Multifunctional propyleneimines-new generation of crosslinkers for ...
Multifunctional propyleneimines-new generation of crosslinkers for ...
Multifunctional propyleneimines-new generation of crosslinkers for ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
504<br />
ARTICLE IN PRESS<br />
Z. Czech / International Journal <strong>of</strong> Adhesion & Adhesives 24 (2004) 503–511<br />
properties <strong>of</strong> the PSA coat, such as tack and peel<br />
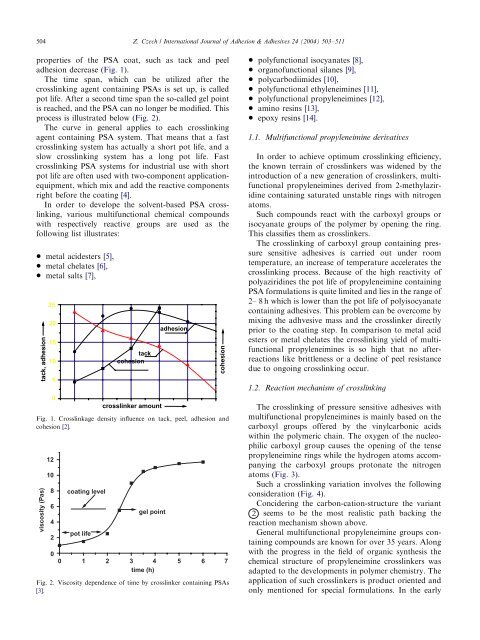
adhesion decrease (Fig. 1).<br />
The time span, which can be utilized after the<br />
crosslinking agent containing PSAs is set up, is called<br />
pot life. After a second time span the so-called gel point<br />
is reached, and the PSA can no longer be modified. This<br />
process is illustrated below (Fig. 2).<br />
The curve in general applies to each crosslinking<br />
agent containing PSA system. That means that a fast<br />
crosslinking systemhas actually a short pot life, and a<br />
slow crosslinking systemhas a long pot life. Fast<br />
crosslinking PSA systems <strong>for</strong> industrial use with short<br />
pot life are <strong>of</strong>ten used with two-component applicationequipment,<br />
which mix and add the reactive components<br />
right be<strong>for</strong>e the coating [4].<br />
In order to develope the solvent-based PSA crosslinking,<br />
various multifunctional chemical compounds<br />
with respectively reactive groups are used as the<br />
following list illustrates:<br />
* metal acidesters [5],<br />
* metal chelates [6],<br />
* metal salts [7],<br />
tack, adhesion<br />
25<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
tack<br />
cohesion<br />
crosslinker amount<br />
adhesion<br />
Fig. 1. Crosslinkage density influence on tack, peel, adhesion and<br />
cohesion [2].<br />
viscosity (Pas)<br />
12<br />
10<br />
8<br />
6<br />
4<br />
2<br />
coating level<br />
pot life<br />
gel point<br />
0<br />
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7<br />
time (h)<br />
Fig. 2. Viscosity dependence <strong>of</strong> time by crosslinker containing PSAs<br />
[3].<br />
cohesion<br />
* polyfunctional isocyanates [8],<br />
* organ<strong>of</strong>unctional silanes [9],<br />
* polycarbodiimides [10],<br />
* polyfunctional ethyleneimines [11],<br />
* polyfunctional <strong>propyleneimines</strong> [12],<br />
* amino resins [13],<br />
* epoxy resins [14].<br />
1.1. <strong>Multifunctional</strong> propyleneimine derivatives<br />
In order to achieve optimum crosslinking efficiency,<br />
the known terrain <strong>of</strong> <strong>crosslinkers</strong> was widened by the<br />
introduction <strong>of</strong> a <strong>new</strong> <strong>generation</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>crosslinkers</strong>, multifunctional<br />
<strong>propyleneimines</strong> derived from 2-methylaziridine<br />
containing saturated unstable rings with nitrogen<br />
atoms.<br />
Such compounds react with the carboxyl groups or<br />
isocyanate groups <strong>of</strong> the polymer by opening the ring.<br />
This classifies themas <strong>crosslinkers</strong>.<br />
The crosslinking <strong>of</strong> carboxyl group containing pressure<br />
sensitive adhesives is carried out under room<br />
temperature, an increase <strong>of</strong> temperature accelerates the<br />
crosslinking process. Because <strong>of</strong> the high reactivity <strong>of</strong><br />
polyaziridines the pot life <strong>of</strong> propyleneimine containing<br />
PSA <strong>for</strong>mulations is quite limited and lies in the range <strong>of</strong><br />
2– 8 h which is lower than the pot life <strong>of</strong> polyisocyanate<br />
containing adhesives. This problemcan be overcome by<br />
mixing the adhvesive mass and the crosslinker directly<br />
prior to the coating step. In comparison to metal acid<br />
esters or metal chelates the crosslinking yield <strong>of</strong> multifunctional<br />
<strong>propyleneimines</strong> is so high that no afterreactions<br />
like brittleness or a decline <strong>of</strong> peel resistance<br />
due to ongoing crosslinking occur.<br />
1.2. Reaction mechanism <strong>of</strong> crosslinking<br />
The crosslinking <strong>of</strong> pressure sensitive adhesives with<br />
multifunctional <strong>propyleneimines</strong> is mainly based on the<br />
carboxyl groups <strong>of</strong>fered by the vinylcarbonic acids<br />
within the polymeric chain. The oxygen <strong>of</strong> the nucleophilic<br />
carboxyl group causes the opening <strong>of</strong> the tense<br />
propyleneimine rings while the hydrogen atoms accompanying<br />
the carboxyl groups protonate the nitrogen<br />
atoms (Fig. 3).<br />
Such a crosslinking variation involves the following<br />
consideration (Fig. 4).<br />
Concidering the carbon-cation-structure the variant<br />
2 seems to be the most realistic path backing the<br />
reaction mechanism shown above.<br />
General multifunctional propyleneimine groups containing<br />
compounds are known <strong>for</strong> over 35 years. Along<br />
with the progress in the field <strong>of</strong> organic synthesis the<br />
chemical structure <strong>of</strong> propyleneimine <strong>crosslinkers</strong> was<br />
adapted to the developments in polymer chemistry. The<br />
application <strong>of</strong> such <strong>crosslinkers</strong> is product oriented and<br />
only mentioned <strong>for</strong> special <strong>for</strong>mulations. In the early