Cells: The Living Units Cell Theory Cytology Cellular Diversity ...
Cells: The Living Units Cell Theory Cytology Cellular Diversity ...
Cells: The Living Units Cell Theory Cytology Cellular Diversity ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
1/30/2013<br />
<strong><strong>Cell</strong>s</strong>: <strong>The</strong> <strong>Living</strong> <strong>Units</strong><br />
<strong>Cell</strong> <strong>The</strong>ory<br />
• 1) <strong><strong>Cell</strong>s</strong> = basic functional & structural units of<br />
the body<br />
• 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells<br />
• 3) All cells have the same DNA<br />
• 4) Maintain homeostasis<br />
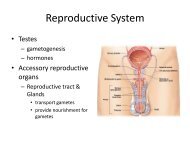
<strong>Cell</strong><br />
Division<br />
<strong>Cytology</strong><br />
US Debt =<br />
16 trillions <strong>Cell</strong>ular <strong>Diversity</strong><br />
• 1) <strong><strong>Cell</strong>s</strong> = basic structural and functional units<br />
of all living things<br />
– A) 30-75 trillion cells<br />
– B) <strong>Cell</strong>ular diversity = 200 different types<br />
• diverse in size, shape, and function<br />
Figure 2.18b<br />
<strong>Cell</strong>ular <strong>Diversity</strong><br />
3 principal parts of a cell<br />
1
1/30/2013<br />
Plasma Membrane<br />
• 1) defines the extent of the cell<br />
• 2) Structure<br />
– A) lipid bilayer<br />
– B) membrane proteins<br />
• Integral proteins<br />
• Peripheral proteins<br />
Plasma Membrane<br />
• 1) Functions<br />
– A) act as receptors<br />
– B) Separates two major fluid compartments<br />
– C) Semi-permeable<br />
• Selective transport across membrane<br />
• 2) Membrane Transport Mechanisms<br />
– A) Passive transport: simple vs. facilitated diffusion<br />
– B) Active transport<br />
• Small molecules: primary vs. secondary active transport<br />
• Macromolecules: vesicular transport (endocytosis vs.<br />
exocytosis)<br />
Osmosis<br />
Vesicular Transport<br />
Cytoplasm<br />
A<br />
• major elements<br />
– 1) Cytosol<br />
• Consists of water, ions, and enzymes<br />
– 2) Organelles<br />
– 3) inclusions<br />
• Melanin<br />
• Lipid droplets<br />
B<br />
2
1/30/2013<br />
organelles<br />
Hereditary Information<br />
• 1) Mitochondria<br />
• 2) Endoplasmic<br />
reticulum<br />
– Protein synthesis<br />
– lipid metabolism<br />
– detoxify poisons & drugs<br />
• 3) Golgi apparatus<br />
• 4) Lysosomes<br />
• 5) peroxisomes<br />
– neutralize free radicals<br />
• 6) Ribosomes<br />
• 7) Centrosomes =<br />
Microtubule-organizing<br />
center<br />
– Centrioles - cylindrical<br />
bodies<br />
• 8) Cytoskeleton<br />
– Maintains cell shape<br />
– <strong>Cell</strong> transport<br />
• 1) Genome = hereditary<br />
information<br />
– 30,000 genes<br />
• 2) 46 chromosomes<br />
• 3) DNA<br />
– Chromatin<br />
– Chromosome<br />
Central Dogma of Biology<br />
• DNA => RNA => Protein<br />
– Transcription<br />
– Translation<br />
• Modification &<br />
Processing<br />
• Export<br />
<strong>Cell</strong> Division<br />
• 1) Meiosis – sex cells<br />
• 2) Mitosis – somatic cells<br />
– A) Interphase: Preparation<br />
– B) Mitotic phase: cell<br />
division<br />
• 1) Mitosis: duplication<br />
of DNA and division of<br />
the nucleus<br />
– Chromosomes<br />
distributed to 2 daughter<br />
nuclei<br />
• 2) Cytokinesis: division<br />
of the cytoplasm<br />
Mitotic phase<br />
3