Micrococcaceae Biochemical Tests and Media - UNMC
Micrococcaceae Biochemical Tests and Media - UNMC
Micrococcaceae Biochemical Tests and Media - UNMC
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
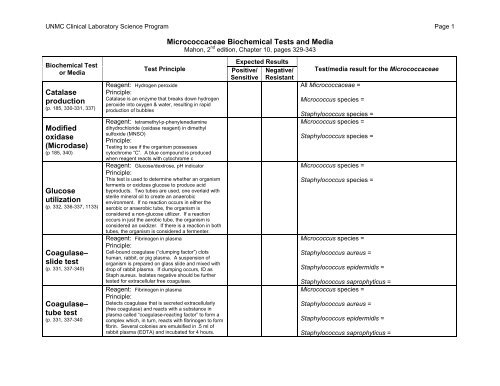
<strong>UNMC</strong> Clinical Laboratory Science Program Page 1<br />
<strong>Micrococcaceae</strong> <strong>Biochemical</strong> <strong>Tests</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Media</strong><br />
Mahon, 2 nd edition, Chapter 10, pages 329-343<br />
<strong>Biochemical</strong> Test<br />
or <strong>Media</strong><br />
Catalase<br />
production<br />
(p. 185, 330-331, 337)<br />
Modified<br />
oxidase<br />
(Microdase)<br />
(p 185, 340)<br />
Glucose<br />
utilization<br />
(p. 332, 336-337, 1133)<br />
Coagulase–<br />
slide test<br />
(p. 331, 337-340)<br />
Coagulase–<br />
tube test<br />
(p. 331, 337-340<br />
Test Principle<br />
Reagent: Hydrogen peroxide<br />
Principle:<br />
Catalase is an enzyme that breaks down hydrogen<br />
peroxide into oxygen & water, resulting in rapid<br />
production of bubbles<br />
Reagent: tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine<br />
dihydrochloride (oxidase reagent) in dimethyl<br />
sulfoxide (MNSO)<br />
Principle:<br />
Testing to see if the organism possesses<br />
cytochrome “C”. A blue compound is produced<br />
when reagent reacts with cytochrome c<br />
Reagent: Glucose/dextrose, pH indicator<br />
Principle:<br />
This test is used to determine whether an organism<br />
ferments or oxidizes glucose to produce acid<br />
byproducts. Two tubes are used, one overlaid with<br />
sterile mineral oil to create an anaerobic<br />
environment. If no reaction occurs in either the<br />
aerobic or anaerobic tube, the organism is<br />
considered a non-glucose utilizer. If a reaction<br />
occurs in just the aerobic tube, the organism is<br />
considered an oxidizer. If there is a reaction in both<br />
tubes, the organism is considered a fermenter.<br />
Reagent: Fibrinogen in plasma<br />
Principle:<br />
Cell-bound coagulase (“clumping factor”) clots<br />
human, rabbit, or pig plasma. A suspension of<br />
organism is prepared on glass slide <strong>and</strong> mixed with<br />
drop of rabbit plasma. If clumping occurs, ID as<br />
Staph aureus. Isolates negative should be further<br />
tested for extracellular free coagulase.<br />
Reagent: Fibrinogen in plasma<br />
Principle:<br />
Detects coagulase that is secreted extracellularly<br />
(free coagulase) <strong>and</strong> reacts with a substance in<br />
plasma called “coagulase-reacting factor” to form a<br />
complex which, in turn, reacts with fibrinogen to form<br />
fibrin. Several colonies are emulsified in .5 ml of<br />
rabbit plasma (EDTA) <strong>and</strong> incubated for 4 hours.<br />
Expected Results<br />
Positive/ Negative/<br />
Sensitive Resistant<br />
Test/media result for the <strong>Micrococcaceae</strong><br />
All <strong>Micrococcaceae</strong> =<br />
Micrococcus species =<br />
Staphylococcus species =<br />
Micrococcus species =<br />
Staphylococcus species =<br />
Micrococcus species =<br />
Staphylococcus species =<br />
Micrococcus species =<br />
Staphylococcus aureus =<br />
Staphylococcus epidermidis =<br />
Staphylococcus saprophyticus =<br />
Micrococcus species =<br />
Staphylococcus aureus =<br />
Staphylococcus epidermidis =<br />
Staphylococcus saprophyticus =
<strong>UNMC</strong> Clinical Laboratory Science Program Page 2<br />
<strong>Micrococcaceae</strong> <strong>Biochemical</strong> <strong>Tests</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Media</strong><br />
Mahon, 2 nd edition, Chapter 10, pages 329-343<br />
<strong>Biochemical</strong> Test<br />
or <strong>Media</strong><br />
Mannitol salt<br />
agar<br />
(p 1130)<br />
DNase activity<br />
(p 1124)<br />
Novobiocin<br />
resistance<br />
(p. 338, 73)<br />
Bacitracin<br />
resistance<br />
(Taxo A disk)<br />
(p 332, 337, 340)<br />
Furazolidone<br />
& Lysostaphin<br />
disks<br />
(p 332, 337)<br />
Test Principle<br />
<strong>Media</strong> classification:<br />
Selective <strong>and</strong> differential for Staph.<br />
Ingredients:<br />
Peptone base, mannitol, <strong>and</strong> phenol red indicator.<br />
Salt concentration of 7.5% inhibits most bacteria.<br />
Principle:<br />
Fermentation of mannitol will produce an acid<br />
byproduct <strong>and</strong> cause a color change of the indicator.<br />
<strong>Media</strong> classification:<br />
Differential<br />
Ingredients:<br />
DNA, metachromatic dyes such as toluidine blue or<br />
methyl green<br />
Principle (include enzyme tested for):<br />
Detects presence of an active DNase exoenzyme.<br />
Incubate organism on agar overnight. Look for color<br />
change surrounding area of growth.<br />
Disk contains:<br />
5 µg Novobiocin<br />
Principle:<br />
Disk diffusion susceptibility test<br />
Disk contains:<br />
0.04 U bacitracin<br />
Principle:<br />
Disk diffusion susceptibility test<br />
Disk contains:<br />
100 ug Furazolidone, or 200 ug/ml Lysostaphin<br />
Principle:<br />
Disk diffusion susceptibility tests<br />
Expected Results<br />
Positive/ Negative/<br />
Sensitive Resistant<br />
>12 mm<br />
= “S”<br />
Any zone<br />
of no<br />
growth<br />
around<br />
disk = “S”<br />
Any zone of<br />
no growth<br />
around disk<br />
= “S”<br />
< 12 mm<br />
= “R”<br />
Growth<br />
right up to<br />
edge of<br />
disk = “R”<br />
Growth right<br />
up to edge<br />
of disk = “R”<br />
Test/media result for the <strong>Micrococcaceae</strong><br />
Micrococcus species =<br />
Staphylococcus aureus =<br />
Staphylococcus epidermidis =<br />
Staphylococcus saprophyticus =<br />
Staphylococcus aureus = positive<br />
Staphylococcus epidermidis = negative<br />
Staphylococcus saprophyticus = negative<br />
Staphylococcus epidermidis =<br />
Staphylococcus saprophyticus =<br />
Other coagulase-negative Staph. =<br />
Micrococcus species =<br />
Staphylococcus species =<br />
Micrococcus species =<br />
Staphylococcus species =