u3QtN
u3QtN
u3QtN
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
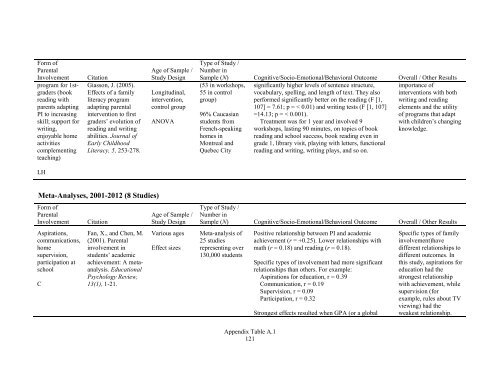
Form of<br />
Parental<br />
Involvement<br />
program for 1stgraders<br />
(book<br />
reading with<br />
parents adapting<br />
PI to increasing<br />
skill; support for<br />
writing,<br />
enjoyable home<br />
activities<br />
complementing<br />
teaching)<br />
Citation<br />
Giasson, J. (2005).<br />
Effects of a family<br />
literacy program<br />
adapting parental<br />
intervention to first<br />
graders’ evolution of<br />
reading and writing<br />
abilities. Journal of<br />
Early Childhood<br />
Literacy, 5, 253-278.<br />
Age of Sample /<br />
Study Design<br />
Longitudinal,<br />
intervention,<br />
control group<br />
ANOVA<br />
Type of Study /<br />
Number in<br />
Sample (N) Cognitive/Socio-Emotional/Behavioral Outcome Overall / Other Results<br />
(53 in workshops,<br />
55 in control<br />
group)<br />
96% Caucasian<br />
students from<br />
French-speaking<br />
homes in<br />
Montreal and<br />
Quebec City<br />
significantly higher levels of sentence structure,<br />
vocabulary, spelling, and length of text. They also<br />
performed significantly better on the reading (F [1,<br />
107] = 7.61; p = < 0.01) and writing tests (F [1, 107]<br />
=14.13; p = < 0.001).<br />
Treatment was for 1 year and involved 9<br />
workshops, lasting 90 minutes, on topics of book<br />
reading and school success, book reading even in<br />
grade 1, library visit, playing with letters, functional<br />
reading and writing, writing plays, and so on.<br />
importance of<br />
interventions with both<br />
writing and reading<br />
elements and the utility<br />
of programs that adapt<br />
with children’s changing<br />
knowledge.<br />
LH<br />
Meta-Analyses, 2001-2012 (8 Studies)<br />
Form of<br />
Parental<br />
Involvement<br />
Aspirations,<br />
communications,<br />
home<br />
supervision,<br />
participation at<br />
school<br />
C<br />
Citation<br />
Fan, X., and Chen, M.<br />
(2001). Parental<br />
involvement in<br />
students’ academic<br />
achievement: A metaanalysis.<br />
Educational<br />
Psychology Review,<br />
13(1), 1-21.<br />
Age of Sample /<br />
Study Design<br />
Various ages<br />
Effect sizes<br />
Type of Study /<br />
Number in<br />
Sample (N) Cognitive/Socio-Emotional/Behavioral Outcome Overall / Other Results<br />
Meta-analysis of<br />
25 studies<br />
representing over<br />
130,000 students<br />
Positive relationship between PI and academic<br />
achievement (r = +0.25). Lower relationships with<br />
math (r = 0.18) and reading (r = 0.18).<br />
Specific types of involvement had more significant<br />
relationships than others. For example:<br />
Aspirations for education, r = 0.39<br />
Communication, r = 0.19<br />
Supervision, r = 0.09<br />
Participation, r = 0.32<br />
Strongest effects resulted when GPA (or a global<br />
Specific types of family<br />
involvement)have<br />
different relationships to<br />
different outcomes. In<br />
this study, aspirations for<br />
education had the<br />
strongest relationship<br />
with achievement, while<br />
supervision (for<br />
example, rules about TV<br />
viewing) had the<br />
weakest relationship.<br />
Appendix Table A.1<br />
121