ITU-T V.150.1
ITU-T V.150.1
ITU-T V.150.1
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
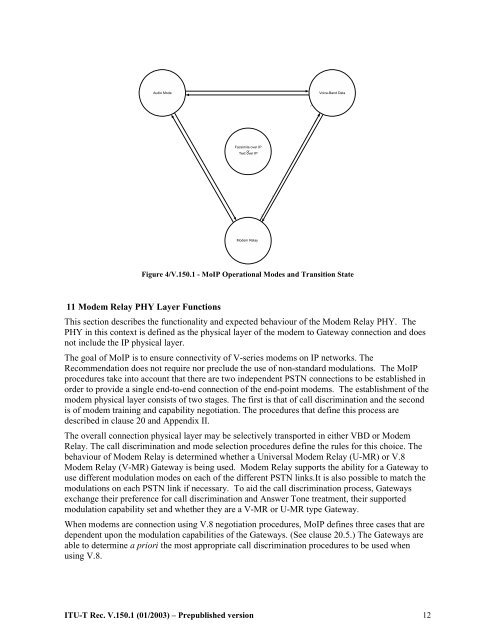
Audio Mode<br />
Voice-Band Data<br />
Facsimile over IP<br />
or<br />
Text over IP<br />
Modem Relay<br />
Figure 4/<strong>V.150.1</strong> - MoIP Operational Modes and Transition State<br />
11 Modem Relay PHY Layer Functions<br />
This section describes the functionality and expected behaviour of the Modem Relay PHY. The<br />
PHY in this context is defined as the physical layer of the modem to Gateway connection and does<br />
not include the IP physical layer.<br />
The goal of MoIP is to ensure connectivity of V-series modems on IP networks. The<br />
Recommendation does not require nor preclude the use of non-standard modulations. The MoIP<br />
procedures take into account that there are two independent PSTN connections to be established in<br />
order to provide a single end-to-end connection of the end-point modems. The establishment of the<br />
modem physical layer consists of two stages. The first is that of call discrimination and the second<br />
is of modem training and capability negotiation. The procedures that define this process are<br />
described in clause 20 and Appendix II.<br />
The overall connection physical layer may be selectively transported in either VBD or Modem<br />
Relay. The call discrimination and mode selection procedures define the rules for this choice. The<br />
behaviour of Modem Relay is determined whether a Universal Modem Relay (U-MR) or V.8<br />
Modem Relay (V-MR) Gateway is being used. Modem Relay supports the ability for a Gateway to<br />
use different modulation modes on each of the different PSTN links.It is also possible to match the<br />
modulations on each PSTN link if necessary. To aid the call discrimination process, Gateways<br />
exchange their preference for call discrimination and Answer Tone treatment, their supported<br />
modulation capability set and whether they are a V-MR or U-MR type Gateway.<br />
When modems are connection using V.8 negotiation procedures, MoIP defines three cases that are<br />
dependent upon the modulation capabilities of the Gateways. (See clause 20.5.) The Gateways are<br />
able to determine a priori the most appropriate call discrimination procedures to be used when<br />
using V.8.<br />
<strong>ITU</strong>-T Rec. <strong>V.150.1</strong> (01/2003) – Prepublished version 12