Naming acids and Bases Ionic Naming Rules
Naming acids and Bases Ionic Naming Rules
Naming acids and Bases Ionic Naming Rules
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
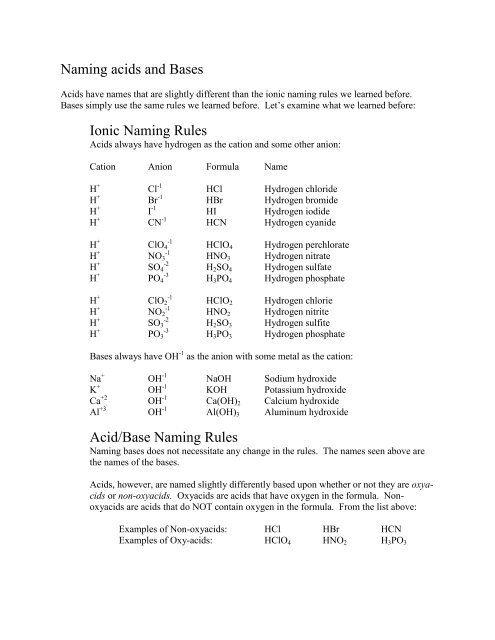
<strong>Naming</strong> <strong>acids</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Bases</strong><br />
Acids have names that are slightly different than the ionic naming rules we learned before.<br />
<strong>Bases</strong> simply use the same rules we learned before. Let’s examine what we learned before:<br />
<strong>Ionic</strong> <strong>Naming</strong> <strong>Rules</strong><br />
Acids always have hydrogen as the cation <strong>and</strong> some other anion:<br />
Cation Anion Formula Name<br />
H + Cl -1 HCl Hydrogen chloride<br />
H + Br -1 HBr Hydrogen bromide<br />
H + I -1 HI Hydrogen iodide<br />
H + CN -1 HCN Hydrogen cyanide<br />
H + -1<br />
ClO 4<br />
H + -1<br />
NO 3<br />
H + -2<br />
SO 4<br />
H + -3<br />
PO 4<br />
H + -1<br />
ClO 2<br />
H + -1<br />
NO 2<br />
H + -2<br />
SO 3<br />
H + -3<br />
PO 3<br />
HClO 4<br />
HNO 3<br />
H 2 SO 4<br />
H 3 PO 4<br />
HClO 2<br />
HNO 2<br />
H 2 SO 3<br />
H 3 PO 3<br />
Hydrogen perchlorate<br />
Hydrogen nitrate<br />
Hydrogen sulfate<br />
Hydrogen phosphate<br />
Hydrogen chlorie<br />
Hydrogen nitrite<br />
Hydrogen sulfite<br />
Hydrogen phosphate<br />
<strong>Bases</strong> always have OH -1 as the anion with some metal as the cation:<br />
Na + OH -1 NaOH Sodium hydroxide<br />
K + OH -1 KOH Potassium hydroxide<br />
Ca +2 OH -1 Ca(OH) 2 Calcium hydroxide<br />
Al +3 OH -1 Al(OH) 3 Aluminum hydroxide<br />
Acid/Base <strong>Naming</strong> <strong>Rules</strong><br />
<strong>Naming</strong> bases does not necessitate any change in the rules. The names seen above are<br />
the names of the bases.<br />
Acids, however, are named slightly differently based upon whether or not they are oxy<strong>acids</strong><br />
or non-oxy<strong>acids</strong>. Oxy<strong>acids</strong> are <strong>acids</strong> that have oxygen in the formula. Nonoxy<strong>acids</strong><br />
are <strong>acids</strong> that do NOT contain oxygen in the formula. From the list above:<br />
Examples of Non-oxy<strong>acids</strong>: HCl HBr HCN<br />
Examples of Oxy-<strong>acids</strong>: HClO 4 HNO 2 H 3 PO 3
Oxy<strong>acids</strong>:<br />
Drop “hydrogen”<br />
-ate ending becomes –ic acid<br />
-ite ending becomes –ous acid<br />
Non-oxyacds: “hydrogen” becomes “hydro-”<br />
-ide ending becomes –ic acid<br />
Consequently each name changes to the following:<br />
Cation Anion Formula Name Acid Name<br />
H + Cl -1 HCl Hydrogen chloride Hydrochloric acid<br />
H + Br -1 HBr Hydrogen bromide Hydrobromic acid<br />
H + I -1 HI Hydrogen iodide Hydroiodic acid<br />
H + CN -1 HCN Hydrogen cyanide Hydrocyanic acid<br />
H + -1<br />
ClO 4<br />
H + -1<br />
NO 3<br />
H + -2<br />
SO 4<br />
H + -3<br />
PO 4<br />
H + -1<br />
ClO 2<br />
H + -1<br />
NO 2<br />
H + -2<br />
SO 3<br />
H + -3<br />
PO 3<br />
HClO 4 Hydrogen perchlorate Perchloric acid<br />
HNO 3 Hydrogen nitrate Nitric acid<br />
H 2 SO 4 Hydrogen sulfate Sulfuric acid<br />
H 3 PO 4 Hydrogen phosphate Phosporic acid<br />
HClO 2 Hydrogen chlorie Chlorous acid<br />
HNO 2 Hydrogen nitrite Nitrous acid<br />
H 2 SO 3 Hydrogen sulfite Sulfurous acid<br />
H 3 PO 3 Hydrogen phosphate Phosphorous acid
Questions<br />
1. Name the following <strong>acids</strong>:<br />
a) HF<br />
b) HBr<br />
c) H 2 S<br />
2. Name the following <strong>acids</strong>:<br />
a) H 2 SO 4<br />
b) H 2 CO 3<br />
c) HClO 3<br />
3. Name the following <strong>acids</strong>:<br />
a) HClO<br />
b) HNO 2<br />
c) H 2 SO 3<br />
4. Name the following bases:<br />
a) Mg(OH) 2<br />
b) LiOH<br />
c) Ba(OH) 2<br />
5. Give the formula for the following <strong>acids</strong> or bases:<br />
a) perchloric acid<br />
b) phosphoric acid<br />
c) nitrous acid<br />
d) hydrofluoric acid<br />
e) cyanic acid<br />
f) thiosulfuric acid<br />
g) copper (II) hydroxide<br />
h) zinc hydroxide<br />
i) rubidium hydroxide<br />
j) strontium hydroxide