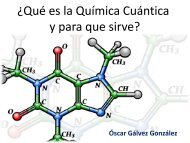
Download the slides
Download the slides
Download the slides
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Running kinetic couplings <br />
0.3<br />
0.25<br />
Running kinetic coupling models<br />
µ=0<br />
(b)<br />
(a) n=2<br />
(b) n=4<br />
The dilatonic running coupling <br />
leads to <strong>the</strong> decrease of r. <br />
r 0.05<br />
0.2<br />
0.15<br />
µ=0.1<br />
µ=−0.03<br />
µ=0<br />
However both <strong>the</strong> quadratic <br />
and quartic potentials are <br />
outside <strong>the</strong> 68 % CL boundary. <br />
0.1<br />
0.05<br />
(a)<br />
µ=0.1<br />
µ=10<br />
µ=10<br />
This comes from <strong>the</strong> fact that <br />
Planck data give tight upper <br />
bounds on <strong>the</strong> scalar spectral <br />
index than that of WMAP. <br />
0<br />
0.945 0.95 0.955 0.96 0.965 0.97 0.975 0.98<br />
n s