Download as PDF - Secunet
Download as PDF - Secunet
Download as PDF - Secunet
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
National<br />
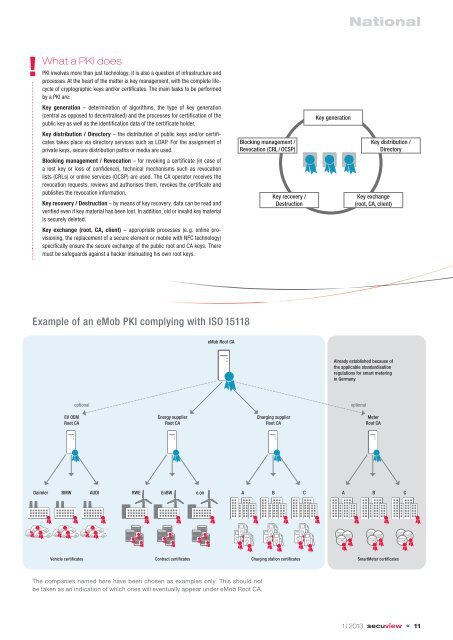
What a PKI does<br />
PKI involves more than just technology; it is also a question of infr<strong>as</strong>tructure and<br />
processes. At the heart of the matter is key management, with the complete lifecycle<br />
of cryptographic keys and/or certifi cates. The main t<strong>as</strong>ks to be performed<br />
by a PKI are:<br />
Key generation – determination of algorithms, the type of key generation<br />
(central <strong>as</strong> opposed to decentralised) and the processes for certifi cation of the<br />
public key <strong>as</strong> well <strong>as</strong> the identifi cation data of the certifi cate holder.<br />
Key distribution / Directory – the distribution of public keys and/or certifi -<br />
cates takes place via directory services such <strong>as</strong> LDAP. For the <strong>as</strong>signment of<br />
private keys, secure distribution paths or media are used.<br />
Blocking management / Revocation – for revoking a certifi cate (in c<strong>as</strong>e of<br />
a lost key or loss of confi dence), technical mechanisms such <strong>as</strong> revocation<br />
lists (CRLs) or online services (OCSP) are used. The CA operator receives the<br />
revocation requests, reviews and authorises them, revokes the certifi cate and<br />
publishes the revocation information.<br />
Key recovery / Destruction – by means of key recovery, data can be read and<br />
verifi ed even if key material h<strong>as</strong> been lost. In addition, old or invalid key material<br />
is securely deleted.<br />
Key exchange (root, CA, client) – appropriate processes (e. g. online provisioning,<br />
the replacement of a secure element or mobile with NFC technology)<br />
specifi cally ensure the secure exchange of the public root and CA keys. There<br />
must be safeguards against a hacker insinuating his own root keys.<br />
Blocking management /<br />
Revocation (CRL / OCSP)<br />
Key recovery /<br />
Destruction<br />
Key generation<br />
Key distribution /<br />
Directory<br />
Key exchange<br />
(root, CA, client)<br />
Example of an eMob PKI complying with ISO 15118<br />
eMob Root CA<br />
Already established because of<br />
the applicable standardisation<br />
regulations for smart metering<br />
in Germany<br />
optional<br />
optional<br />
EV OEM<br />
Root CA<br />
Energy supplier<br />
Root CA<br />
Charging supplier<br />
Root CA<br />
Meter<br />
Root CA<br />
Daimler<br />
BMW<br />
AUDI RWE EnBW e.on A B<br />
C<br />
A<br />
B<br />
C<br />
Vehicle certificates Contract certificates Charging station certificates SmartMeter certificates<br />
The companies named here have been chosen <strong>as</strong> examples only. This should not<br />
be taken <strong>as</strong> an indication of which ones will eventually appear under eMob Root CA.<br />
1 | 2013 « 11