- Page 1:
Evidence Report/Technology Assessme
- Page 5 and 6:
Structured Abstract Objectives: Pat
- Page 7 and 8:
CONTENTS Summary...................
- Page 9 and 10:
Chapter 37. Pain Management........
- Page 11 and 12:
Summary Overview Patient safety has
- Page 13 and 14:
from the domains of commercial avia
- Page 15 and 16:
section above. The editorial team c
- Page 17 and 18:
Clear Opportunities for Research Un
- Page 19:
Evidence Report
- Page 23 and 24:
Chapter 1. An Introduction to the R
- Page 25 and 26:
The Evidence Chapter 3 describes ou
- Page 27 and 28:
never occur. Although some of these
- Page 29 and 30:
• Potential for Harm - Many pract
- Page 31 and 32:
• John W. Gosbee, MD, MS, Directo
- Page 33:
23. Brennan TA, Leape LL, Laird NM,
- Page 36 and 37:
As outlined in Chapter 24, signific
- Page 38 and 39:
21. Roberts KH, Libuser C. From Bho
- Page 40 and 41:
literature and were meant to be as
- Page 42 and 43:
Table 3.3. Hierarchy of study desig
- Page 44 and 45:
Table 3.5. Ten Required Abstraction
- Page 46 and 47:
References 1. Thurfjell E, Thurfjel
- Page 49:
PART II. REPORTING AND RESPONDING T
- Page 52 and 53:
Incident reports may target events
- Page 54 and 55:
Opportunities for Impact Most hospi
- Page 56 and 57:
incident reporting and analysis cou
- Page 58 and 59:
References 1. Brennan TA, Leape LL,
- Page 60 and 61:
41. Weingart SN, Ship AN, Aronson M
- Page 62 and 63:
Despite legitimate concerns about t
- Page 64 and 65:
Evidence for Effectiveness of the P
- Page 66 and 67:
17. Rasmussen J. Human error and th
- Page 68 and 69:
Section A. Adverse Drug Events (ADE
- Page 70 and 71:
Prevalence and Severity of the Targ
- Page 72 and 73:
egimen 27 (Level 2); another study
- Page 74 and 75:
few data describing reductions in A
- Page 76 and 77:
Table 6.2. Studies of clinical deci
- Page 78 and 79:
15. Bates DW, Boyle DL, Vander Vlie
- Page 81 and 82:
Chapter 7. The Clinical Pharmacist
- Page 83 and 84:
Evidence for Effectiveness of the P
- Page 85 and 86:
Table 7.1. Studies of clinical phar
- Page 87:
18. Beney J, Bero LA, Bond C. Expan
- Page 90 and 91:
to alert the monitoring clinician i
- Page 92 and 93:
Comment Computerized real-time moni
- Page 94 and 95:
References 1. Kellaway GS, McCrae E
- Page 97 and 98:
Chapter 9. Protocols for High-Risk
- Page 99 and 100:
egarded as a case-control study. 29
- Page 101 and 102:
Comment The primary purpose of hepa
- Page 103 and 104:
Table 9.1. Studies focused primaril
- Page 105 and 106:
Table 9.2. Inpatient anticoagulatio
- Page 107 and 108:
References 1. Bates DW, Cullen DJ,
- Page 109 and 110:
37. Ellis RF, Stephens MA, Sharp GB
- Page 111 and 112:
Chapter 10. Unit-Dose Drug Distribu
- Page 113 and 114:
Study Designs The 5 studies meeting
- Page 115 and 116:
hospitals that wish to do much of t
- Page 117 and 118:
When wrong time errors were omitted
- Page 119 and 120:
21. Barker KN, McConnell WE. The pr
- Page 121 and 122:
Chapter 11. Automated Medication Di
- Page 123 and 124:
system. 5 We classified this as a L
- Page 125 and 126:
Table 11.1. Six studies reviewing a
- Page 127 and 128:
117
- Page 129 and 130:
Chapter 12. Practices to Improve Ha
- Page 131 and 132:
interventions to assess effectivene
- Page 133 and 134:
Table 12.1. Fourteen studies of pra
- Page 135 and 136:
References 1. Haley RW, Culver DH,
- Page 137 and 138:
Chapter 13. Impact of Barrier Preca
- Page 139 and 140:
poor, 20 often below 50%. 21 Purpor
- Page 141 and 142:
the annual expenses due directly to
- Page 143 and 144:
254-bed long-term care facility in
- Page 145 and 146:
Table 13.2. Studies of barrier prec
- Page 147 and 148:
References 1. Handwerger S, Raucher
- Page 149 and 150:
35. Gammon J. The psychological con
- Page 151 and 152:
Chapter 14. Impact of Changes in An
- Page 153 and 154:
Evidence for Effectiveness of the P
- Page 155 and 156:
Table 14.1. Before-after studies of
- Page 157 and 158:
18. MacGowan AP, Brown I, Feeney R,
- Page 159 and 160:
Chapter 15. Prevention of Nosocomia
- Page 161 and 162:
Evidence for Effectiveness of the P
- Page 163 and 164:
Table 15.1.1. Studies of silver all
- Page 165 and 166:
9. Kunin CM. Urinary Tract Infectio
- Page 167 and 168:
probably appropriate to use since i
- Page 169 and 170:
Table 15.2.1. Prospective studies c
- Page 171 and 172:
6. Saint S, Veenstra DL, Sullivan S
- Page 173 and 174:
Chapter 16. Prevention of Intravasc
- Page 175 and 176:
Prevention Unnecessarily prolonged
- Page 177 and 178:
Table 16.1.1. Studies of vascular c
- Page 179 and 180:
Subchapter 16.2. Use of Central Ven
- Page 181 and 182:
Comment In light of the substantial
- Page 183 and 184:
Ramsay 41 §: 397 hospital patients
- Page 185 and 186:
Subchapter 16.3. Use of Chlorhexidi
- Page 187 and 188:
Table 16.3.1. Characteristics of st
- Page 189 and 190:
support the routine use of tunnelin
- Page 191 and 192:
32. Maki DG, Stolz SM, Wheeler S, M
- Page 193 and 194:
Final Comment to Chapter 16 Infecti
- Page 195 and 196:
Chapter 17. Prevention of Ventilato
- Page 197 and 198:
Potential for Harm No adverse effec
- Page 199 and 200:
Table 17.1.1. Patient positioning*
- Page 201 and 202:
Opportunities for Impact Continuous
- Page 203 and 204:
Table 17.2.1. Randomized trials of
- Page 205 and 206:
total antibiotic costs. 14-16 decre
- Page 207 and 208:
References 1. D'Amico R, Pifferi S,
- Page 209 and 210:
Evidence for Effectiveness of the P
- Page 211 and 212:
Table 17.4.1. Studies of stress ulc
- Page 213 and 214:
12. Slaughter S, Hayden MK, Nathan
- Page 215 and 216:
Chapter 18. Localizing Care to High
- Page 217 and 218:
showed an association) and physicia
- Page 219 and 220:
In addition to the potential use of
- Page 221 and 222:
References 1. Luft HS, Bunker JP, E
- Page 223 and 224:
Chapter 19. Learning Curves for New
- Page 225 and 226:
Thus, determination of a minimum nu
- Page 227 and 228:
References 1. Gallstones and laparo
- Page 229 and 230:
39. Crawford DL, Phillips EH. Lapar
- Page 231 and 232:
Chapter 20. Prevention of Surgical
- Page 233 and 234:
Costs and Implementation A number o
- Page 235 and 236:
• Single dose vs. multiple dose r
- Page 237 and 238:
All Cesarean section: RR 0.37 (0.33
- Page 239 and 240:
17. Vegas AA, Jodra VM, Garcia ML.
- Page 241 and 242:
Subchapter 20.2. Perioperative Norm
- Page 243 and 244:
Comment Given the evidence of effec
- Page 245 and 246:
Opportunities for Impact Administra
- Page 247 and 248:
5. Greif R, Laciny S, Rapf B, Hickl
- Page 249 and 250:
Evidence for Effectiveness of the P
- Page 251 and 252:
Table 20.4.1. Prospective, before-a
- Page 253 and 254:
29. Lazar HL, Chipkin S, Philippide
- Page 255 and 256:
Chapter 21. Ultrasound Guidance of
- Page 257 and 258:
after 1996 9,15,17 and one that inc
- Page 259 and 260:
Comment Real-time US guidance for C
- Page 261 and 262:
References 1. Civetta JM, Taylor RW
- Page 263 and 264:
38. Kaufmann C, Rhee P, Burris D. T
- Page 265 and 266:
Chapter 22. The Retained Surgical S
- Page 267 and 268:
prevalence of this error and the ef
- Page 269 and 270:
Chapter 23. Pre-Anesthesia Checklis
- Page 271 and 272:
to anesthesia providers’ own meth
- Page 273 and 274:
References 1. Reason JT. Human Erro
- Page 275 and 276:
Chapter 24. The Impact Of Intraoper
- Page 277 and 278:
complications. During anesthesia an
- Page 279 and 280:
References 1. American Society of A
- Page 281 and 282:
Chapter 25. Beta-blockers and Reduc
- Page 283 and 284:
27 Accounting for these differences
- Page 285 and 286:
The use of beta-blockers to reduce
- Page 287 and 288:
defined as systolic blood pressure
- Page 289 and 290:
28. Litwack R, Gilligan D, DeGrutto
- Page 291 and 292:
Chapter 26. Prevention of Falls in
- Page 293 and 294:
facilities and a 31% reduction in m
- Page 295 and 296:
as to whether identification bracel
- Page 297 and 298:
36. Mitchell A, Jones N. Striving t
- Page 299 and 300:
has been good. In fact, given adequ
- Page 301 and 302:
References 1. Health Care Financing
- Page 303 and 304:
Table 26.3.1. Study of bed alarms f
- Page 305 and 306:
Table 26.4. Study of special floori
- Page 307 and 308:
Costs and Implementation An Austral
- Page 309 and 310:
7. Lauritzen JB, Petersen MM, Lund
- Page 311 and 312:
Chapter 27. Prevention of Pressure
- Page 313 and 314:
employed, ranging from Grade 1 (dis
- Page 315 and 316:
5. Norton D, McLaren R, Exton-Smith
- Page 317 and 318:
Chapter 28. Prevention of Delirium
- Page 319 and 320:
aseline co-morbidities of the enrol
- Page 321 and 322:
References 1. Elie M, Cole MG, Prim
- Page 323 and 324:
Chapter 29. Multidisciplinary Geria
- Page 325 and 326:
Study Outcomes Ten studies reported
- Page 327 and 328:
experienced geriatric team in a hos
- Page 329 and 330:
Marcantoni 126 orthopedic patients
- Page 331 and 332:
19. Gayton D, Wood-Dauphinee S, de
- Page 333 and 334:
Chapter 30. Geriatric Evaluation an
- Page 335 and 336:
Cognitive function, as measured by
- Page 337 and 338:
Table 30.1. Randomized Controlled T
- Page 339 and 340:
References 1. Creditor MC. Hazards
- Page 341 and 342:
Section E. General Clinical Topics
- Page 343 and 344:
Chapter 31. Prevention of Venous Th
- Page 345 and 346:
patients, the incidence of DVT was
- Page 347 and 348:
data show that aspirin (6 studies,
- Page 349 and 350:
Medical Patients VTE prevention in
- Page 351 and 352:
LMWH was more cost-effective than L
- Page 353 and 354:
Table 31.1. Mechanical and pharmaco
- Page 355 and 356:
Table 31.3. Recommended VTE prophyl
- Page 357 and 358:
17. Vanek VW. Meta-analysis of effe
- Page 359 and 360:
Chapter 32. Prevention of Contrast-
- Page 361 and 362:
the studies used aminophylline, rat
- Page 363 and 364:
Table 32.1. Studies of strategies f
- Page 365 and 366:
References 1. Parfrey PS, Griffiths
- Page 367 and 368:
33. Tippins RB, Torres WE, Baumgart
- Page 369 and 370:
Chapter 33. Nutritional Support Nei
- Page 371 and 372:
Evidence for Effectiveness of the P
- Page 373 and 374:
developing major infectious complic
- Page 375 and 376:
Table 33.1. Studies evaluating nutr
- Page 377 and 378:
19. Moore FA, Moore EE, Jones TN, M
- Page 379 and 380:
literature during that time. 17 Ide
- Page 381 and 382:
Costs and Implementation One cost-e
- Page 383 and 384:
6. Beejay U, Wolfe M. Acute gastroi
- Page 385 and 386:
375
- Page 387 and 388:
inferior to film interpretation for
- Page 389 and 390:
Study Outcomes Most studies reporte
- Page 391 and 392:
Table 35.1. Educational interventio
- Page 393 and 394:
31. Herman PG, Gerson DE, Hessel SJ
- Page 395 and 396:
Chapter 36. Pneumococcal Vaccinatio
- Page 397 and 398:
andomized controlled trials (RCTs)
- Page 399 and 400:
All studies of the effectiveness of
- Page 401 and 402:
Table 36.1. 1. Pneumococcal vaccine
- Page 403 and 404:
9. Whitney CG, Farley MM, Hadler J,
- Page 405 and 406:
395
- Page 407 and 408:
surgeons indicate that the majority
- Page 409 and 410:
Table 37.1.1. Randomized controlled
- Page 411 and 412:
anesthesiologists, specially traine
- Page 413 and 414:
Table 37.2.1. Studies of acute pain
- Page 415 and 416:
Opportunities for Impact The degree
- Page 417 and 418:
Practice Description Non-pharmacolo
- Page 419 and 420:
Table 37.4.1. Studies of non-pharma
- Page 421 and 422:
Section F. Organization, Structure,
- Page 423 and 424:
Chapter 38. “Closed” Intensive
- Page 425 and 426:
pediatric multidisciplinary ICUs. I
- Page 427 and 428:
adjusted hospital mortality and a n
- Page 429 and 430:
RRR is the unadjusted mortality rel
- Page 431 and 432:
19. DiCosmo BFM. Addition of an int
- Page 433 and 434:
Chapter 39. Nurse Staffing, Models
- Page 435 and 436:
interventions to reduce pain, nause
- Page 437 and 438:
al 30 also does not find an associa
- Page 439 and 440:
associated with in-hospital mortali
- Page 441 and 442:
Table 39.3 Structural measures: ava
- Page 443 and 444:
8. Data from HCFA Medicare Level 3,
- Page 445 and 446:
Table 39.4 Structural variables: nu
- Page 447 and 448:
Table 39.5 Process measures: nurse
- Page 449 and 450:
10. Finnigan SA, Abel M, Dobler T,
- Page 451 and 452:
50. Kite K. Changing mouth care pra
- Page 453 and 454:
91. Medicare. Available at: www.sta
- Page 455 and 456:
138. Jones J, Rowan K. Is there a r
- Page 457 and 458:
Chapter 40. Promoting a Culture of
- Page 459 and 460:
organizational culture in high reli
- Page 461 and 462:
vary, depending on the type of acci
- Page 463 and 464:
Table 40.1. Checklist of elements t
- Page 465 and 466:
References 1. Roberts KH, Gargano G
- Page 467 and 468:
42. Helmreich RL. On error manageme
- Page 469 and 470:
Chapter 41. Human Factors and Medic
- Page 471 and 472:
Device Evaluation Prior to Purchase
- Page 473 and 474:
Identification of Alarm Source and
- Page 475 and 476:
Decreasing the Frequency of Alarms
- Page 477 and 478:
checklists in medicine have been li
- Page 479 and 480:
31. Stanford L, McIntyre J, Hogan J
- Page 481 and 482:
Chapter 42. Information Transfer Ha
- Page 483 and 484:
surveyed also wished to be provided
- Page 485 and 486:
Table 42.1.1. Practices to improve
- Page 487 and 488:
adverse medical event occurring dur
- Page 489 and 490:
Table 42.2.1. Computerized sign-out
- Page 491 and 492:
Costs and Implementation The direct
- Page 493 and 494:
Practice Description Our search rev
- Page 495 and 496:
Table 42.4.1. Randomized controlled
- Page 497 and 498:
Chapter 43. Prevention of Misidenti
- Page 499 and 500:
Medical record keeping Radiology an
- Page 501 and 502:
Study Outcomes Some of the studies
- Page 503 and 504:
References 1. Rappoport A. A hospit
- Page 505 and 506:
payments in 84% of cases, compared
- Page 507 and 508:
Evidence for Effectiveness of the P
- Page 509 and 510:
12. Cowell HR. Wrong-site surgery.
- Page 511 and 512:
Chapter 44. Crew Resource Managemen
- Page 513 and 514:
Representative Studies Several stud
- Page 515 and 516:
on Crisis Management Training in He
- Page 517 and 518:
practice, relatively little about t
- Page 519 and 520:
21. Halamek LP, Kaegi DM, Gaba DM,
- Page 521 and 522:
Chapter 45. Simulator-Based Trainin
- Page 523 and 524:
e difficult, 19 initial work has be
- Page 525 and 526:
factors that contribute to negative
- Page 527 and 528:
25. Sica GT, Barron DM, Blum R, Fre
- Page 529 and 530:
Chapter 46. Fatigue, Sleepiness, an
- Page 531 and 532:
fellowships. 34, 35 These shifts ar
- Page 533 and 534:
patient outcomes. Any effort to cha
- Page 535 and 536:
hour prophylactic nap in the evenin
- Page 537 and 538:
11. Cox T K, GP, ed. Stress and Sus
- Page 539 and 540:
53. Overland DW. Comparison of Effe
- Page 541 and 542:
97. Nicholson AN, Pascoe PA, Roehrs
- Page 543 and 544: 533
- Page 545 and 546: eceive special training in skills n
- Page 547 and 548: availability and different scoring
- Page 549 and 550: Potential for Harm Inadequate maint
- Page 551 and 552: Table 47.2 Manual versus mechanical
- Page 553 and 554: 20. Duke G, Green J. Outcome of cri
- Page 555 and 556: 545
- Page 557 and 558: Legislation governing the requireme
- Page 559 and 560: obtaining informed consent often re
- Page 561 and 562: patients that had been treated surg
- Page 563 and 564: References 1. Edwards SJ, Lilford R
- Page 565 and 566: 555
- Page 567 and 568: Failure to Document Preferences The
- Page 569 and 570: Evidence for Effectiveness of the P
- Page 571 and 572: have demonstrated that most medical
- Page 573 and 574: Costs and Implementation Estimating
- Page 575 and 576: References 1. Jonsen AR SM, Winslad
- Page 577 and 578: 39. Kurent J. Death and Dying in Am
- Page 579 and 580: Chapter 50. Other Practices Related
- Page 581 and 582: analyzed these competing views, and
- Page 583 and 584: PART IV. PROMOTING AND IMPLEMENTING
- Page 585 and 586: Chapter 51. Practice Guidelines Rob
- Page 587 and 588: Evidence for Effectiveness of Pract
- Page 589 and 590: 4. Weingarten S. Using practice gui
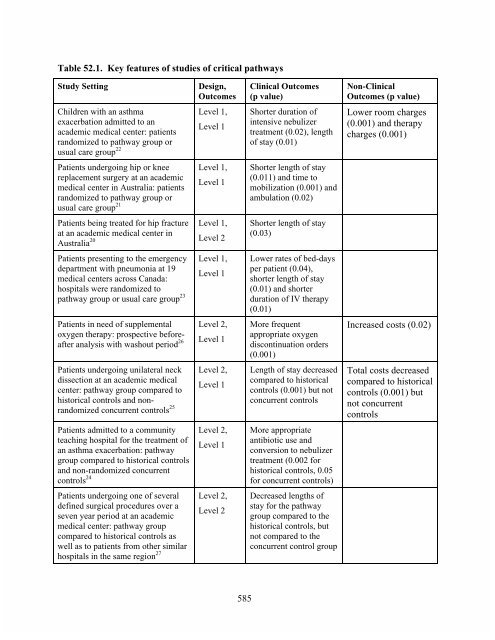
- Page 591 and 592: Chapter 52. Critical Pathways Rober
- Page 593: not reach statistical significance)
- Page 597 and 598: 19. Willis B, Kim LT, Anthony T, Be
- Page 599 and 600: Chapter 53. Clinical Decision Suppo
- Page 601 and 602: A final systematic review analyzed
- Page 603 and 604: Costs and Implementation Very few s
- Page 605 and 606: Chapter 54. Educational Techniques
- Page 607 and 608: interventions with at least 3 compo
- Page 609 and 610: Table 54.1. Studies of techniques f
- Page 611 and 612: Chapter 55. Legislation, Accreditat
- Page 613 and 614: hospitals and other health care ins
- Page 615 and 616: for bias, particularly when the rec
- Page 617 and 618: Table 55.2. A comparison of non-loc
- Page 619 and 620: 21. Yessian M. The external review
- Page 621 and 622: PART V. ANALYZING THE PRACTICES Cha
- Page 623 and 624: Chapter 56. Methodology for Summari
- Page 625 and 626: Details about Decision Rules and Ju
- Page 627 and 628: determining the specific elements t
- Page 629 and 630: Chapter 57. Practices Rated by Stre
- Page 631 and 632: Table 57.2 Patient Safety Practices
- Page 633 and 634: 17.1 Ventilator-associated pneumoni
- Page 635 and 636: 57.5 Patient Safety Practices with
- Page 637 and 638: Chapter 58. Practices Rated by Rese
- Page 639 and 640: 9 Adverse events related to anticoa
- Page 641 and 642: 42.4 Failures to communicate signif
- Page 643 and 644: Chapter 59. Listing of All Practice
- Page 645 and 646:
Ch. # Patient Safety Target 16.4 Ce
- Page 647 and 648:
Ch. # Patient Safety Target Patient
- Page 649 and 650:
Ch. # Patient Safety Target Patient
- Page 651 and 652:
Comments Section 1 Medium strength
- Page 653 and 654:
29 High complexity for implementati
- Page 655 and 656:
55 Rated as low, but this practices
- Page 657 and 658:
84 Most evidence available outside
- Page 659 and 660:
Appendix: List of Contributors Edit
- Page 661 and 662:
Sharon K. Inouye, MD, MPH Associate
- Page 663 and 664:
Jean Ann Seago, PhD, RN Assistant P
- Page 665 and 666:
Index abdominal pain, acute analges
- Page 667 and 668:
described, 601 research needs, 604
- Page 669 and 670:
Natural Death Acts, 561 nursing iss
- Page 671 and 672:
decision rules and judgment conside