You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Alexander Y. Shin, MD, and Allen T. Bishop, MD<br />
Otherwise, a salvage procedure<br />
should be done. Under direct visualization<br />
and fluoroscopic image,<br />
necrotic bone is removed from the<br />
lunate with a burr or curettes, leaving<br />
a shell of intact cartilage and<br />
subchondral bone through a dorsal<br />
opening. If collapsed, the lunate is<br />
gently expanded to normal dimensions<br />
with a small blunt-ended<br />
spreader. At this time, the tourniquet<br />
is deflated to verify blood flow<br />
to the graft. Cancellous bone graft<br />
harvested from the distal radius<br />
bone graft defect is packed into the<br />
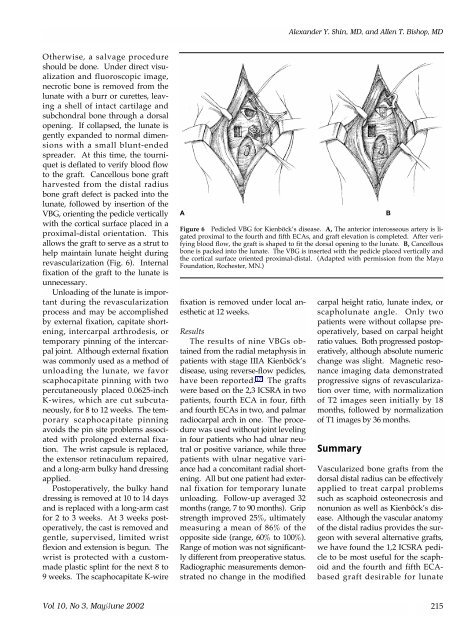
lunate, followed by insertion of the<br />
VBG, orienting the pedicle vertically<br />
with the cortical surface placed in a<br />
proximal-distal orientation. This<br />
allows the graft to serve as a strut to<br />
help maintain lunate height during<br />
revascularization (Fig. 6). Internal<br />
fixation of the graft to the lunate is<br />
unnecessary.<br />
Unloading of the lunate is important<br />
during the revascularization<br />
process and may be accomplished<br />
by external fixation, capitate shortening,<br />
intercarpal arthrodesis, or<br />
temporary pinning of the intercarpal<br />
joint. Although external fixation<br />
was commonly used as a method of<br />
unloading the lunate, we favor<br />
scaphocapitate pinning with two<br />
percutaneously placed 0.0625-inch<br />
K-wires, which are cut subcutaneously,<br />
for 8 to 12 weeks. The temporary<br />
scaphocapitate pinning<br />
avoids the pin site problems associated<br />
with prolonged external fixation.<br />
The wrist capsule is replaced,<br />
the extensor retinaculum repaired,<br />
and a long-arm bulky hand dressing<br />
applied.<br />
Postoperatively, the bulky hand<br />
dressing is removed at 10 to 14 days<br />
and is replaced with a long-arm cast<br />
for 2 to 3 weeks. At 3 weeks postoperatively,<br />
the cast is removed and<br />
gentle, supervised, limited wrist<br />
flexion and extension is begun. The<br />
wrist is protected with a custommade<br />
plastic splint for the next 8 to<br />
9 weeks. The scaphocapitate K-wire<br />
A<br />
Figure 6 Pedicled VBG for Kienböck’s disease. A, The anterior interosseous artery is ligated<br />
proximal to the fourth and fifth ECAs, and graft elevation is completed. After verifying<br />
blood flow, the graft is shaped to fit the dorsal opening to the lunate. B, Cancellous<br />
bone is packed into the lunate. The VBG is inserted with the pedicle placed vertically and<br />
the cortical surface oriented proximal-distal. (Adapted with permission from the Mayo<br />
Foundation, Rochester, MN.)<br />
fixation is removed under local anesthetic<br />
at 12 weeks.<br />
Results<br />
The results of nine VBGs obtained<br />
from the radial metaphysis in<br />
patients with stage IIIA Kienböck’s<br />
disease, using reverse-flow pedicles,<br />
have been reported. 17 The grafts<br />
were based on the 2,3 ICSRA in two<br />
patients, fourth ECA in four, fifth<br />
and fourth ECAs in two, and palmar<br />
radiocarpal arch in one. The procedure<br />
was used without joint leveling<br />
in four patients who had ulnar neutral<br />
or positive variance, while three<br />
patients with ulnar negative variance<br />
had a concomitant radial shortening.<br />
All but one patient had external<br />
fixation for temporary lunate<br />
unloading. Follow-up averaged 32<br />
months (range, 7 to 90 months). Grip<br />
strength improved 25%, ultimately<br />
measuring a mean of 86% of the<br />
opposite side (range, 60% to 100%).<br />
Range of motion was not significantly<br />
different from preoperative status.<br />
Radiographic measurements demonstrated<br />
no change in the modified<br />
carpal height ratio, lunate index, or<br />
scapholunate angle. Only two<br />
patients were without collapse preoperatively,<br />
based on carpal height<br />
ratio values. Both progressed postoperatively,<br />
although absolute numeric<br />
change was slight. Magnetic resonance<br />
imaging data demonstrated<br />
progressive signs of revascularization<br />
over time, with normalization<br />
of T2 images seen initially by 18<br />
months, followed by normalization<br />
of T1 images by 36 months.<br />
Summary<br />
Vascularized bone grafts from the<br />
dorsal distal radius can be effectively<br />
applied to treat carpal problems<br />
such as scaphoid osteonecrosis and<br />
nonunion as well as Kienböck’s disease.<br />
Although the vascular anatomy<br />
of the distal radius provides the surgeon<br />
with several alternative grafts,<br />
we have found the 1,2 ICSRA pedicle<br />
to be most useful for the scaphoid<br />
and the fourth and fifth ECAbased<br />
graft desirable for lunate<br />
B<br />
Vol 10, No 3, May/June 2002 215