RBI FUNCTIONS.pdf
RBI FUNCTIONS.pdf
RBI FUNCTIONS.pdf
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
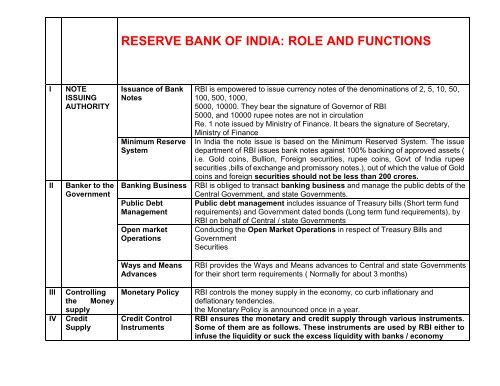
RESERVE BANK OF INDIA: ROLE AND <strong>FUNCTIONS</strong><br />
I<br />
II<br />
NOTE<br />
ISSUING<br />
AUTHORITY<br />
Banker to the<br />
Government<br />
Issuance of Bank<br />
Notes<br />
Minimum Reserve<br />
System<br />
Banking Business<br />
Public Debt<br />
Management<br />
Open market<br />
Operations<br />
<strong>RBI</strong> is empowered to issue currency notes of the denominations of 2, 5, 10, 50,<br />
100, 500, 1000,<br />
5000, 10000. They bear the signature of Governor of <strong>RBI</strong><br />
5000, and 10000 rupee notes are not in circulation<br />
Re. 1 note issued by Ministry of Finance. It bears the signature of Secretary,<br />
Ministry of Finance<br />
In India the note issue is based on the Minimum Reserved System. The issue<br />
department of <strong>RBI</strong> issues bank notes against 100% backing of approved assets (<br />
i.e. Gold coins, Bullion, Foreign securities, rupee coins, Govt of India rupee<br />
securities ,bills of exchange and promissory notes.), out of which the value of Gold<br />
coins and foreign securities should not be less than 200 crores.<br />
<strong>RBI</strong> is obliged to transact banking business and manage the public debts of the<br />
Central Government, and state Governments.<br />
Public debt management includes issuance of Treasury bills (Short term fund<br />
requirements) and Government dated bonds (Long term fund requirements), by<br />
<strong>RBI</strong> on behalf of Central / state Governments<br />
Conducting the Open Market Operations in respect of Treasury Bills and<br />
Government<br />
Securities<br />
Ways and Means<br />
Advances<br />
<strong>RBI</strong> provides the Ways and Means advances to Central and state Governments<br />
for their short term requirements ( Normally for about 3 months)<br />
III<br />
IV<br />
Controlling<br />
the Money<br />
supply<br />
Credit<br />
Supply<br />
Monetary Policy<br />
Credit Control<br />
Instruments<br />
<strong>RBI</strong> controls the money supply in the economy, co curb inflationary and<br />
deflationary tendencies.<br />
the Monetary Policy is announced once in a year.<br />
<strong>RBI</strong> ensures the monetary and credit supply through various instruments.<br />
Some of them are as follows. These instruments are used by <strong>RBI</strong> either to<br />
infuse the liquidity or suck the excess liquidity with banks / economy
Bank Rate<br />
CRR<br />
It is the rate at which <strong>RBI</strong> rediscounts the Bills of commercial banks. Presently it<br />
is 8%<br />
Cash Reserve Ratio: It specifies the cash balances required to be maintained by<br />
banks <strong>RBI</strong> as a specific percentage on their adjusted net demand and time<br />
liabilities.CRR is hiked by <strong>RBI</strong> to curb the inflation. Presently it is 4%<br />
SLR<br />
Statutory Liquidity Ratio. It specifies the minimum investment by a Bank in the<br />
approved securities. It is mentioned as a percentage of adjusted demand and time<br />
liabilities of a Bank. Presently it is 22%. . A higher percentage may be specified<br />
by <strong>RBI</strong> (Presently the maximum is 40%), to curb the excess liquidity with a Bank.<br />
V<br />
Banker to<br />
Banks<br />
Open Market<br />
Operations<br />
Selective Credit<br />
Control<br />
Market<br />
stabilization<br />
scheme<br />
Fixation of<br />
Inventory Norms<br />
Directed Lending<br />
Control over<br />
Interest rates<br />
Licensing<br />
Authority<br />
Scheduled Bank<br />
Status to banks<br />
Refinance<br />
Open market operations include the buying and selling of government securities.<br />
When the economy is having the excess liquidity <strong>RBI</strong> sells government securities<br />
at attractive rate of interest, so that people having excess money invest money in<br />
these securities there by excess liquidity in the economy is removed.<br />
This is a Qualitative Control. <strong>RBI</strong> stipulates higher margin and rate of interest in<br />
respect of loans and advances against essential commodities and some other<br />
selected items to ensure hoarding of stock and black marketing.<br />
Normally <strong>RBI</strong> borrows funds from whenever required by Government. Sometimes<br />
<strong>RBI</strong> resorts to public borrowing to suck the excess liquidity in the economy.<br />
Whenever required <strong>RBI</strong> fixes the Inventory norms for banks finance Eg: Tandon<br />
Commiittee norms, Chore Committee norms, Nayak committee norms.<br />
<strong>RBI</strong> specifies the targets to be achieved by banks in respect of certain sector. Eg:<br />
Priority sector advances. 40% to priority sectors, 18% to weaker sections etc<br />
Even though the deposit interest rates and lending rates are deregulated , certain<br />
interest rates like interest rate on S.B a/c (4%),Inte4rest rates on export credit etc<br />
are regulated by <strong>RBI</strong><br />
A bank should comply with the minimum stipulations of <strong>RBI</strong> to do banking<br />
business<br />
A bank whose name is entered in the second schedule to the BR Act is called a<br />
scheduled bank<br />
Finance against the long term loans to the borrowers
Rediscounting of<br />
Bill<br />
Liquidity<br />
Adjustment<br />
Facility<br />
Lender of last<br />
resort<br />
Liquidity to banks against the bills discounted by them to their clients<br />
Repo and Reverse Repo both put together is called Liquidity adjustment facility.<br />
<strong>RBI</strong> finances to banks against purchase of securities upon a condition that such<br />
securities are sold back by <strong>RBI</strong> to concerned bank on repayment of the loan.<br />
Presently the Repo rate is 8%.<br />
Reverse repo facilitates the banks to park their excess funds with <strong>RBI</strong>. Now the<br />
Reverse Repo rate is 7%<br />
Banks look towards <strong>RBI</strong> as a lender of last resort.<br />
VI<br />
Regulator of<br />
Financial<br />
system<br />
VII Management<br />
of Forex<br />
Reserves<br />
VIII Improvement<br />
of Customer<br />
service in<br />
Bank<br />
Regulation of<br />
Financial Markets<br />
Rating System for<br />
Banks<br />
Issuance of<br />
directions to<br />
commercial banks<br />
Regulator of<br />
Payment and<br />
settlement system<br />
Forex reserves<br />
Institution of<br />
customer service<br />
committees<br />
Ombudsman<br />
scheme<br />
Reserve Bank of India is the regulator of money market,Credit market and Forex<br />
Markets<br />
<strong>RBI</strong> adopts CAMELS rating for rating the performance of Banks<br />
<strong>RBI</strong> as per the powers derived from B.R.Act issues guidelines to banks in respect<br />
of certain key areas of operations. Like IRAC nors , CAR etc.<br />
Payment systems like EFT, RTGS are effected through <strong>RBI</strong><br />
<strong>RBI</strong> controls the forex reserves as per the powers drawn from FEMA<br />
Committees like Talwar committee, FGoiporia committee are instituted for<br />
framing guidelines for customer service<br />
Ombudsman scheme is instituted to redress the grievances of customers against<br />
the banks