squamous<br />
epithelial cells<br />
Optochin disk<br />
Staph aureus<br />
Optochin +<br />
Klebsiella pneumoniae<br />
Bile solubility +<br />
#5<br />
Identify & perform susceptibilities<br />
on significant pathogens<br />
#3<br />
Plate to Choc,<br />
BAP, Mac<br />
#4<br />
Incubate up<br />
to 48 hours<br />
in CO 2<br />
Haemophilus influenzae<br />
© Ellen Jo Baron 2007; Use with proper attribution
# 1<br />
# 9<br />
Throat Culture<br />
Primary pathogen: Grp. A Beta streptococcus<br />
Optional report: Arcanobacterium haemolyticum<br />
Swab # 2<br />
Swab pharynx and<br />
tonsils. Avoid tongue<br />
and cheeks.<br />
Rub swab on 1/5 area of<br />
blood agar plate (sheep<br />
or horse)<br />
# 8<br />
Report results:<br />
# 3<br />
Loop<br />
Streak in 3 or 4<br />
quadrants<br />
1+ to 4+ Group A Beta strep<br />
or<br />
1+ to 4+ Beta strep, not group A<br />
or<br />
No beta strep detected<br />
# 4<br />
Place Co-trimoxazole (SxT)<br />
disk next to Bacitracin disk in<br />
first quadrant<br />
# 5<br />
Bacitracin<br />
& SxT disks<br />
Incubate candle jar at 37° C<br />
overnight and examine<br />
plates; if negative, incubate<br />
another night.<br />
Total = 48 h incubation<br />
Bacitracin<br />
SxT<br />
DO NOT REPORT<br />
Non-pathogens in pharyngitis:<br />
• Staphylococcus aureus<br />
• Streptococcus pneumoniae<br />
• Haemophilus influenzae<br />
• Moraxella catarrhalis<br />
• Alpha hemolytic strep<br />
• ANY gram negative rod<br />
• ANY yeast<br />
# 7<br />
Confirm Group A<br />
Strep by positive PYR<br />
# 6<br />
Beta hemolytic colonies, > 0.5<br />
mm, resistant to SxT & sensitive<br />
to Bacitracin = Group A Strep<br />
(catalase negative)<br />
© Ellen Jo Baron 2007; Use with proper attribution
Urine Culture<br />
Primary pathogens: E. coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, other Gram negative rods,<br />
Enterococcus, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Staph aureus (if pure)<br />
a<br />
b<br />
a<br />
b<br />
#2 Plate onto BAP and<br />
MacConkey<br />
0.001 ml loop<br />
#1<br />
Collect midstream urine<br />
#3<br />
Incubate up to 24 h<br />
in air incubator<br />
GPC<br />
#6<br />
Criteria for evaluating urine <strong>culture</strong>s<br />
Patient Specimen type Significant pathogen CFU/ml<br />
Asymptomatic Voided, clean-catch 100,000<br />
or indwelling cath<br />
Symptomatic<br />
ambulatory<br />
Voided, clean-catch 10,000 1-2 species of potential<br />
pathogen. If > 2 species, urine<br />
considered to be "contaminated"<br />
Symptomatic,<br />
sexually active<br />
female<br />
Note: •Gram negative rods<br />
grow well on both<br />
BAP & Mac<br />
•Gram + cocci grow<br />
well on BAP only<br />
Voided, clean-catch<br />
100 pure <strong>culture</strong><br />
Enterobacteriaceae<br />
Males Voided, clean-catch 1,000 potential pathogen<br />
All<br />
Obtained by straight<br />
catheterization<br />
100 any number of species of<br />
potential pathogens<br />
All<br />
Surgery or bladder<br />
aspirate<br />
Any numbers (broth enrichment,<br />
anaerobes)<br />
All Controversial Any isolates of yeast<br />
#5<br />
GNR<br />
If ≤ 2 pathogens,<br />
perform identification &<br />
susceptibility on each<br />
If >2 pathogens, report<br />
“mixed flora”<br />
50,000 cfu/ml<br />
75,000 cfu/ml<br />
100,000 cfu/ml<br />
#4<br />
Count colonies<br />
© Ellen Jo Baron 2007; Use with proper attribution
Fungus Culture<br />
Important pathogens: Cryptococcous neoformans, Blastocystis hominis, Dermatophytes, and<br />
other fungi depending on source of specimen and status of patient<br />
#1<br />
Important fungi: Tissue<br />
biopsy, sputum, CSF,<br />
<strong>Blood</strong> <strong>culture</strong>s<br />
Dermatophytes: skin<br />
scraping, nail clipping,<br />
hair pulled from root<br />
Do not grind up tissue:<br />
use scalpels to mince it<br />
into small pieces<br />
#2<br />
Swabs OK ONLY for<br />
isolation of yeast – plate<br />
onto BAP and Sab Dex<br />
#3<br />
Routine: Plate onto Sabouraud<br />
Dextrose and Mycobiotic. Incubate<br />
at 30° C in air up to 4 weeks<br />
For dermatophytes: Plate onto<br />
Mycobiotic and DTM (derm test<br />
medium) if available.<br />
If tissue, skin scraping, or nail, push<br />
one small piece of intact sample into<br />
agar surface halfway.<br />
#4<br />
Tape plates with porous<br />
tape or tape on two sides<br />
#6<br />
Examine plates daily for<br />
7 days, then 2x /week<br />
Smooth colonies = yeast<br />
Fuzzy growth = mold<br />
#5<br />
Place material in drop of<br />
10% KOH, add coverslip,<br />
and examine for fungal<br />
elements.<br />
© Ellen Jo Baron 2008; Use with proper attribution





![Download presentation [1.5 Mo PDF] - GLOBE Network](https://img.yumpu.com/46262019/1/190x134/download-presentation-15-mo-pdf-globe-network.jpg?quality=85)
![Download presentation [75.75 Ko PDF] - GLOBE Network](https://img.yumpu.com/41976455/1/190x245/download-presentation-7575-ko-pdf-globe-network.jpg?quality=85)



![Download presentation [160.19 Ko PDF] - GLOBE Network](https://img.yumpu.com/36251372/1/190x245/download-presentation-16019-ko-pdf-globe-network.jpg?quality=85)
![Presentation [4.79 Mb PDF] - GLOBE Network](https://img.yumpu.com/32872413/1/190x146/presentation-479-mb-pdf-globe-network.jpg?quality=85)


