Advanced Pilot (PG) certificate Application - Hang Gliding ...
Advanced Pilot (PG) certificate Application - Hang Gliding ...
Advanced Pilot (PG) certificate Application - Hang Gliding ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
CER-07_v2.0 Oct 2012<br />
HANG GLIDING FEDERATION OF AUSTRALIA<br />
4c/60 Keilor Park Dr ,Keilor Park Vic 3042 Ph (03) 9336 7155 Fax (03) 9336 7177<br />
Website: www.hgfa.asn.au Email: office@hgfa.asn.au ABN: 15 276 389 269<br />
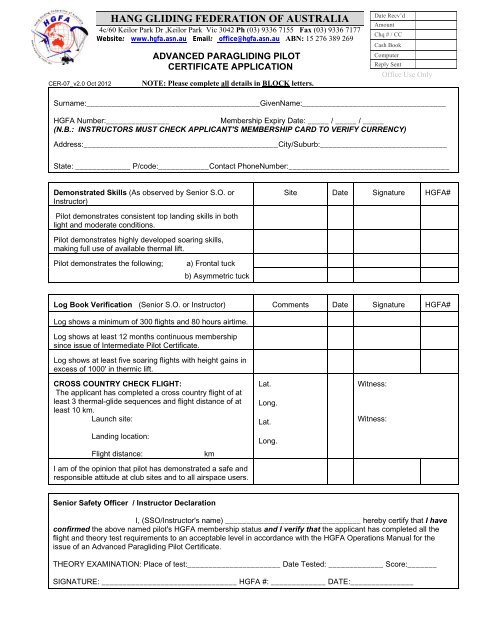
ADVANCED PARAGLIDING PILOT<br />
CERTIFICATE APPLICATION<br />
NOTE: Please complete all details in BLOCK letters.<br />
Date Recv’d<br />
Amount<br />
Chq # / CC<br />
Cash Book<br />
Computer<br />
Reply Sent<br />
Office Use Only<br />
Surname:_________________________________________GivenName:__________________________________<br />
HGFA Number:_______________<br />
Membership Expiry Date: _____ / _____ / _____<br />
(N.B.: INSTRUCTORS MUST CHECK APPLICANT'S MEMBERSHIP CARD TO VERIFY CURRENCY)<br />
Address:______________________________________________City/Suburb:______________________________<br />
State: _____________ P/code:____________Contact PhoneNumber:______________________________________<br />
Demonstrated Skills (As observed by Senior S.O. or<br />
Instructor)<br />
Site Date Signature HGFA#<br />
<strong>Pilot</strong> demonstrates consistent top landing skills in both<br />
light and moderate conditions.<br />
<strong>Pilot</strong> demonstrates highly developed soaring skills,<br />
making full use of available thermal lift.<br />
<strong>Pilot</strong> demonstrates the following;<br />
a) Frontal tuck<br />
b) Asymmetric tuck<br />
Log Book Verification (Senior S.O. or Instructor) Comments Date Signature HGFA#<br />
Log shows a minimum of 300 flights and 80 hours airtime.<br />
Log shows at least 12 months continuous membership<br />
since issue of Intermediate <strong>Pilot</strong> Certificate.<br />
Log shows at least five soaring flights with height gains in<br />
excess of 1000' in thermic lift.<br />
CROSS COUNTRY CHECK FLIGHT:<br />
The applicant has completed a cross country flight of at<br />
least 3 thermal-glide sequences and flight distance of at<br />
least 10 km.<br />
Launch site:<br />
Landing location:<br />
Flight distance:<br />
km<br />
I am of the opinion that pilot has demonstrated a safe and<br />
responsible attitude at club sites and to all airspace users.<br />
Lat.<br />
Long.<br />
Lat.<br />
Long.<br />
Witness:<br />
Witness:<br />
Senior Safety Officer / Instructor Declaration<br />
I, (SSO/Instructor's name) ________________________________ hereby certify that I have<br />
confirmed the above named pilot's HGFA membership status and I verify that the applicant has completed all the<br />
flight and theory test requirements to an acceptable level in accordance with the HGFA Operations Manual for the<br />
issue of an <strong>Advanced</strong> Paragliding <strong>Pilot</strong> Certificate.<br />
THEORY EXAMINATION: Place of test:______________________ Date Tested: _____________ Score:_______<br />
SIGNATURE: ________________________________ HGFA #: _____________ DATE:_______________
HANG GLIDING FEDERATION OF AUSTRALIA<br />
ADVANCED EXAMINATION STUDY PAPER - PARAGLIDING<br />
This study guide is provided to enable pilots to prepare for the multiple choice <strong>Advanced</strong> Paragliding<br />
<strong>Pilot</strong> Certificate theory examination. The theory examination must be passed prior to the issue of an<br />
HGFA <strong>Advanced</strong> Paragliding <strong>Pilot</strong> Certificate. The multiple choice examination is in two parts, to<br />
achieve a pass an applicant must correctly answer all Part A questions (1 to 20) and correctly<br />
answer 75% of Part B questions (20 to 80). Failure in either part will require entire re-examination.<br />
A student must be able to answer the questions and understand the subjects listed below.<br />
PART A Required Pass 100%<br />
Select the correct VMC criteria below 10000' amsl.<br />
Other than during the launch and landing phase, what is the<br />
minimum height a glider may be flown over any city, town or<br />
populous area<br />
What is the minimum distance a glider may be flown from<br />
spectators<br />
Which glider gives way:<br />
when two gliders are approaching at different heights;<br />
when two gliders are converging at right angles;<br />
when joining a thermal; when overtaking;<br />
when two gliders are approaching head-on along a ridge; and<br />
when two gliders are approaching head-on in clear air<br />
What technique would you use to recover from a left hand wing tip<br />
tuck<br />
What is the recovery technique from a stall whilst in a turn<br />
How do you recover from a full stall<br />
What is the rule in regard to absolute right of way<br />
What flight restrictions are applied to hang gliders and paragliders<br />
via CAO 95.8 in regard to:<br />
Flying with an altimeter; Flying in military airspace;<br />
Flying in Controlled Airspace; Holding a <strong>Pilot</strong> Certificate;<br />
What are the priorities of First Aid; Which hang gliding/<br />
paragliding rule of the air differs from those of sailplanes<br />
What is the HGFA recommended maximum time between<br />
emergency parachute repacks<br />
What problems may be encountered when hang gliders and<br />
paragliders are flying together<br />
PART B Required Pass 75%<br />
Define Aspect ratio. Define Wing loading.<br />
Define Parasitic drag. Define Induced drag.<br />
Define High speed stall. What problems are associated with a<br />
large tip tuck on a high performance glider<br />
How does the density of moist air vary from dry air.<br />
What is the meaning of an AVFAX forecast showing 2000 above<br />
045/10.<br />
Define Indicated airspeed. Define True airspeed.<br />
After a collapse you have a cravat which is causing you to go into<br />
a spiral dive, what are your options<br />
What should you do if you are about to entangle with another<br />
paraglider<br />
How do you recover from a parachutal stall<br />
What are the symptoms of a parachutal stall<br />
What relationship do weight, drag, lift, angle of attack and relative<br />
airflow have to a wing in flight<br />
What action would you take you stall a wing tip whilst thermalling<br />
in a tight turn<br />
What action would you take if you are thermalling with deep brake<br />
settings in light lift, you get hit by a stronger thermal and the glider<br />
stalls<br />
How would rain on the glider affect handling and performance<br />
When landing in strong turbulent conditions, which technique<br />
could be used to aid in a safe landing<br />
How does wing loading affect stall speed<br />
What do you do to increase the chances of seeing and being<br />
seen if you hear a powered aircraft when flying at 5000'<br />
What is the possible significance of alto-cumulus clouds early in<br />
the day<br />
What is the difference between over-development (OD) and overclouding<br />
(OC) and how might they affect soaring strategies<br />
Can you identify the following cloud types: Cb, Sc, Cu, St & Ns<br />
What techniques are used to utilise wave lift and what are the<br />
associated dangers<br />
What is a dust devil (willy willy) and what causes it to form Why<br />
are they more likely to form in dry conditions At what height<br />
should you enter one (if at all)<br />
Under total cloud cover what cloud formations and types may hold<br />
hope of convective lift<br />
A large high pressure system is centred over NSW/VIC border.<br />
The isobars show a fairly uniform shape except a dip toward the<br />
south along a line from central west Qld to central NSW. What<br />
does this dip indicate and what are the likely developments the<br />
next day along the eastern seaboard, the great divide, the central<br />
west of NSW and Qld, Nth Vic and other places west of the "dip"<br />
What is the nature of thermal lift early in the day (average Aust.<br />
conditions)<br />
What is trigger temperature<br />
Rate the following in order from stable to unstable:<br />
dry/cold air mass; warm/dry air mass; warm/moist air<br />
mass; and cold/moist air mass.<br />
What air causes the most severe mechanical turbulence<br />
Define the term 'dry adiabatic lapse rate=.<br />
On a mean sea level synoptic chart of Australia showing a typical<br />
synoptic situation for a given season, identify the point(s) of the<br />
following features: high pressure systems;<br />
low pressure systems; warm and cold fronts; an isobar of 1016<br />
Hpa; a tropical revolving storm; a trough; and<br />
wind directions around highs and lows.<br />
On an ERC:<br />
how can you differentiate controlled airspace from<br />
uncontrolled airspace;<br />
what does an area labelled "LL FL120" indicate;<br />
on an ERC what does "CTR 0-3000" indicate and<br />
what would you need to do if you wished to fly from a site<br />
inside the area marked with a red boundary and labelled<br />
"R592B 0-10000"<br />
What radio procedure you would use to report your position to a<br />
pick up car following you.<br />
What is the maximum height a glider may be flown in class 'G'<br />
airspace<br />
How would you increase your chances of being found if you<br />
landed in tiger country or were injured out landing<br />
What are hypoxia and hypothermia and how would you recognise<br />
the symptoms<br />
How does alcohol effect your performance and judgement How<br />
does marijuana effect your performance and judgement How<br />
long do the residual effects of alcohol affect your flying ability<br />
How long do the residual effects of marijuana affect your flying<br />
ability<br />
What are the dangers of flying in severe turbulence<br />
What is the standard approach pattern for unobstructed LZ's for<br />
gliders<br />
What is the accepted standard approach and landing pattern for<br />
paragliders at general aviation aerodromes where paragliding<br />
operations are permitted<br />
You are circling in a thermal in moderate wind. If you lost the<br />
thermal, where would you search for it<br />
When a stall is induced what section of the wing collapses first<br />
What is the standard navigational maps used by paragliders in<br />
Australia How would you gain a map reference from a Natmap