Levodopa - epgonline.org
Levodopa - epgonline.org
Levodopa - epgonline.org
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
ENT416_NURSES LEAVEPIECE.qxd 2/10/06 14:08 Page 5<br />
<strong>Levodopa</strong>: the most effective<br />
therapy for Parkinson’s disease<br />
• As PD is caused by reduced levels of dopamine in the brain, replacing<br />
dopamine with levodopa (a precursor to dopamine) or mimicking its<br />
action with dopamine agonists are key approaches to treatment<br />
• Patients have fewer symptoms and function better with levodopa than<br />
with other dopaminergic therapies<br />
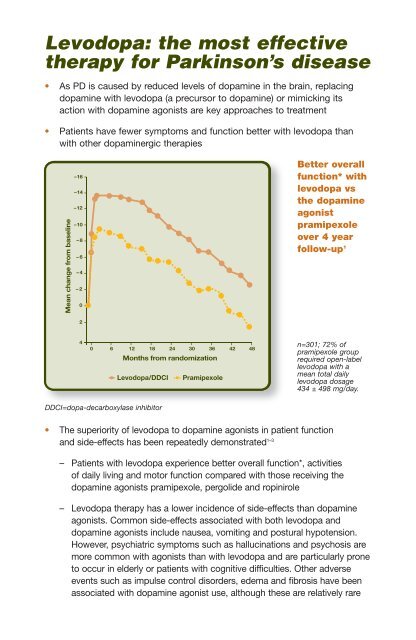
Mean change from baseline<br />
–16<br />
–14<br />
–12<br />
–10<br />
–8<br />
–6<br />
–4<br />
–2<br />
0<br />
Better overall<br />
function* with<br />
levodopa vs<br />
the dopamine<br />
agonist<br />
pramipexole<br />
over 4 year<br />
follow-up 1<br />
2<br />
4<br />
0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48<br />
Months from randomization<br />
<strong>Levodopa</strong>/DDCI Pramipexole<br />
n=301; 72% of<br />
pramipexole group<br />
required open-label<br />
levodopa with a<br />
mean total daily<br />
levodopa dosage<br />
434 ± 498 mg/day.<br />
DDCI=dopa-decarboxylase inhibitor<br />
• The superiority of levodopa to dopamine agonists in patient function<br />
and side-effects has been repeatedly demonstrated 1–3<br />
– Patients with levodopa experience better overall function*, activities<br />
of daily living and motor function compared with those receiving the<br />
dopamine agonists pramipexole, pergolide and ropinirole<br />
– <strong>Levodopa</strong> therapy has a lower incidence of side-effects than dopamine<br />
agonists. Common side-effects associated with both levodopa and<br />
dopamine agonists include nausea, vomiting and postural hypotension.<br />
However, psychiatric symptoms such as hallucinations and psychosis are<br />
more common with agonists than with levodopa and are particularly prone<br />
to occur in elderly or patients with cognitive difficulties. Other adverse<br />
events such as impulse control disorders, edema and fibrosis have been<br />
associated with dopamine agonist use, although these are relatively rare