Assessing Pain in the Nonverbal or Cognitively Impaired
Assessing Pain in the Nonverbal or Cognitively Impaired
Assessing Pain in the Nonverbal or Cognitively Impaired
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Assess<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>Pa<strong>in</strong></strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Nonverbal</strong> <strong>or</strong> <strong>Cognitively</strong> <strong>Impaired</strong> 3rd Ed, 9/09<br />
ADULTS<br />
The most accurate and reliable evidence of <strong>the</strong> presence and <strong>in</strong>tensity of pa<strong>in</strong> is <strong>the</strong> patient’s self‐rep<strong>or</strong>t.<br />
Even patients with mild to moderate cognitive impairment may be able to use pa<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>tensity scales (e.g.,<br />
0‐10, mild‐moderate‐severe). F<strong>or</strong> patients unable to rep<strong>or</strong>t pa<strong>in</strong>, screen f<strong>or</strong> <strong>the</strong> presence of pa<strong>in</strong> by<br />
observ<strong>in</strong>g behavi<strong>or</strong>s and watch<strong>in</strong>g f<strong>or</strong> changes <strong>in</strong> function (e.g., changes <strong>in</strong> gait, withdrawn <strong>or</strong> agitated<br />
behavi<strong>or</strong>, moan<strong>in</strong>g, groan<strong>in</strong>g, and cry<strong>in</strong>g). UW Health recommends <strong>the</strong> follow<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>strument as an<br />
option to assess and document pa<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> an adult with cognitive impairment.<br />
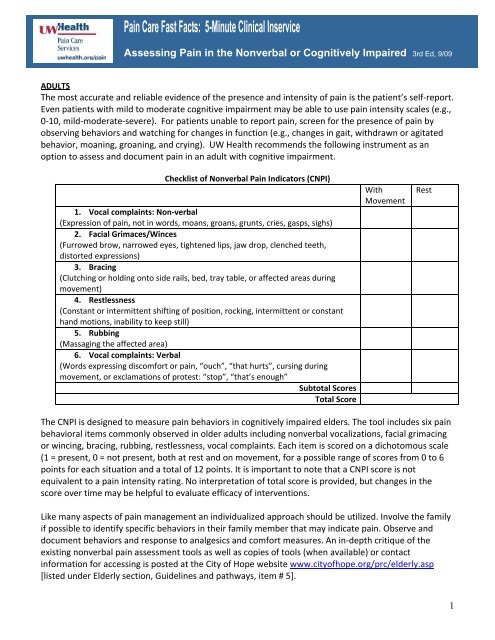
Checklist of <strong>Nonverbal</strong> <strong>Pa<strong>in</strong></strong> Indicat<strong>or</strong>s (CNPI)<br />
1. Vocal compla<strong>in</strong>ts: Non‐verbal<br />
(Expression of pa<strong>in</strong>, not <strong>in</strong> w<strong>or</strong>ds, moans, groans, grunts, cries, gasps, sighs)<br />
2. Facial Grimaces/W<strong>in</strong>ces<br />
(Furrowed brow, narrowed eyes, tightened lips, jaw drop, clenched teeth,<br />
dist<strong>or</strong>ted expressions)<br />
3. Brac<strong>in</strong>g<br />
(Clutch<strong>in</strong>g <strong>or</strong> hold<strong>in</strong>g onto side rails, bed, tray table, <strong>or</strong> affected areas dur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
movement)<br />
4. Restlessness<br />
(Constant <strong>or</strong> <strong>in</strong>termittent shift<strong>in</strong>g of position, rock<strong>in</strong>g, <strong>in</strong>termittent <strong>or</strong> constant<br />
hand motions, <strong>in</strong>ability to keep still)<br />
5. Rubb<strong>in</strong>g<br />
(Massag<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> affected area)<br />
6. Vocal compla<strong>in</strong>ts: Verbal<br />
(W<strong>or</strong>ds express<strong>in</strong>g discomf<strong>or</strong>t <strong>or</strong> pa<strong>in</strong>, “ouch”, “that hurts”, curs<strong>in</strong>g dur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
movement, <strong>or</strong> exclamations of protest: “stop”, “that’s enough”<br />
Subtotal Sc<strong>or</strong>es<br />
Total Sc<strong>or</strong>e<br />
With<br />
Movement<br />
Rest<br />
The CNPI is designed to measure pa<strong>in</strong> behavi<strong>or</strong>s <strong>in</strong> cognitively impaired elders. The tool <strong>in</strong>cludes six pa<strong>in</strong><br />
behavi<strong>or</strong>al items commonly observed <strong>in</strong> older adults <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g nonverbal vocalizations, facial grimac<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>or</strong> w<strong>in</strong>c<strong>in</strong>g, brac<strong>in</strong>g, rubb<strong>in</strong>g, restlessness, vocal compla<strong>in</strong>ts. Each item is sc<strong>or</strong>ed on a dichotomous scale<br />
(1 = present, 0 = not present, both at rest and on movement, f<strong>or</strong> a possible range of sc<strong>or</strong>es from 0 to 6<br />
po<strong>in</strong>ts f<strong>or</strong> each situation and a total of 12 po<strong>in</strong>ts. It is imp<strong>or</strong>tant to note that a CNPI sc<strong>or</strong>e is not<br />
equivalent to a pa<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>tensity rat<strong>in</strong>g. No <strong>in</strong>terpretation of total sc<strong>or</strong>e is provided, but changes <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
sc<strong>or</strong>e over time may be helpful to evaluate efficacy of <strong>in</strong>terventions.<br />
Like many aspects of pa<strong>in</strong> management an <strong>in</strong>dividualized approach should be utilized. Involve <strong>the</strong> family<br />
if possible to identify specific behavi<strong>or</strong>s <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>ir family member that may <strong>in</strong>dicate pa<strong>in</strong>. Observe and<br />
document behavi<strong>or</strong>s and response to analgesics and comf<strong>or</strong>t measures. An <strong>in</strong>‐depth critique of <strong>the</strong><br />
exist<strong>in</strong>g nonverbal pa<strong>in</strong> assessment tools as well as copies of tools (when available) <strong>or</strong> contact<br />
<strong>in</strong>f<strong>or</strong>mation f<strong>or</strong> access<strong>in</strong>g is posted at <strong>the</strong> City of Hope website www.cityofhope.<strong>or</strong>g/prc/elderly.asp<br />
[listed under Elderly section, Guidel<strong>in</strong>es and pathways, item # 5].<br />
1
<strong>Pa<strong>in</strong></strong> Fast Facts: <strong>Pa<strong>in</strong></strong> Fast Fact: <strong>Assess<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>Pa<strong>in</strong></strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Nonverbal</strong> <strong>or</strong> <strong>Cognitively</strong> <strong>Impaired</strong><br />
cont<strong>in</strong>ued<br />
CHILDREN<br />
Use <strong>the</strong> UW Children’s Hospital <strong>Pa<strong>in</strong></strong> Scale f<strong>or</strong> Preverbal and <strong>Nonverbal</strong> Children developed and tested<br />
on preverbal children (less than 3 years old) and cognitively impaired children to assess pa<strong>in</strong>.<br />
This <strong>in</strong>strument is f<strong>or</strong> pediatric patients and is NOT appropriate f<strong>or</strong> adults.<br />
References<br />
• Soetenga D, Frank J, Pell<strong>in</strong>o TA. Assessment of <strong>the</strong> validity and reliability of <strong>the</strong> University of Wiscons<strong>in</strong> Children’s<br />
Hospital <strong>Pa<strong>in</strong></strong> scale f<strong>or</strong> Preverbal and <strong>Nonverbal</strong> Children. Pediatric Nurs<strong>in</strong>g 1999;25(6):670‐676.<br />
• Feldt, KS. Checklist of <strong>Nonverbal</strong> <strong>Pa<strong>in</strong></strong> Indicat<strong>or</strong>s. <strong>Pa<strong>in</strong></strong> Management Nurs<strong>in</strong>g 2000; 1(1):13‐21.<br />
• Herr K et al. Tools f<strong>or</strong> assessment of pa<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> nonverbal older adults with dementia: a state‐of‐<strong>the</strong>‐science review.<br />
Journal of <strong>Pa<strong>in</strong></strong> and Symptom Management 2006;31(2):170‐192.<br />
Permission granted to modify <strong>or</strong> adapt provided written credit is given to <strong>the</strong><br />
University of Wiscons<strong>in</strong> Hospital & Cl<strong>in</strong>ics, Madison, WI<br />
Internet: Visit www.uwhealth.<strong>or</strong>g/pa<strong>in</strong><br />
Intranet: M<strong>or</strong>e Fast Facts <strong>in</strong> UConnect under Cl<strong>in</strong>ical Guidel<strong>in</strong>es/<strong>Pa<strong>in</strong></strong> Management Resources<br />
2